Internet connection problems tend to have terrible timing. They typically happen when you have critical things to do and come in different forms.
Signal fluctuations and timeouts are among the most prevalent Internet issues that users face. They result from various device glitches, misconfigurations, and conflicts.
This article focuses on answering the question, “Why does my Internet keep going in and out?” We’ll talk about the different causes of the problem and how to resolve it.
Also Read: Boost Internet on Your PC: Tips on How to Speed Up Your Internet Connection
Why Does My Internet Keep Going Out?
As mentioned earlier, this issue has different causes, from router to operating system glitches. Let’s go through them and tell you what to do.
Your Router is Due for a Reboot
Routers and modems are also computers. They have processors, system memory, drivers, and circuit boards. Like your computer, these devices also need periodic reboots. Memory can become clogged and burdened with backlogs if they work non-stop for too long.
Also Read: Laptop Lifespan: Why You Should Definitely Shut Down Your PC Every NIght
So if your internet goes in and out after using your router or modem for a long time, start with rebooting the device. Doing that will clear the memory backlog and other glitches affecting it.
A simple restart also allows the device to reestablish a more robust and stable connection, as it will choose a less congested frequency the next time it comes on.
What You Should Do
Unplug the router directly from its power source. If your device uses a battery, remove it. Wait for some minutes after powering it down. It’s also recommended to restart your computer alongside your router.
Plug your router back into its power source after a few minutes. If you removed its battery, put it back in before plugging it.
Some routers have light indicators that show when the network is fully set up. Wait until your device initializes and signals that everything is up and running.
You can now connect your computer and check if the reboot resolves the “Internet keeps disconnecting” problem.
Network Congestion
Your computer uses the data packets your router or modem transmits to perform Internet-dependent tasks, whether it’s syncing docs or running Microsoft Teams.
These data packets, like small information packages, must travel through your router’s radio frequency environment.
So, if too many devices are connected to your router, the device will have to send more data packets. The radio frequency pathway may struggle to handle all of them simultaneously, causing drops in your internet connection.
While some routers are advertised to handle numerous devices, the reality is that your connection will grow weaker as you add more gadgets to the network.
Sometimes, using a few devices and running many tasks, such as heavy downloads and uploads, can stress the router.
What You Should Do
Consider reducing the number of devices connected to the network if you do not need them. You can temporarily disconnect them whenever you have important tasks.
You can also look at the possibility of upgrading to a router with a larger bandwidth capacity.
Signal Interference
People commonly overlook their home or office layout and the position of their WiFi routers. However, these factors significantly affect internet connection stability, especially when using a wireless device.
Distance and physical obstacles like walls can impede your router’s range and cause your internet to go in and out. The further away you are from your router, the weaker the connection. Also, you’ll experience more issues if you have many barriers between you and the internet device.
Other electronic devices can also diminish your WiFi signal, even if they’re not connected to the router or configured to broadcast signals. For example, Microwave ovens are known to halve WiFi signals because they often emit signals on the same 2.4 GHz frequency band.
What You Should Do
You can do the following to try and fix the interference problem:
- Go closer to the router when working.
- Disconnect devices that may be interfering with the signal. These devices may include thermostats, smart speakers, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, and microwave ovens.
- Reposition the router to a more central location.
- Get rid of other physical things that can disrupt your connection.
- Switch to your router’s 2.4 GHz network if you must work far away from it. The frequency can handle routine internet tasks, such as browsing websites, checking emails, and going through social media.
You may need to move closer to the device and choose the 5 GHz frequency if you want a reliable connection to do heavier things like video calls, large data uploads and downloads, and streaming high-definition videos.
Outdated or Faulty Wireless Card Drivers
Connection outages are among the many symptoms of a faulty wireless adapter driver. Device drivers are small software programs that facilitate interactions between the operating system and hardware devices. They also allow hardware components to talk to each other.
In this case, the wireless adapter driver tells the device what the operating system needs and how to deliver network connectivity. It is central to the computer’s network infrastructure if you rely on a wireless router.
The “Internet going in and out” problem will continue if the driver is faulty or out of date.
What You Should Do
The best way to fix the problem here is to update the driver. That said, starting by reinstalling the software application will be a good idea.
Follow these steps to reinstall the driver:
- Tap the Win+X keyboard combo and select Device Manager in the menu.
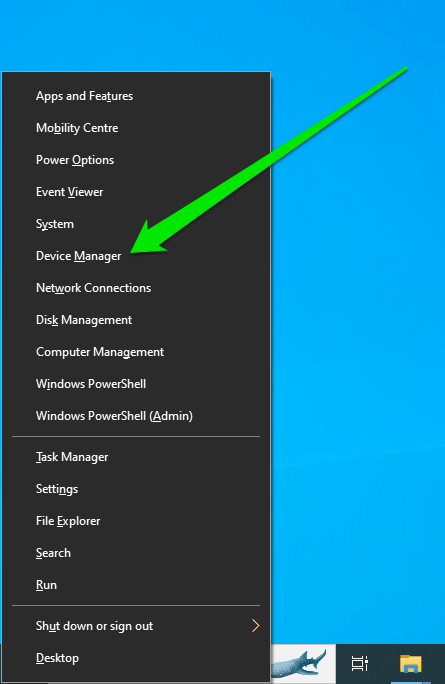
- Expand the Network Adapters category and right-click your wireless card (for example, “Intel(R) wireless-AC 9560 160MHz) after the Device Manager window opens.
- Select Uninstall Device from the driver menu, and click Uninstall.

- If you have the updated driver, select “Attempt to remove the driver for this device” before selecting Uninstall.
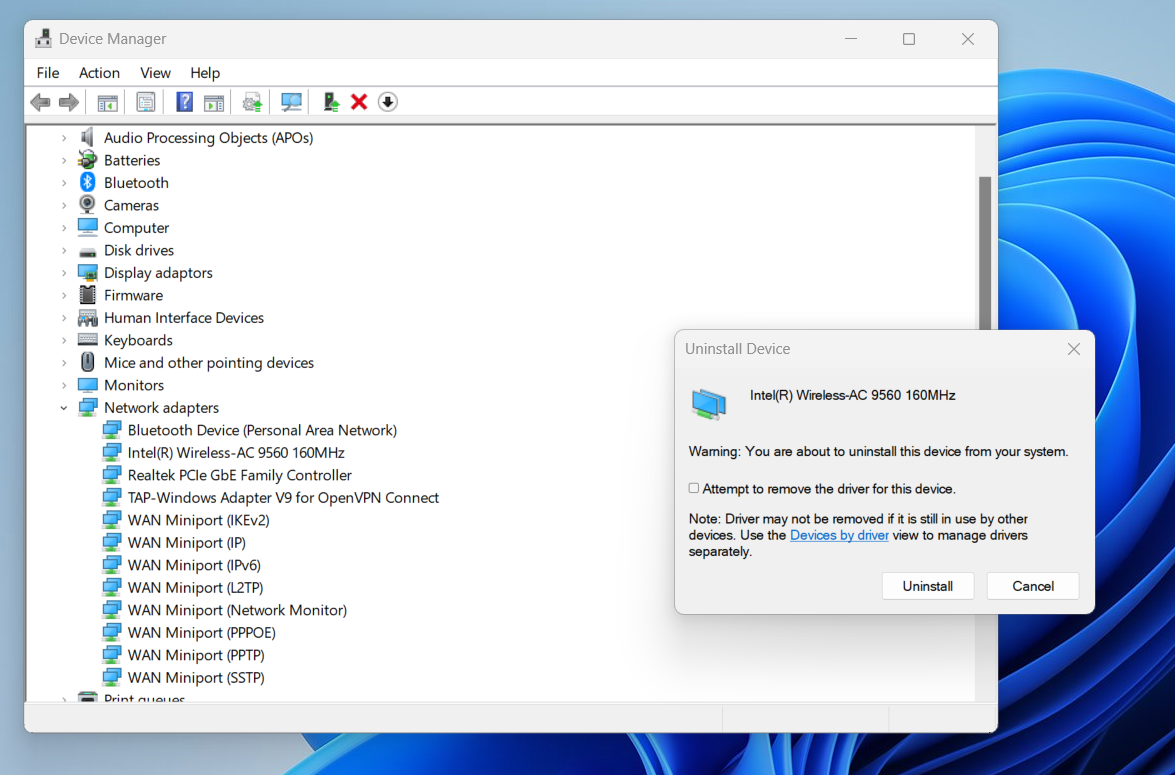
- Once you restart your computer, Windows will attempt to reinstall the driver. Windows will automatically install its generic wireless card driver if you completely uninstalled the software application.
You can now check if your Internet keeps disconnecting after reestablishing your connection.
Your next step will be updating the driver. You can go through Device Manager or the network card manufacturer’s website to install the update. Follow our driver-updating guide to learn how to update device drivers on Windows.
If you want to avoid being caught off guard by driver failures in the future, download Auslogics Driver Updater. The tool excels at detecting problematic device drivers and fetching and installing the latest official driver software. You can also use it to download and install multiple verified drivers at once.
Also Read: How to Roll Back Any Driver in Windows 10?
DNS Problems
Your computer’s DNS configuration is a critical part of its network infrastructure. DNS (Domain name system) servers are responsible for matching every website’s alphanumeric address, such as “www.microsoft.com,” with their correct IP address (usually a string of numbers). Connection to the website will fail if your computer cannot find its IP address.
By default, your computer uses the DNS server provided by your internet service provider. These servers are notoriously unreliable and tend to cause network stability problems.
So, the “Internet going in and out” problem could be a case of DNS inconsistency.
What You Should Do
Fixing DNS issues involves changing the default server to a more stable one. You’ll have to go through your computer’s network settings interface. You can follow our guide on how to change DNS servers on Windows 10 to learn how to fix the problem. The methods also work for Windows 11.
After changing your DNS settings, check to see if the “Internet going in and out” issue persists.
Malware
Malicious applications and viruses can affect your network in many ways. Firstly, they can hog system resources and force your router to work harder. This activity could congest your network as your connection usage spikes.
Malware can also infect your router and cause signal issues. Since many people stick to their router’s default passwords, attackers can exploit that weakness and infiltrate the network.
Viruses can infect your DNS settings, add malicious entries into your Hosts file and DNS cache, and completely reconfigure your IP address. This can trigger redirect problems and cause websites to block your connection.
Also Read: [FIXED] “Windows Has Detected an IP Address Conflict”
Lastly, a malicious program can hijack your bandwidth and use everything for itself. Some applications that are capable of this include adware and nefarious cryptocurrency miners.
So don’t rule out malware whenever you’re asking, “Why is my WiFi going in and out,” or “Why does my Internet keep disconnecting?”
What You Should Do
The first step is running a system-wide malware scan to find and eliminate the program. You have to use the Full Scan option in your antivirus program.
Depending on your antivirus program, the option may go by a different name, such as Deep Scan.
Since the Virus & Threat Protection tool in Windows Security is quite capable, you can use it to run a full scan to find the culprit.
But before you start, it’s crucial that you update the program. That’s because thousands of new malware programs are released each day, and antivirus programs require updates to catch up and detect them.
Follow these steps to update Windows’s native antivirus program:
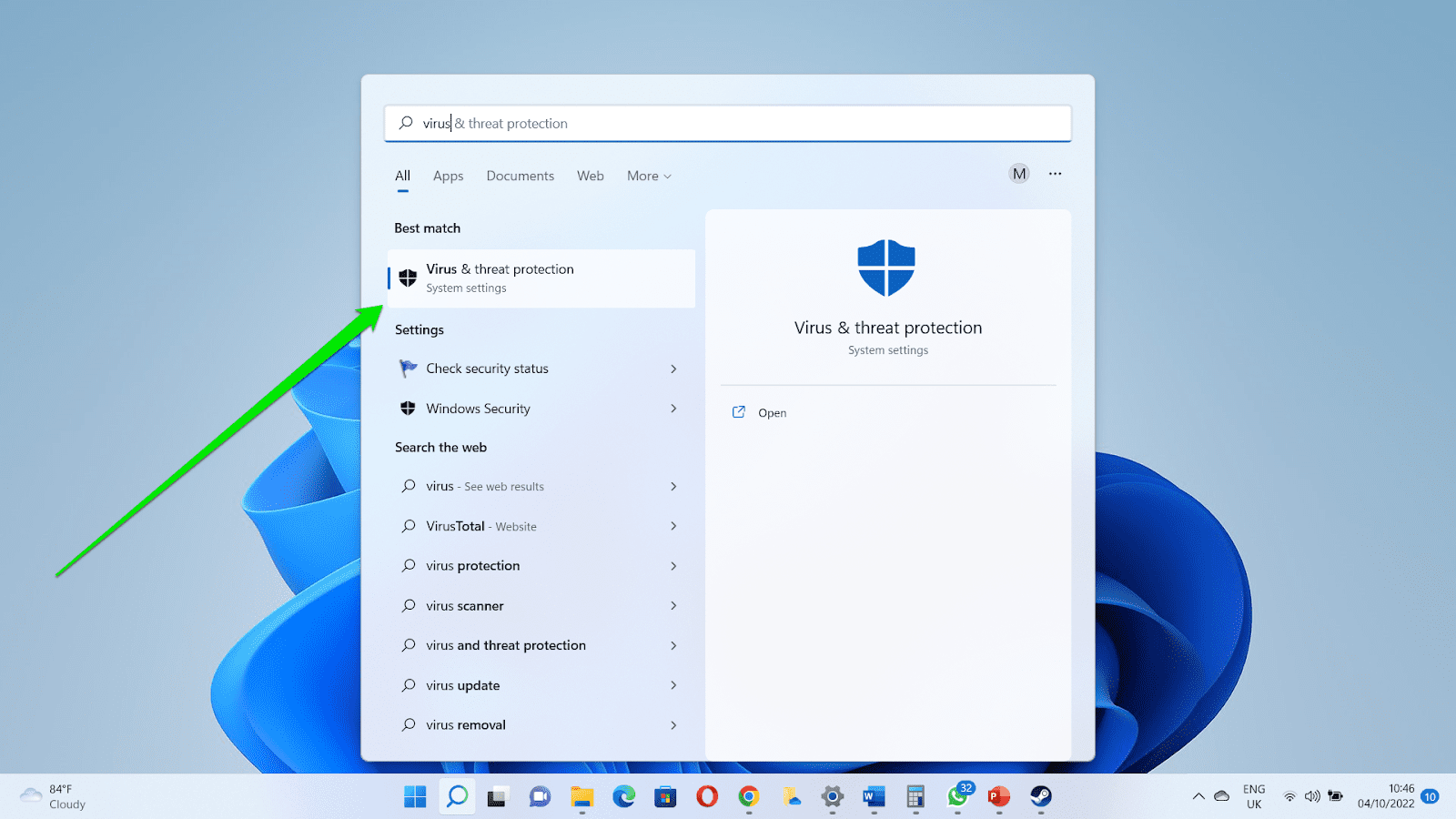
- Launch the Start menu, type “Virus,” and select “Virus & threat protection” in the search result.
- Scroll through the antivirus page and click “Protection updates” under “Virus & threat protection updates.”

- Once the “Protection updates” page appears, click the “Check for updates” button under “Security intelligence.”

- Allow Windows to check for updates and download them.
You can now return to the “Virus & threat protection” page and click “Scan options” under the “Quick scan” button.
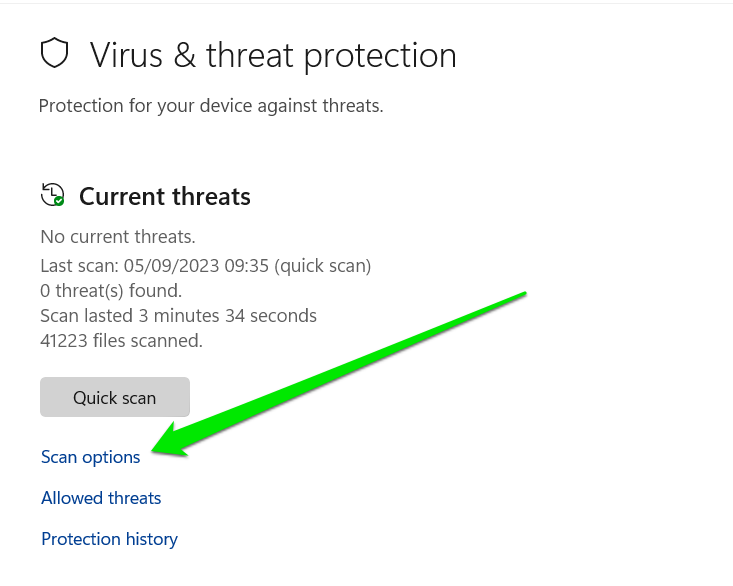
- Select the “Full scan” option and click the “Scan now” button to begin.
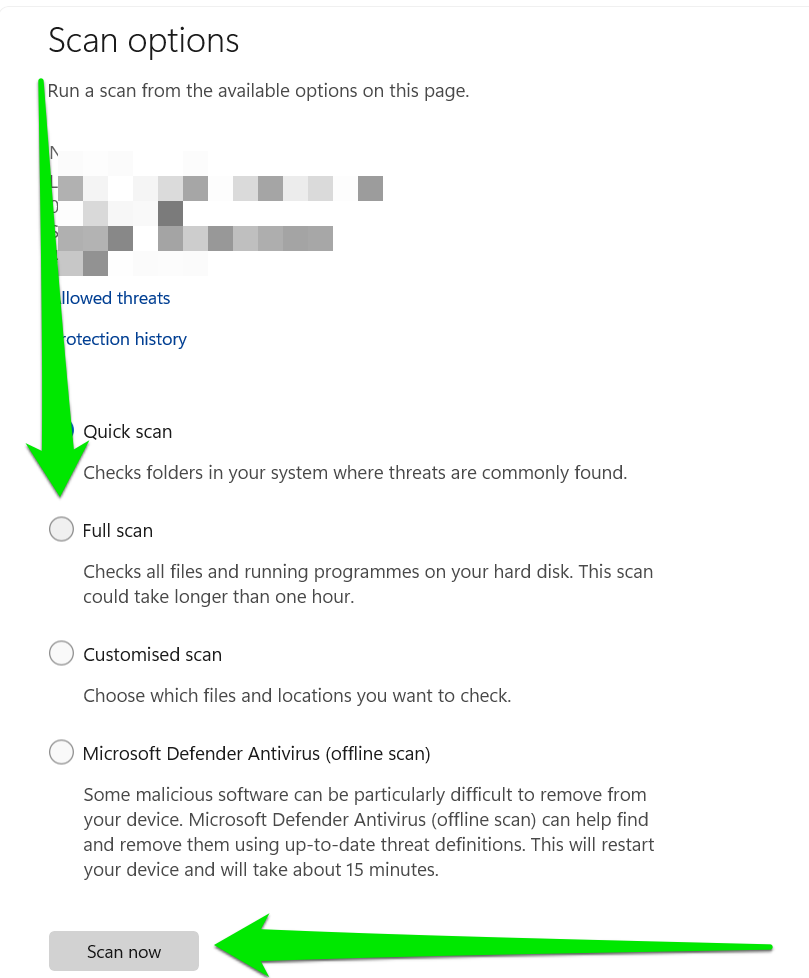
The scan may take a while and use a lot of your system resources. So don’t panic if it runs for hours and slows down your computer a little.
Also Read: Signs of Malware: How to Know if Your Computer is Infected
You can also restart your router to remove the malware application’s hold on it. Follow the same principle of unplugging the device and waiting for some minutes before turning it back on. You should try changing your router’s password regularly to reduce the risk of such issues in the future.
Another way to beef up your computer’s security is by using a protection tool like Auslogics Anti-Malware that can work side-by-side with your main security program.
Also Read: How to Prevent Malware: Lock Down Your Online Safety
ISP Throttling
ISP throttling is a bandwidth management practice that internet service providers use to regulate their subscribers’ data usage. When your network runs at specific speeds, there’s only so much Internet data that you can exhaust.
They may throttle (slow down) the signal speed for users on a specific plan after they reach a threshold. For example, your internet speed may be capped at 2mbps after you use 500 GB of data.
The downside of this policy is that it can slow things down and cause terrible network fluctuations, especially if you use multiple devices.
So, if you find yourself asking, “Why does my Internet keep disconnecting,” consider going through your ISP contract again to check if they have a throttling policy.
What You Should Do
You can upgrade your plan or use an ISP with better data plans and higher speed caps. If you want to use a new ISP, confirm other things like customer service, contract terms and pricing, and uptime.
Malfunctioning Equipment
You should not rule out the fact that you may need a new router. Wireless routers generally have short lifespans, and the timeframe for each device may be reduced depending on how you use it. Experts believe you should upgrade your router every five years.
However, if you connect the device to many smart gadgets, from your speakers to your thermostats, all year round, you may want to get a new one after three years.
If your current router is already that old, it could be the reason your internet goes in and out intermittently.
You can also test things out with a different router. If your connection works without issues, especially with the same ISP, it’s a sign that you’re due for a new wireless device.
Additional Tips
Are you still asking “Why is my WiFi going in and out?“
You can follow these additional tips to troubleshoot the “Internet goes in and out” problem if none of the fixes above worked.
Remove Recent Windows Update
In some cases, the latest version of Windows 10 or Windows 11 may not agree with your wireless card’s drivers, even if those drivers are updated. It’s another reason why your internet goes in and out repeatedly.
If you noticed that the problem started after updating your PC, the update you installed might be the culprit.
You should still note that installing the latest programs for your operating system is highly recommended. So, before you uninstall any update, try updating Windows again to check if the bug has been fixed in the newly released software for your computer.
If the issue persists, you have to remove the update that triggered the network stability problem.
Also Read: The Ultimate Reset Guide for Windows Update: Fixing Update Problems
Follow these quick steps to get rid of the problematic update:
- Launch Control Panel by typing “Control” in the Start menu and selecting the “Control Panel” result.
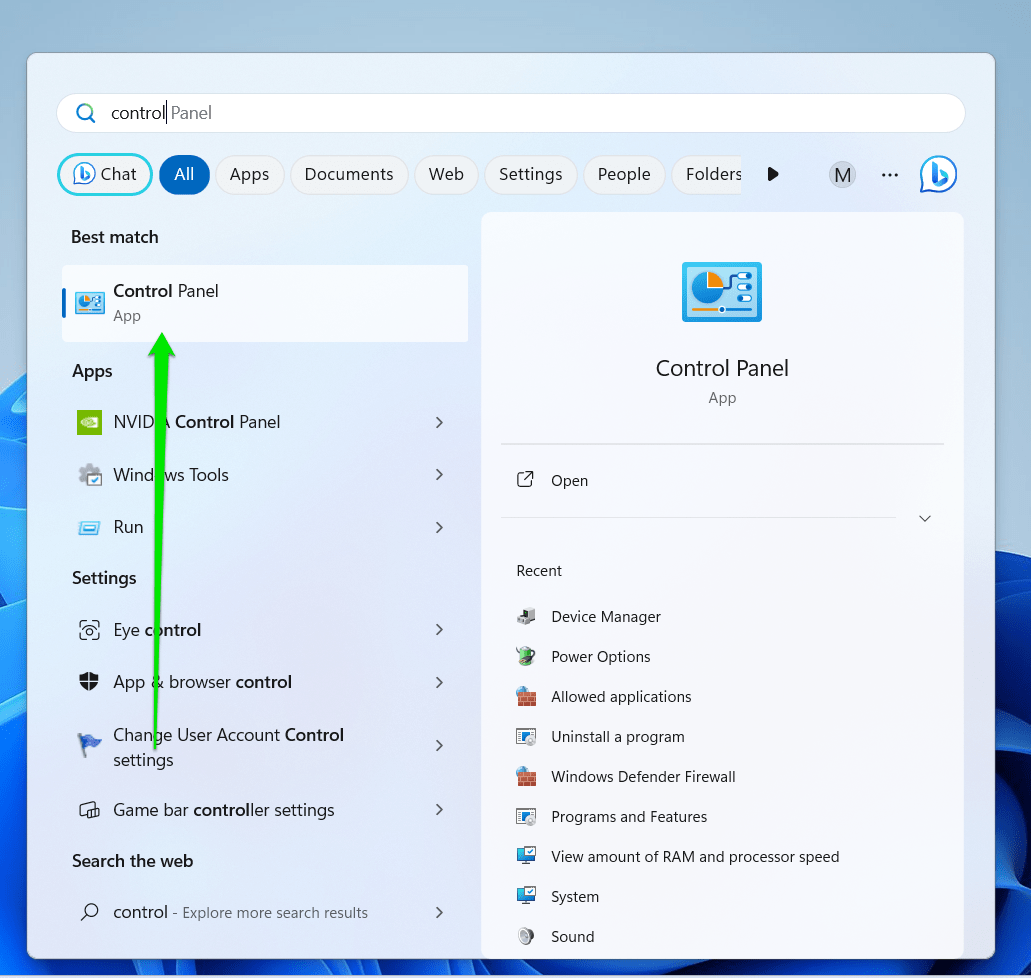
- Go to the Programs section and click “Uninstall a program” after Control Panel opens.

- Now, switch to the left sidebar of the “Programs and Features” window and select the “View installed updates” link.
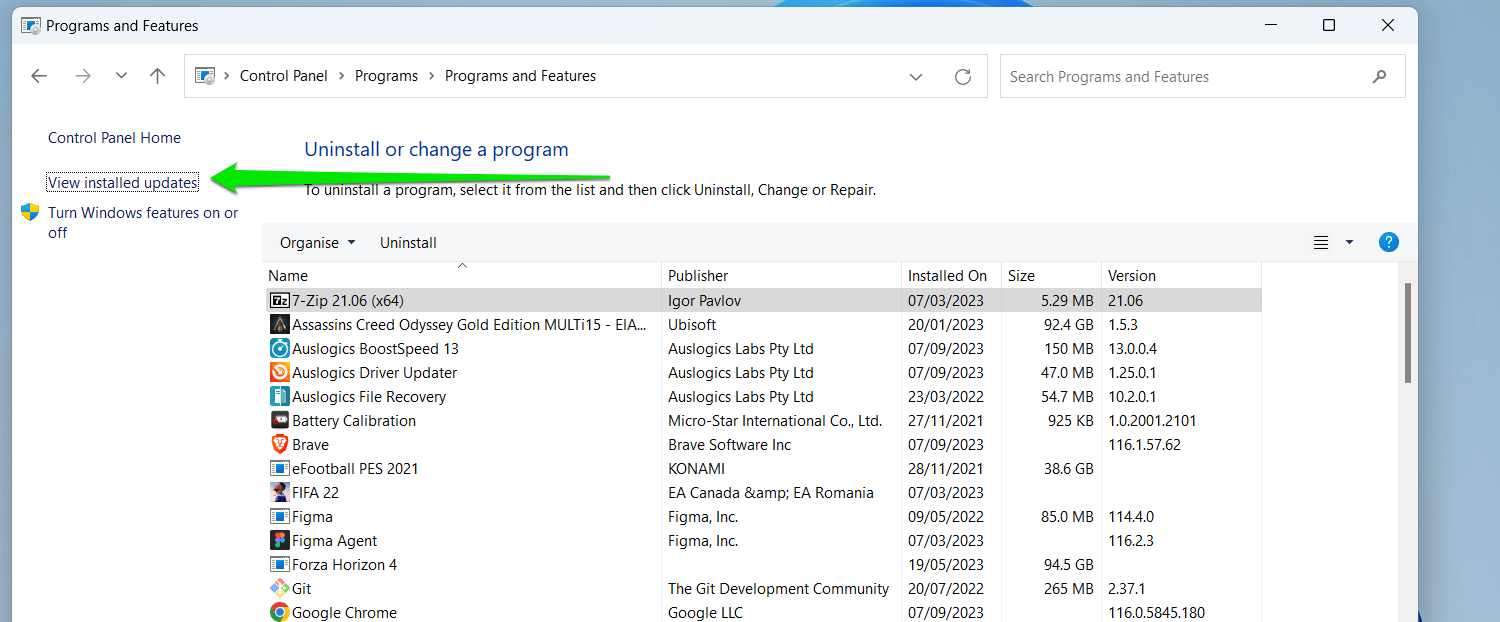
- If you’re running Windows 10, your update history will appear in the “Programs and Features” window, and you can click the update you want to remove and select Uninstall.
- On Windows 11, you’ll be redirected to the “Windows Update > Uninstall updates” Settings page, where you can click “Uninstall” beside the Windows update you want to remove.
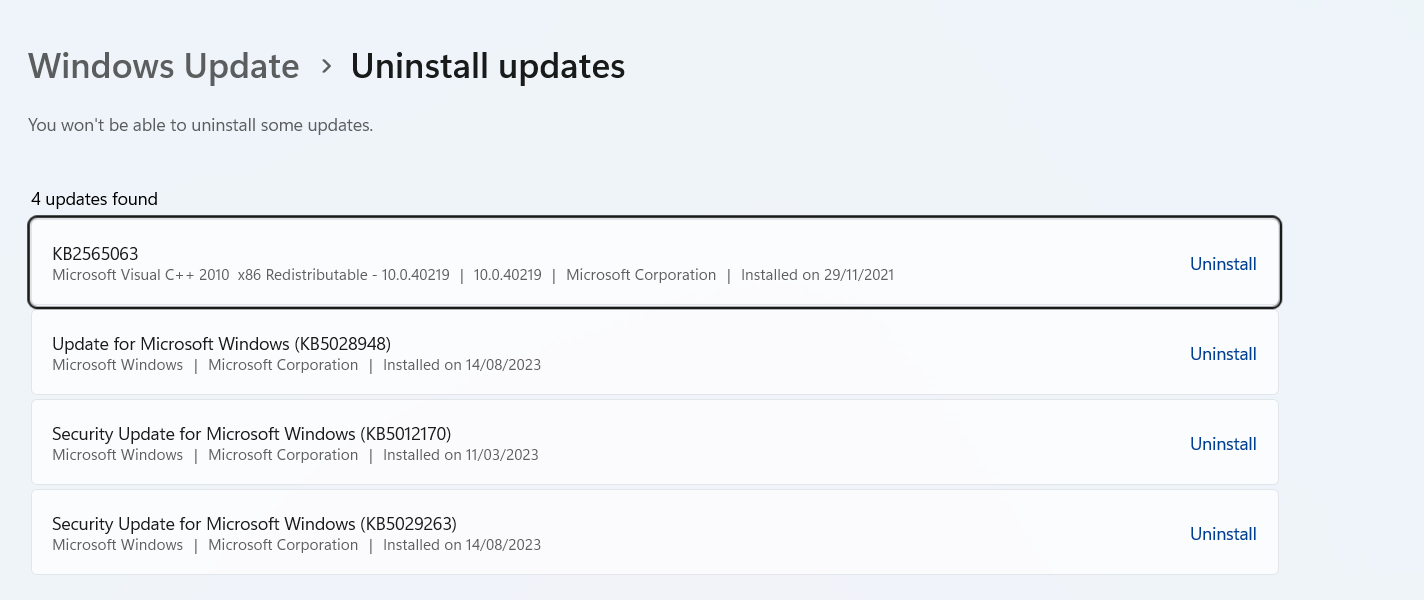
Check for the problem after removing the update.
Run the Built-In Network Troubleshooter
The native network troubleshooter is a tool that runs automated diagnostics on your system’s network infrastructure. It attempts to find problems and fix them.
It typically checks if network services are running optimally, if there are software conflicts, and if the right components are turned on. It will notify you if it finds any problem it can’t fix.
Note that starting the Network Troubleshooter in Windows 11 will activate the Get Help app.
Follow these steps:
- Open the Troubleshoot page:
- In Windows 11, open Settings, scroll down under “System,” and click “Troubleshoot.”
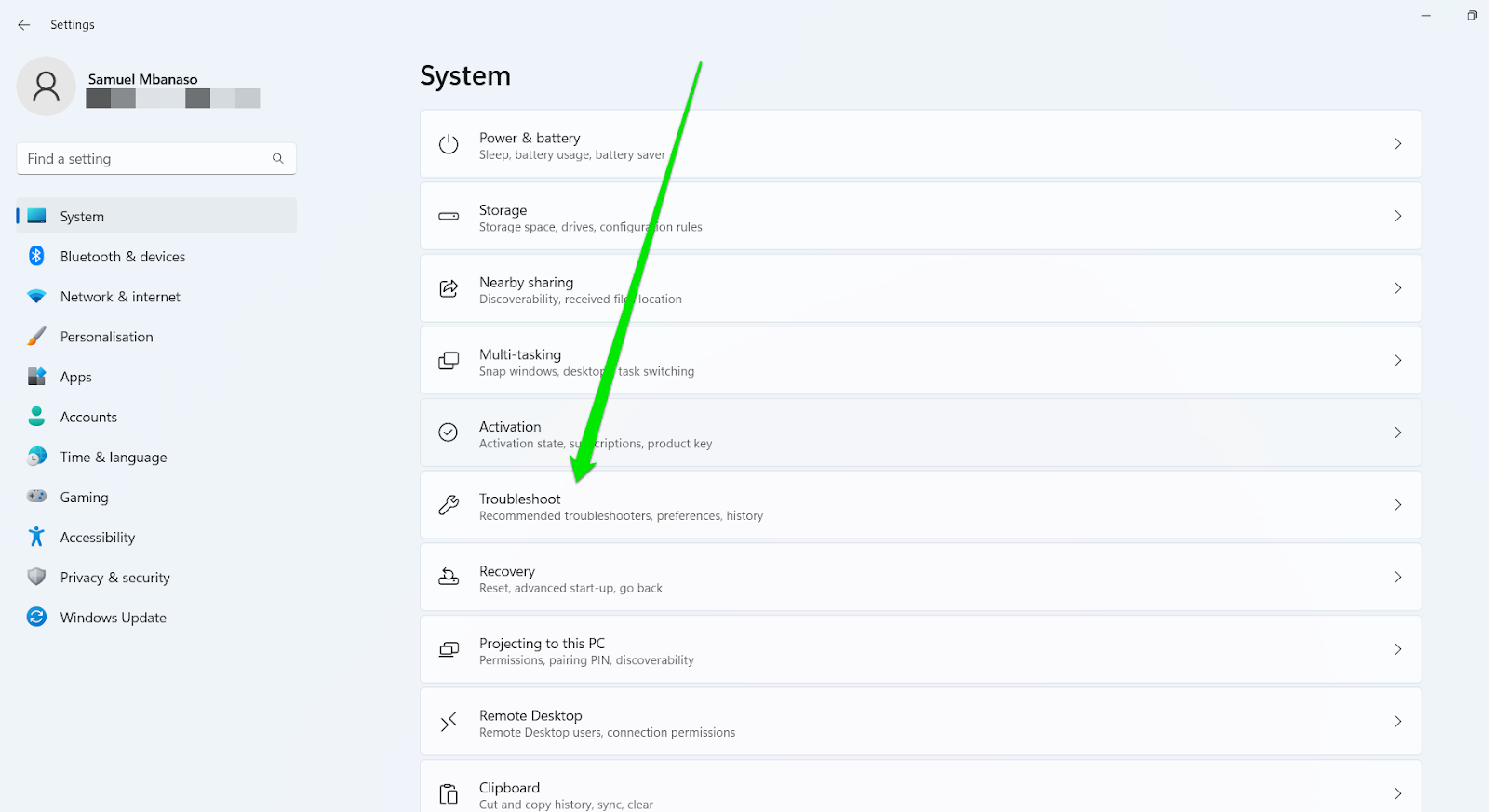
- On Windows 10, open Settings, click “Update & security,” and select “Troubleshoot” in the left sidebar.
- Run the Troubleshooter:
- In Windows 11, click “Other trouble-shooters” and select “Run” beside “Network and Internet.”
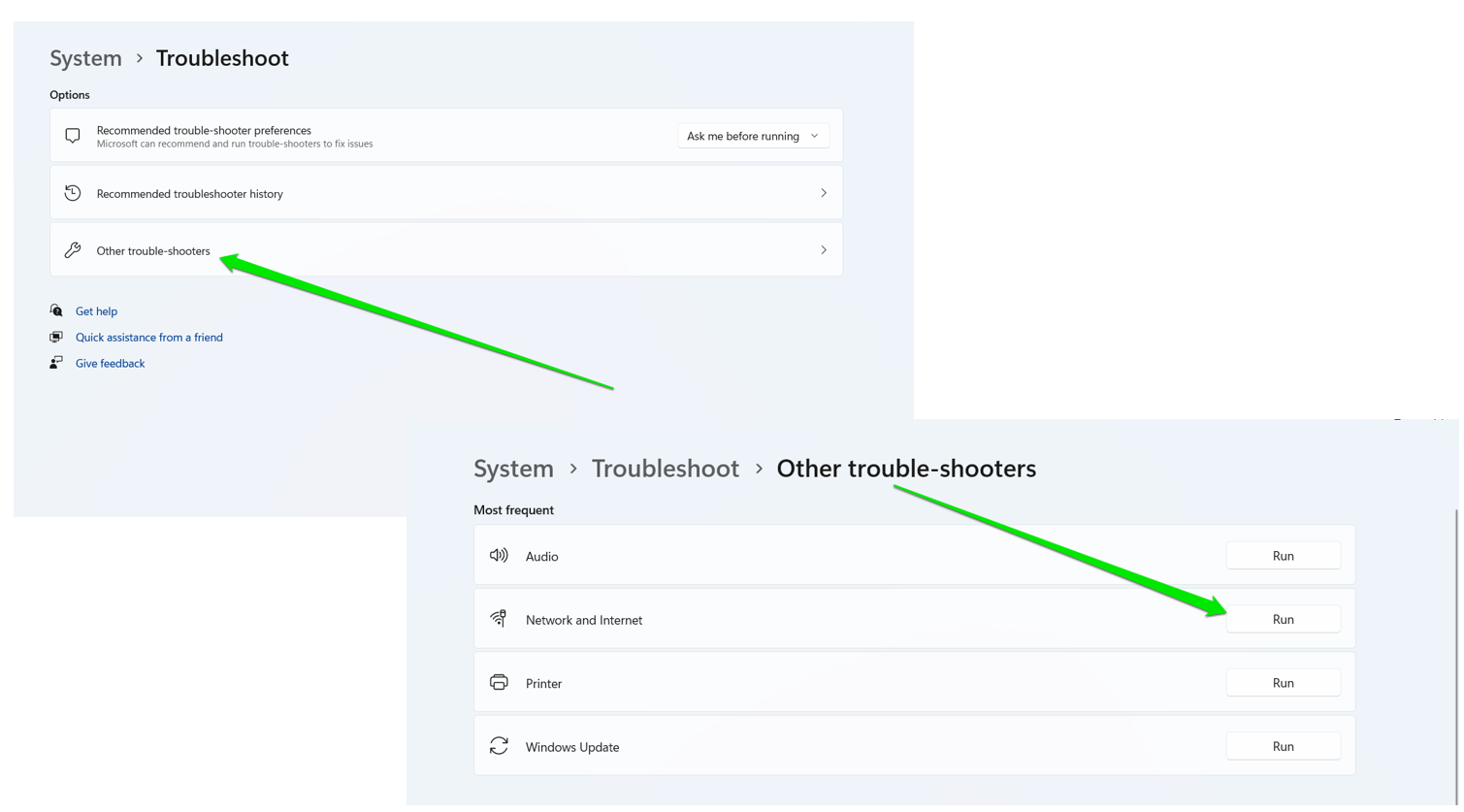
- In Windows 10, click “Additional troubleshooters,” click “Network adapted,” and select “Run the Troubleshooter.”
- Allow the troubleshooter to search for problems and attempt to fix them.
- If you’re on Windows 11, permit the Get Help utility to run automated diagnostics and follow the instructions for each step.
Reset Your Computer’s Network
The frequent disconnects may result from some settings you applied that don’t work for your setup. Corrupt WiFi profiles and other network configuration issues could also cause them.
Setting your network to its default mode can clear these faults.
When you reset your network, Windows will uninstall your network adapters and remove their settings. It will prompt you to restart your PC, reinstall the adapters, and apply their default settings.
According to Microsoft, you can only reset your network if you’re running version 1607 of Windows 10 or later.
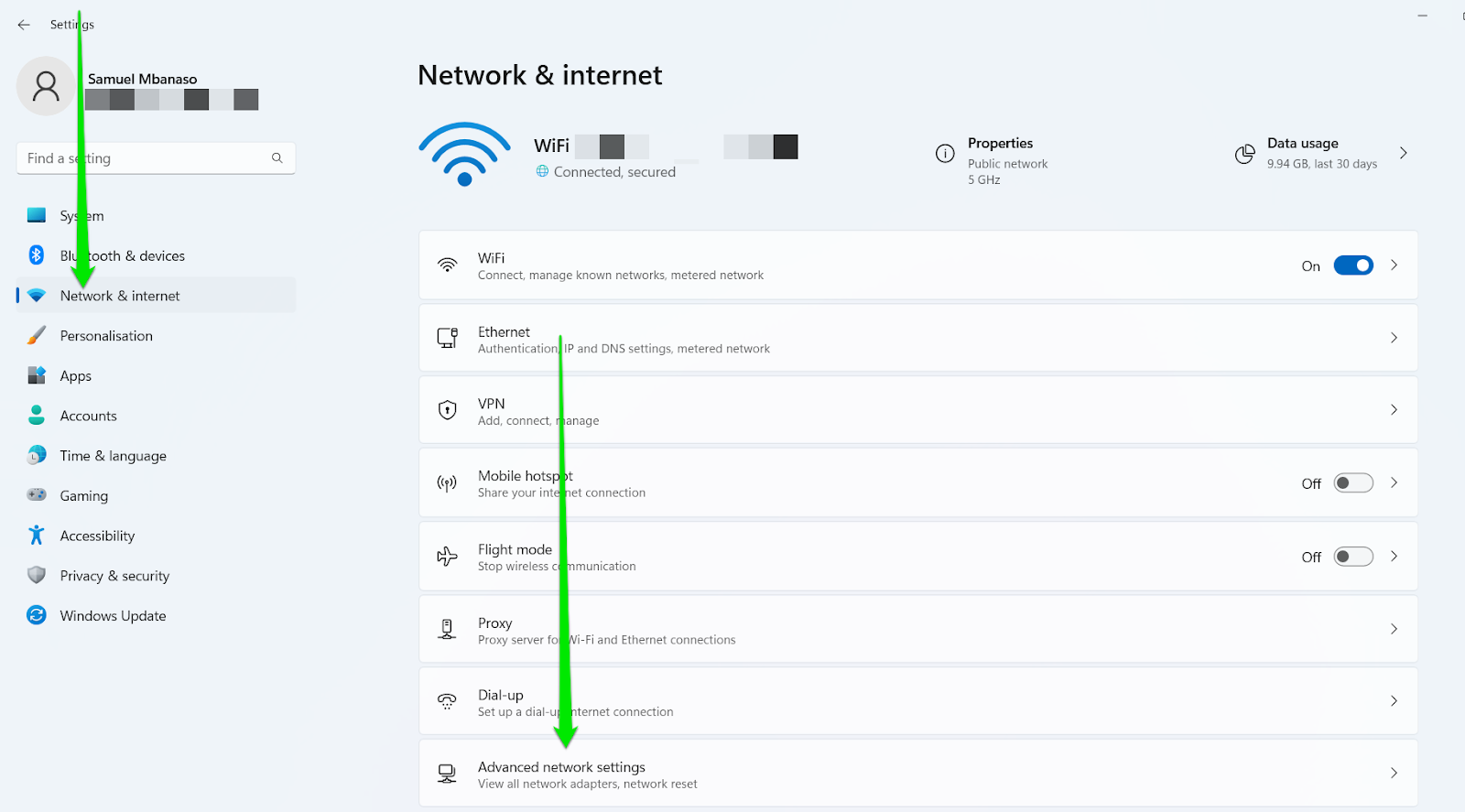
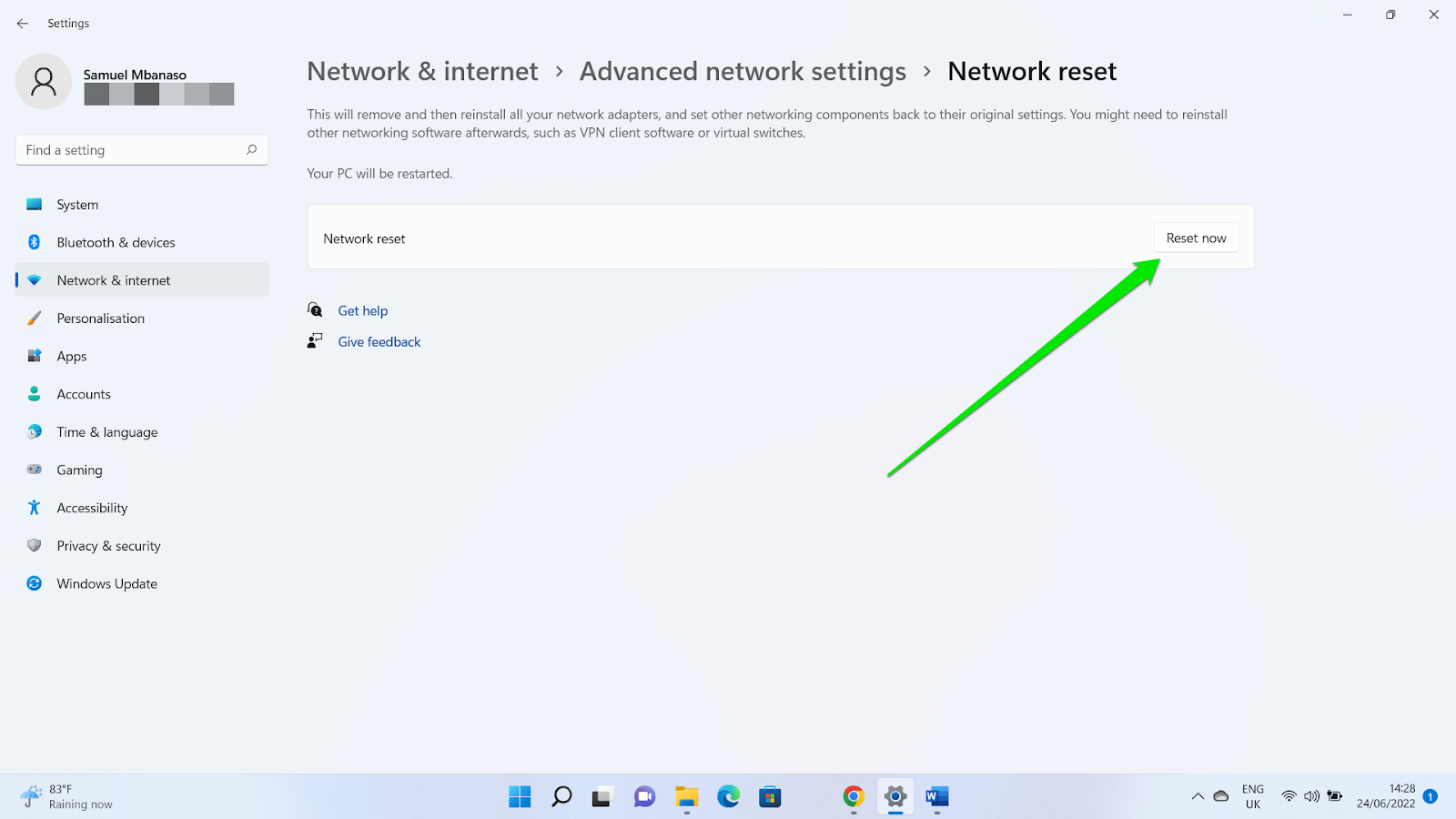
If you’re running Windows 11, follow these steps to reset your network:
- Launch the Settings app and click “Network & internet” in the left sidebar.
- Select “Advanced network settings” under the “Network & internet” page.
- Go to the “More settings” section and click “Network reset.”
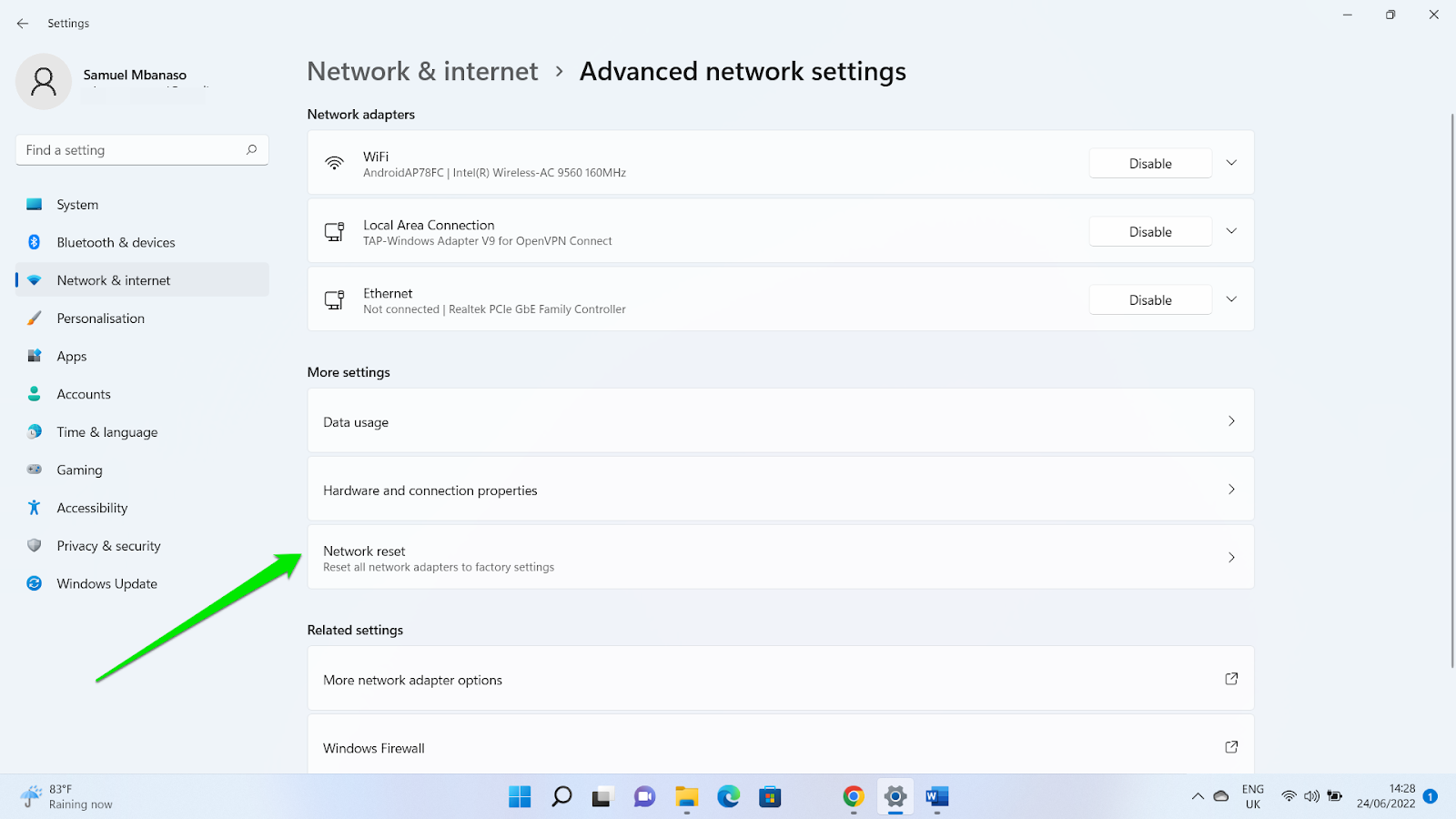
- Click “Reset now” on the next page.
Restart your computer after Windows resets your network. Follow these steps if you use a Windows 10 computer:
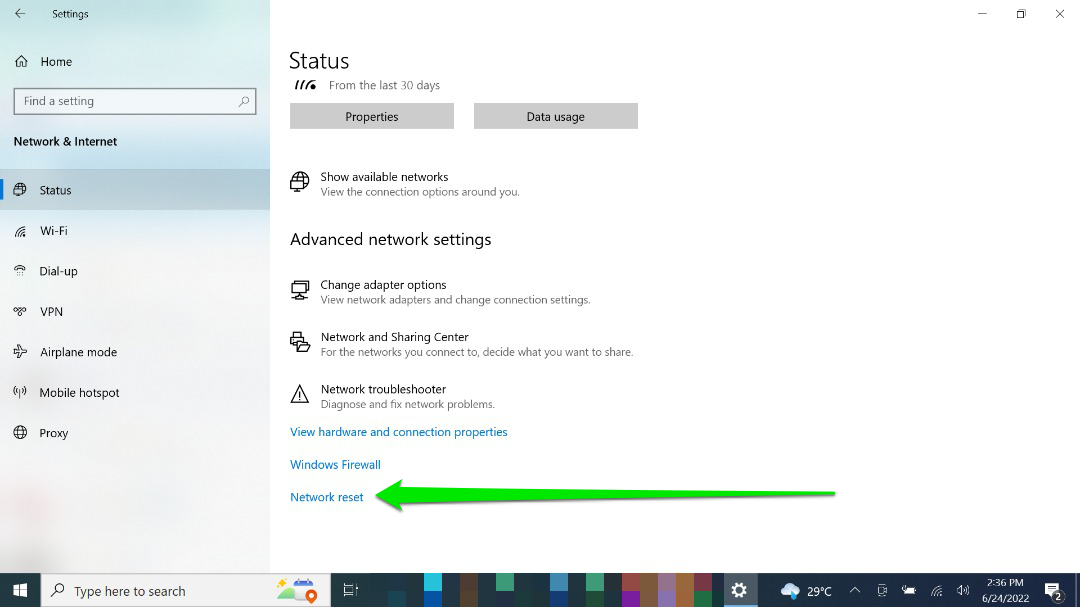
- Launch the Settings window and click “Network & Internet.&
- Once the Network & Internet page opens, stay on the Status screen and click “Network reset.”
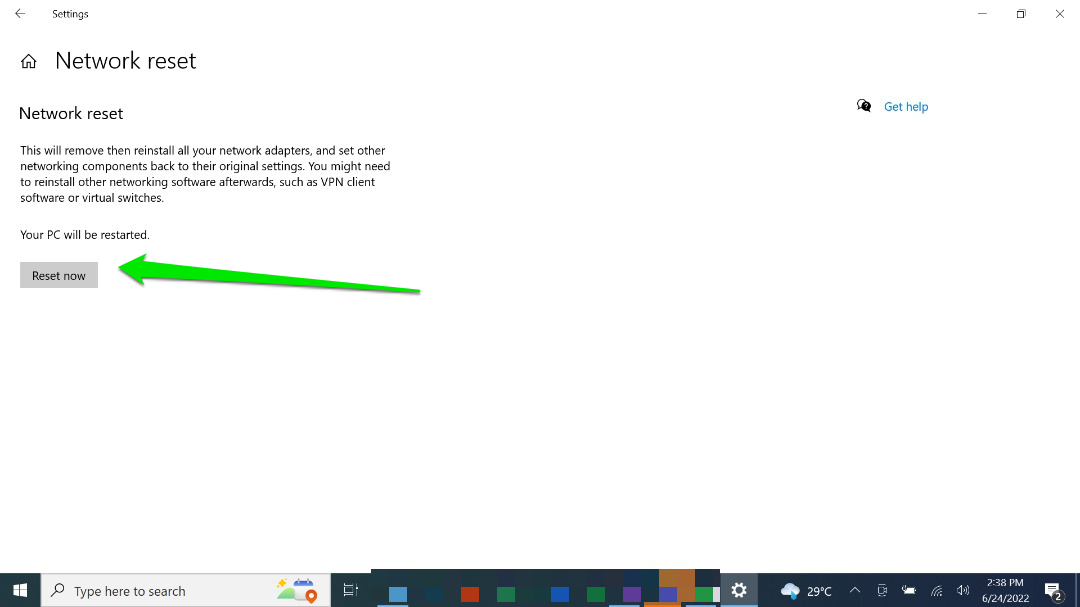
- Now, click “Reset now” after the “Network reset” page opens.
- Select “Yes” in the confirmation dialog.
- Allow your computer to restart.
Reconfigure the WiFi Profile
Windows normally saves WiFi connection details so that it can automatically connect to your router. These details include the SSID (network name), password/security key, and security type. That way, you don’t have to enter the router password whenever you want to connect.
If you change the router’s password at any point, every connection attempt will fail. However, if the WiFi profile becomes corrupt, you may start experiencing the “Internet keeps disconnecting” problem.
The solution here is to delete the profile and create a new one.
Follow these steps:
- Open your Settings application.
- Click “Network & internet.”
- Select WiFi under “Network & internet.”
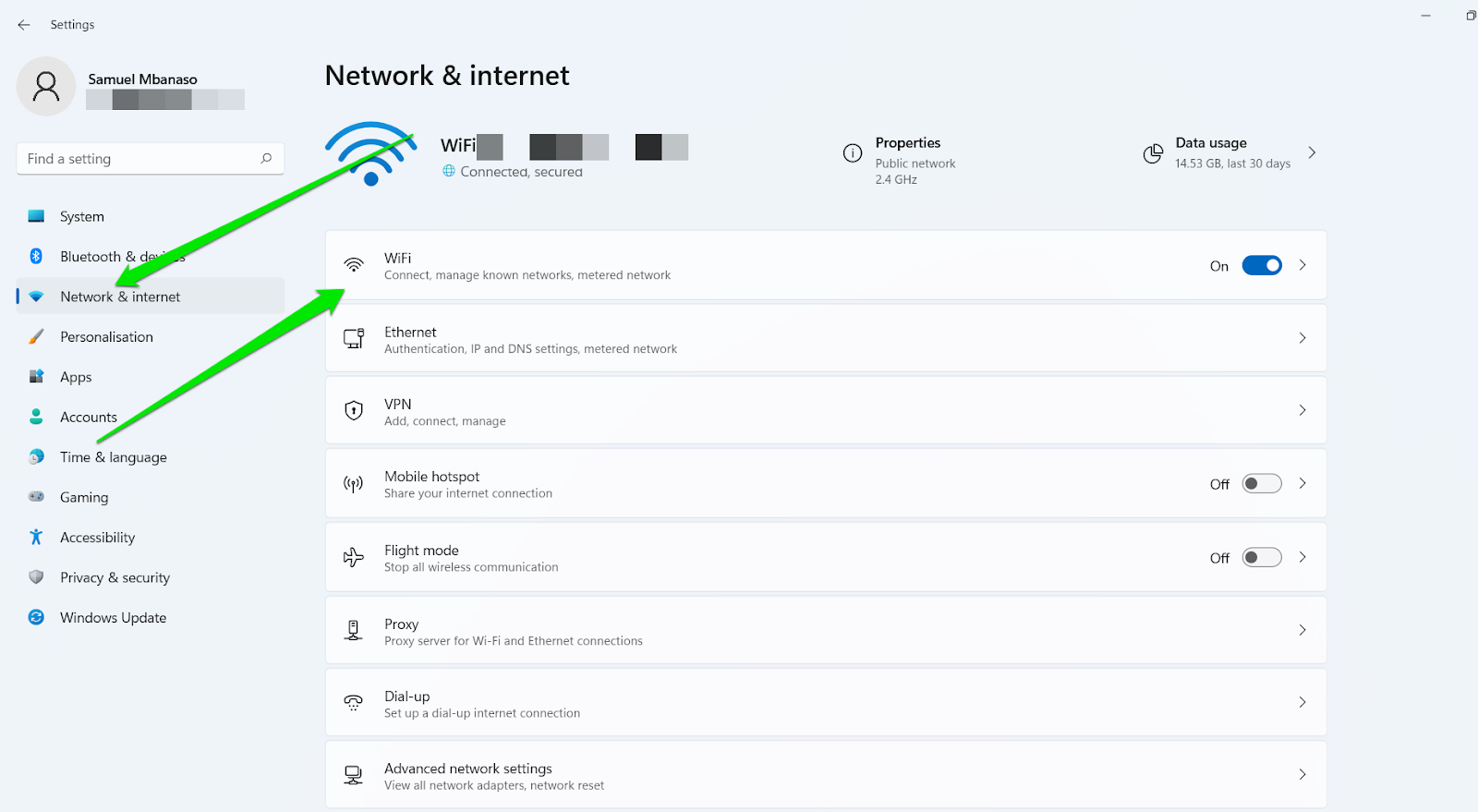
- Click “Manage known networks.”
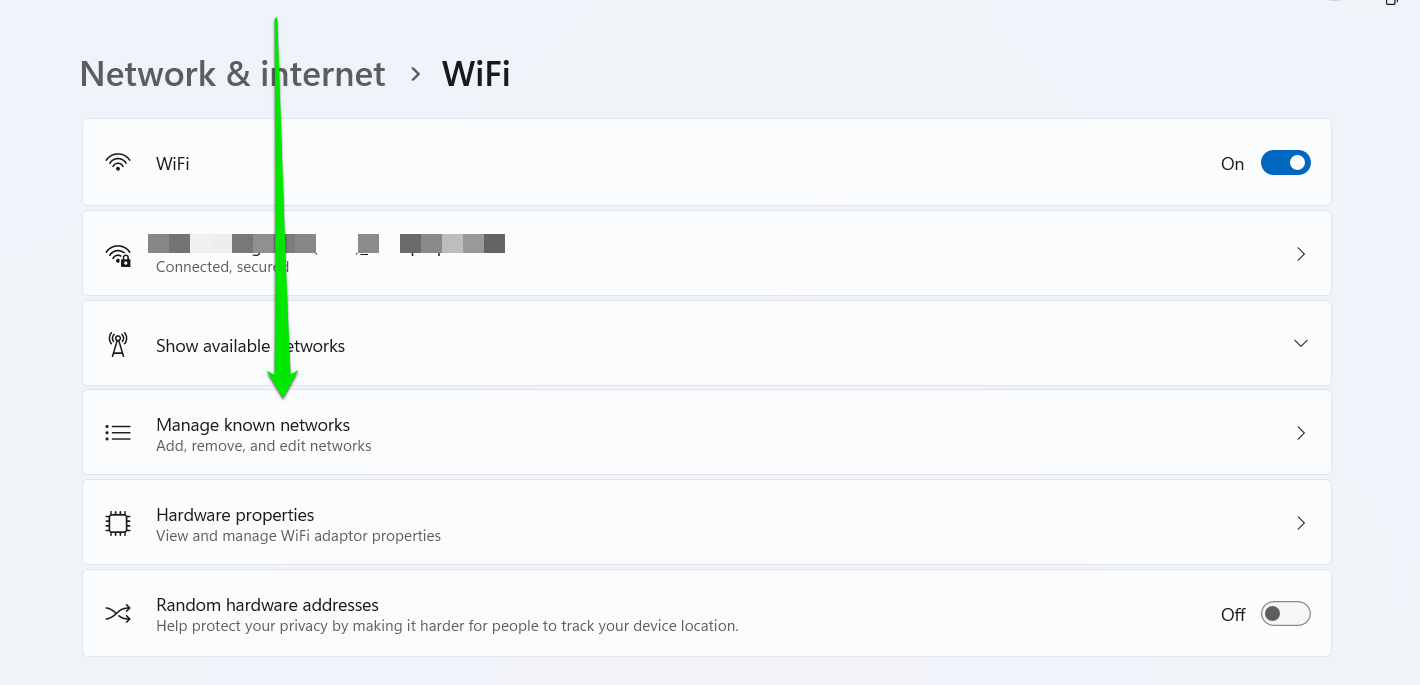
- Now, select “Forget” beside the saved network or click the network and tap “Forget.”
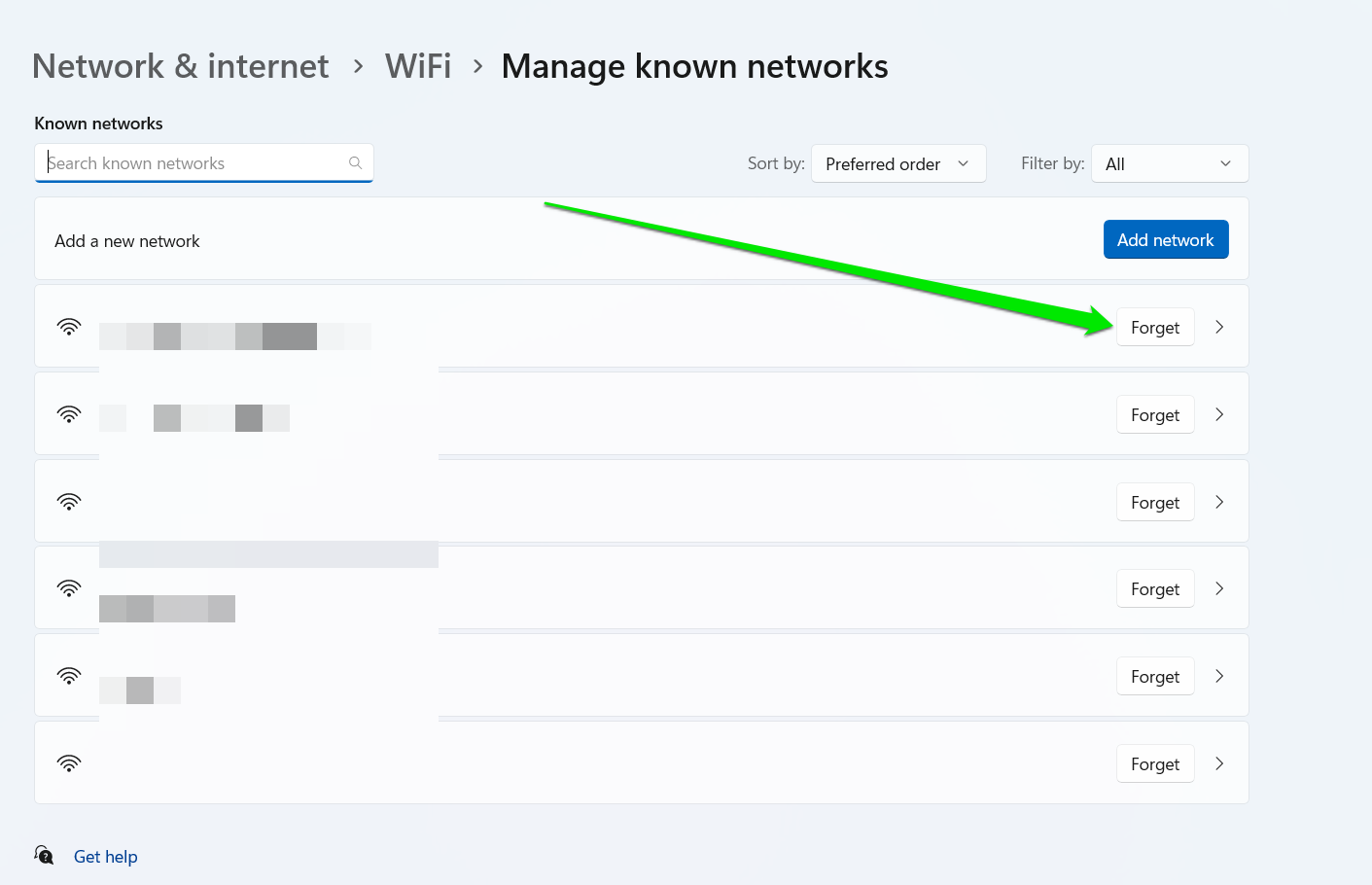
- Try connecting to the network again and provide the required details.
Preventing Future Internet Connection Outages
There are steps you can take to ensure you no longer ask, “Why is my WiFi going in and out.” Let’s go through them.
1. Use Auslogics BoostSpeed
Auslogics BoostSpeed is a top-level system optimization tool packed with all the utilities you need to keep your computer in good shape. It ensures your PC is always free of temporary and junk files and offers you options to tweak certain software features as you see fit.
The tool also comes with the Internet Optimizer utility that helps you boost your network speed.
Using the Internet Optimizer
To open the Internet Optimizer, launch BoostSpeed, use the arrow key beside the right side of the last tab to slide the tabs, and click All Tools.
Scroll through the All Tools tab and click Internet Optimizer under Internet & Browser Tools.
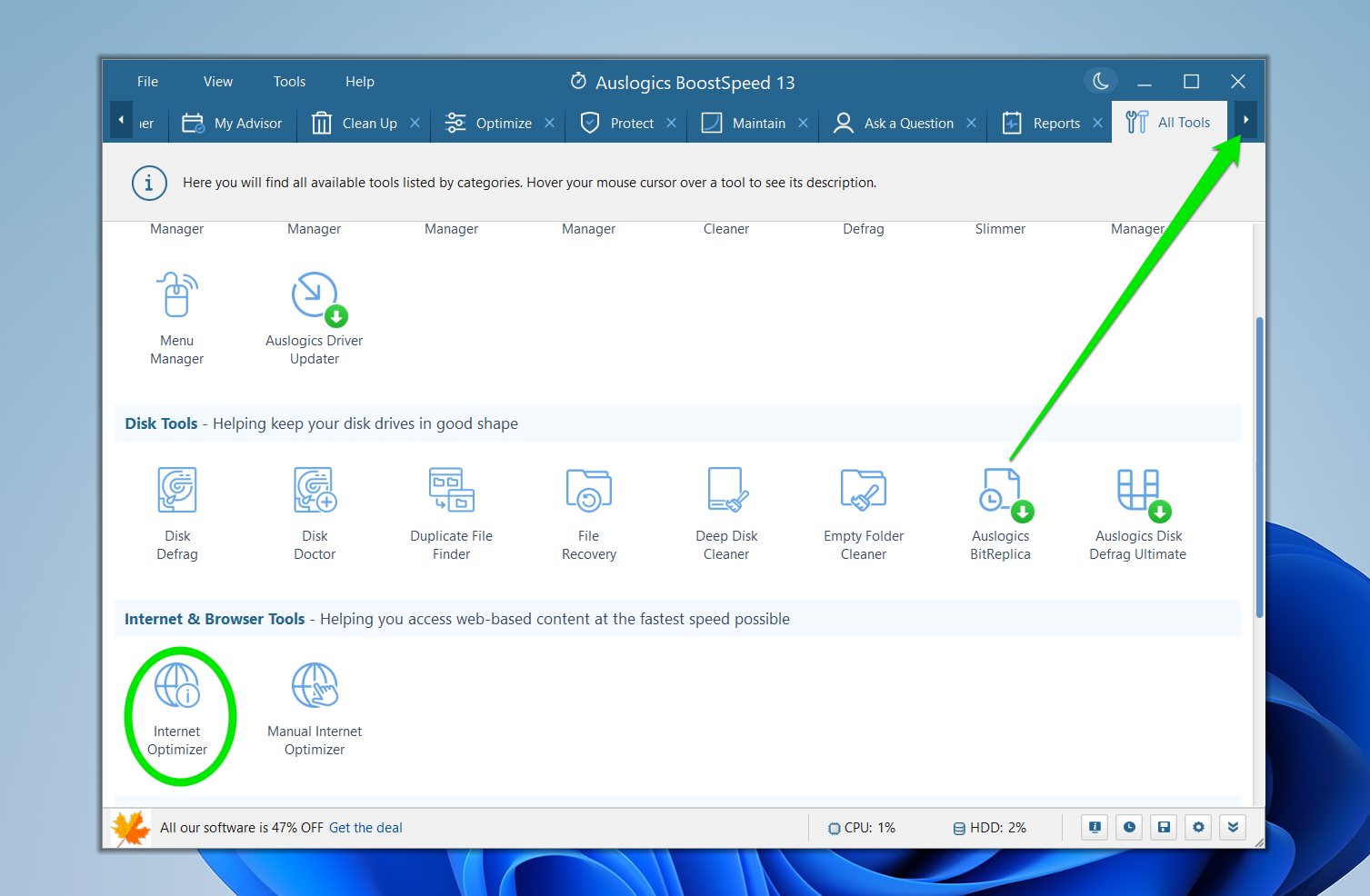
You can now use the Auto and Manual Optimization tools to fine-tune your internet connection.
Check Your Network Speed
Under “Auto Optimization,” click “Check my actual Internet connection speed.” Select OK, and you’ll be redirected to the Speedtest website. Follow the recommendations that pop up.
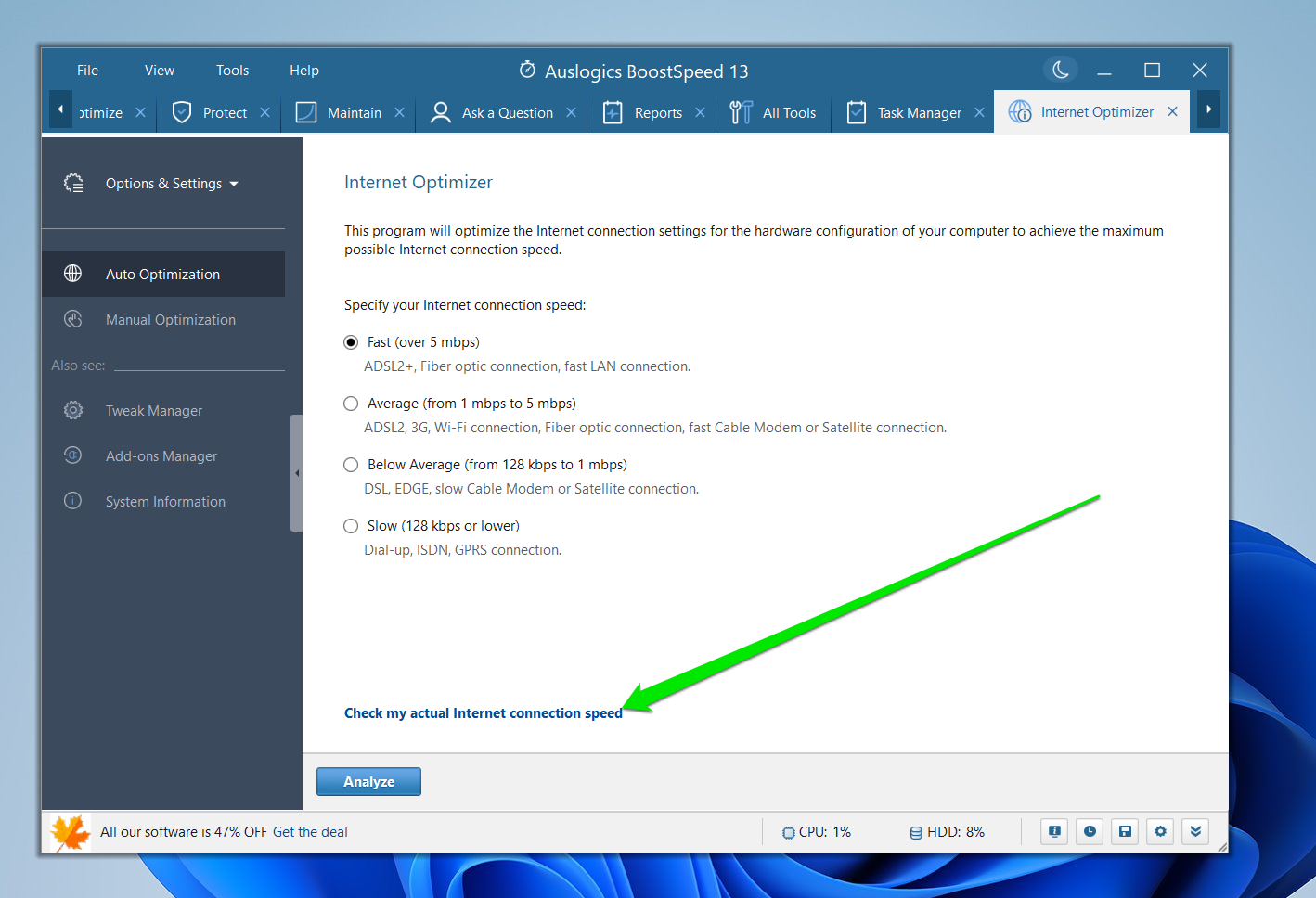
Fine-Tune Your Connection
Now that you know your network speed, click the “Analyze” button to test different aspects of your network infrastructure.
It will now show different parameters, detailing their current and recommended values. Click the “Optimize” button to boost your Internet speed.
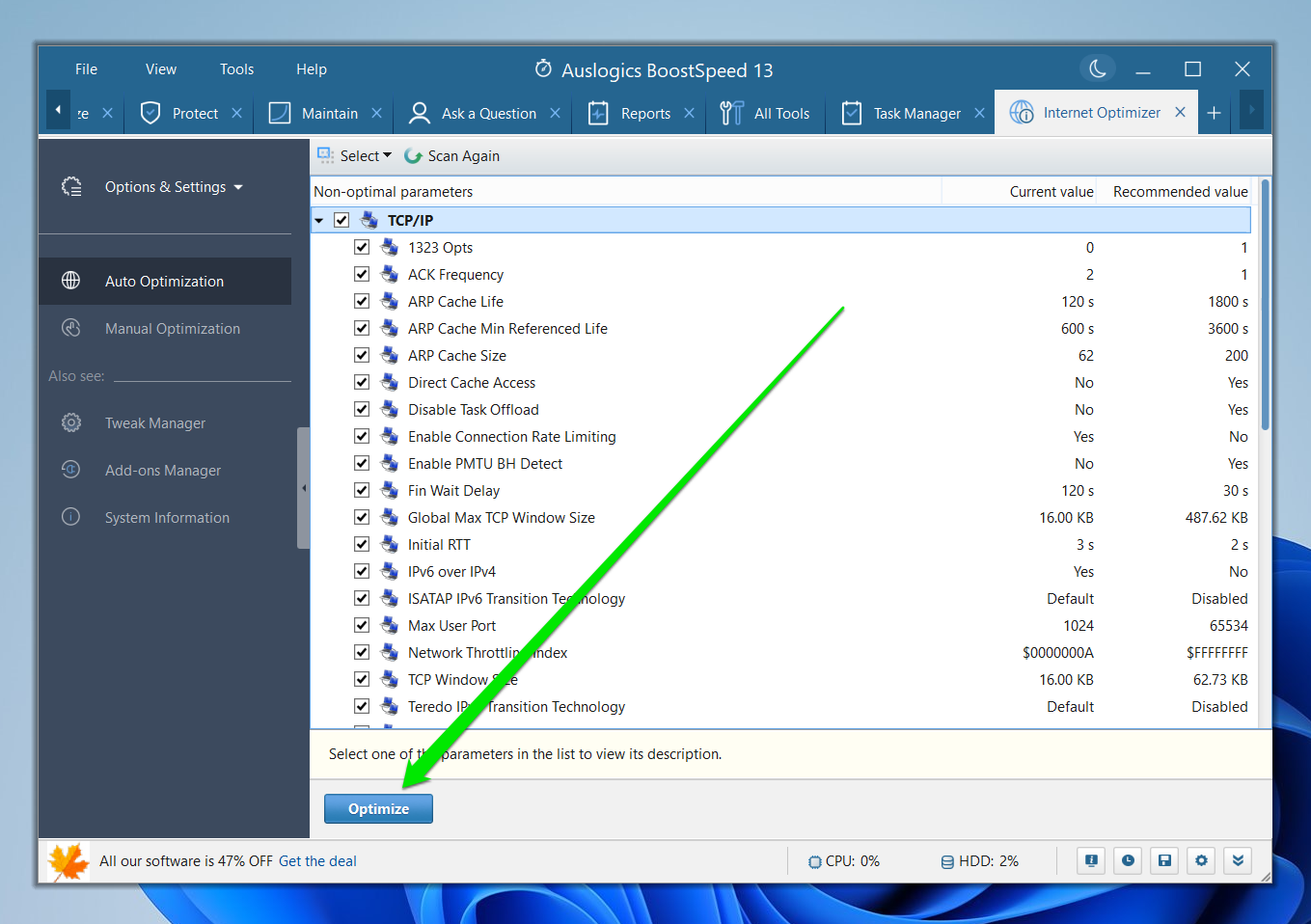
You may have to reboot Windows for the settings to take effect.
Manual Optimization
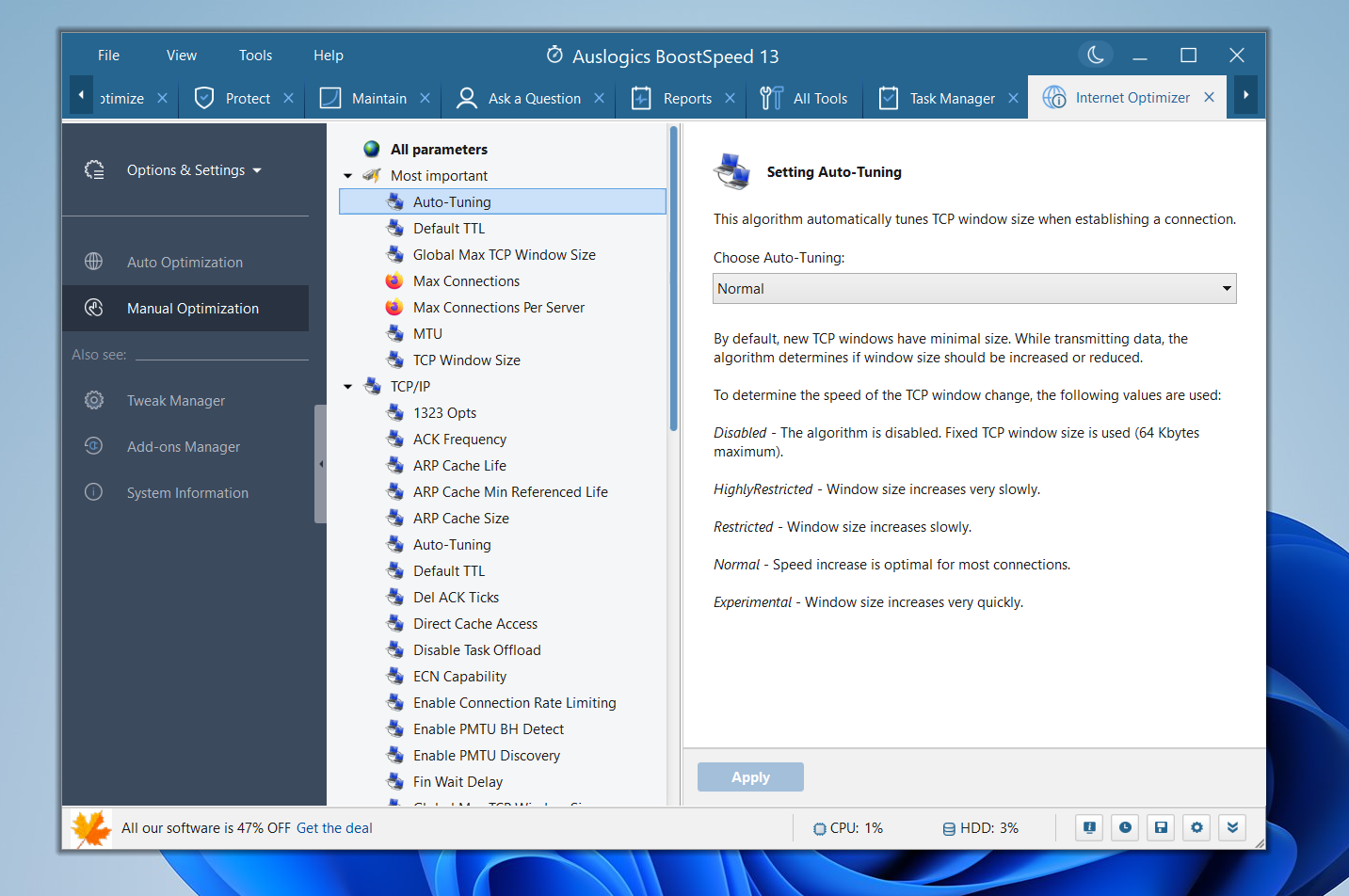
The Manual Optimization tab allows you to tweak different network infrastructure components yourself. You must know what you’re doing to use this tab, as it contains some advanced controls. You’re almost always better off using the Auto Optimization tab.
Also Read: Tricks to Get the Most out of Auslogics BoostSpeed Free Trial
2. Keep Malware Away
As mentioned earlier, attackers always search for new systems and networks to infect with malware.
To be on the safe side, update your antivirus regularly and keep it running. You should also keep your Firewall program up to date and stay away from suspicious websites.
You should also change your router’s password occasionally to tighten your security.
Also Read: Ultimate Guide: How to Find Wi-Fi Password on Windows 10 Computer
3. Apply Regular Updates
Ensure you regularly download and install the latest software for your operating system and devices, including your router and network adapters.
Also Read: How to Keep Your Software Up to Date
4. Go for High-Speed Internet Plans
You can also migrate to a different, more reliable data plan because the frequent disconnections can be due to the service you currently use.
Conclusion
Internet connection issues are never fun. But with the right practices, it’s possible to avoid them. You can try having a backup device or another ISP you can switch to if your internet abruptly starts to fluctuate. That way, you can rid yourself of the “Internet going in and out” issue for good.
FAQ
Why Does My Modem Keep Going Offline?
Your modem might be going offline intermittently because it has been working for too long and needs to be rebooted, its firmware is out of date, and there may be connection interference.
Why Does My Internet Randomly Go Out?
Causes of random internet connection disconnects include a full router or modem memory, malfunctioning network services, and faulty or out-of-date network adapter drivers. Other possible causes include corrupt WiFi profiles, DNS configuration issues, and malware.
How Can I Secure My Wi-Fi Network?
You can secure your network by using strong passwords and regularly changing your login credentials, using a firewall, keeping your router and modem firmware up to date, and restricting remote router access.
What Is Network Congestion, And How Does It Affect My Internet?
Network congestion is when your router has to deal with more data packet traffic than it can handle. This traffic overload causes a reduction in your internet speed and can trigger frequent disconnections.
What Is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
An ISP is a company that sells internet access to its subscribers.



