The Internet has made it convenient for us to find any information we need. You can visit websites directly or use a search engine like Google to access various types of data.
However, there are times when we are not able to open web pages, and there could be several reasons behind this.
In some cases, it may have something to do with your network connection. On the other hand, another common issue that causes this problem is a TLS handshake failure.
Now, you might ask, “What does a TLS handshake mean?”
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security, which is an encryption protocol. Communications made via this protocol remain private and secure.
In this post, we are going to explain what happens in a TLS handshake. In this way, you will gain a better grasp of the concept. Moreover, we will teach you how to fix the “TLS handshake failed” error.
What Does a TLS Handshake Mean?
As we all know, when there is a form of negotiation or greeting between two people, we traditonally seal it with a handshake. Similarly, when two servers communicate and acknowledge each other, they form a TLS handshake. During this process, the servers go through verification. They establish encryption while exchanging keys. Once all the details have been proven to be authentic, the data exchange will begin.
Here are the four steps involved in a TLS handshake:
- Indicating the TLS version which will be used for communication.
- Selecting the encryption algorithm for communication.
- A public key and the digital signature of the SSL certificate issuer will be used to verify authenticity.
- Session keys will be generated, which will then be exchanged between the two servers.
To make things simple, both parties will say ‘hello’ first. Then, the server will provide a certificate, which the client will verify. Once the certificate has been proven to be authentic, the session will begin. Before that, a key will be created, which will allow the data exchange between the servers.
How to Fix TLS Handshake Issues
Unfortunately, if the problem stems from the server, there is nothing you can do. For instance, if the certificate from the server cannot be authenticated, then the matter is out of your hands.
Also, some TLS signatures and versions are now obsolete and removed for safety reasons. Modern browsers will block connections to websites using those protocols, which can produce the error.
It is best to stay away from such websites if you can’t personally vouch for their safety.
However, if you are having issues with the browser you’re using, then there are still plenty of workarounds you can try. Also, if you’re dealing with a mismatch in the TLS protocol, you can fix the problem from the browser.
Various reasons could be behind a TLS handshake error. Before you try to fix the problem, you should ensure that you’re definitely dealing with a TLS handshake error.
In most cases, you can follow these rules:
- Try visiting other sites and see if the problem persists.
- If you’re using a WiFi network, try switching to a wired one.
- Try other network connections. For instance, use a different router or switch to a public network.
- Try using another web browser.
Once you’ve established the cause of the problem, you might ask, “Should I disable a TLS handshake on my browser?”
We understand your frustration, but we do not recommend doing it. After all, the TLS protocol is one of the best ways to ensure a secure browsing experience.
Indeed, you can continue browsing a website even with an invalid certificate. However, you should never perform any form of transaction with it. For example, do not submit password credentials or use your credit card.
On the other hand, there are times when the TLS handshake problem stems from issues with your browser. In this case, you can fix the problem by reconfiguring some settings on your browser.
We’ll share some of the best workarounds below.
Solution 1: Ensuring the Correct System Time
Most of the time, a TLS handshake fails because of incorrect system time settings. Keep in mind that the system time is a vital factor in testing whether a certificate is still valid or expired.
So, if the time on your PC does not match the server’s, then it will seem like the certificates are no longer valid. So, we recommend that you set the system time to ‘automatic’. Here are the steps:
- On your keyboard, press Windows Key+I. Doing so will open the Settings app.
- Once you’re on the Settings app, select Time & Language.
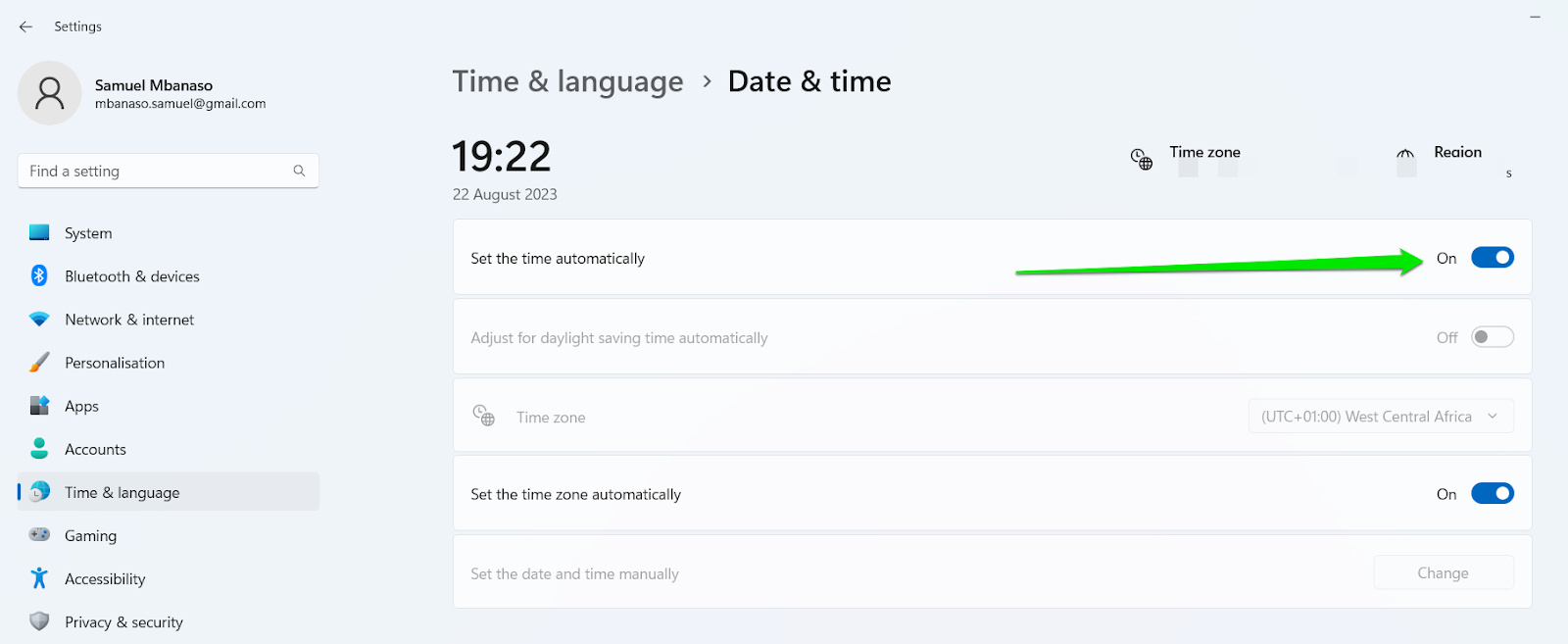
- Go to the right pane, then toggle the switch under Set Time Automatically to On.
- Restart your computer, then try visiting the site again to see if the TLS handshake error is gone.
Follow these steps for Windows 11:
- Launch the Settings app using the Win+I combo.
- Click on Time & Language in the left pane.
- Select Date & Time on the Time & Language page.
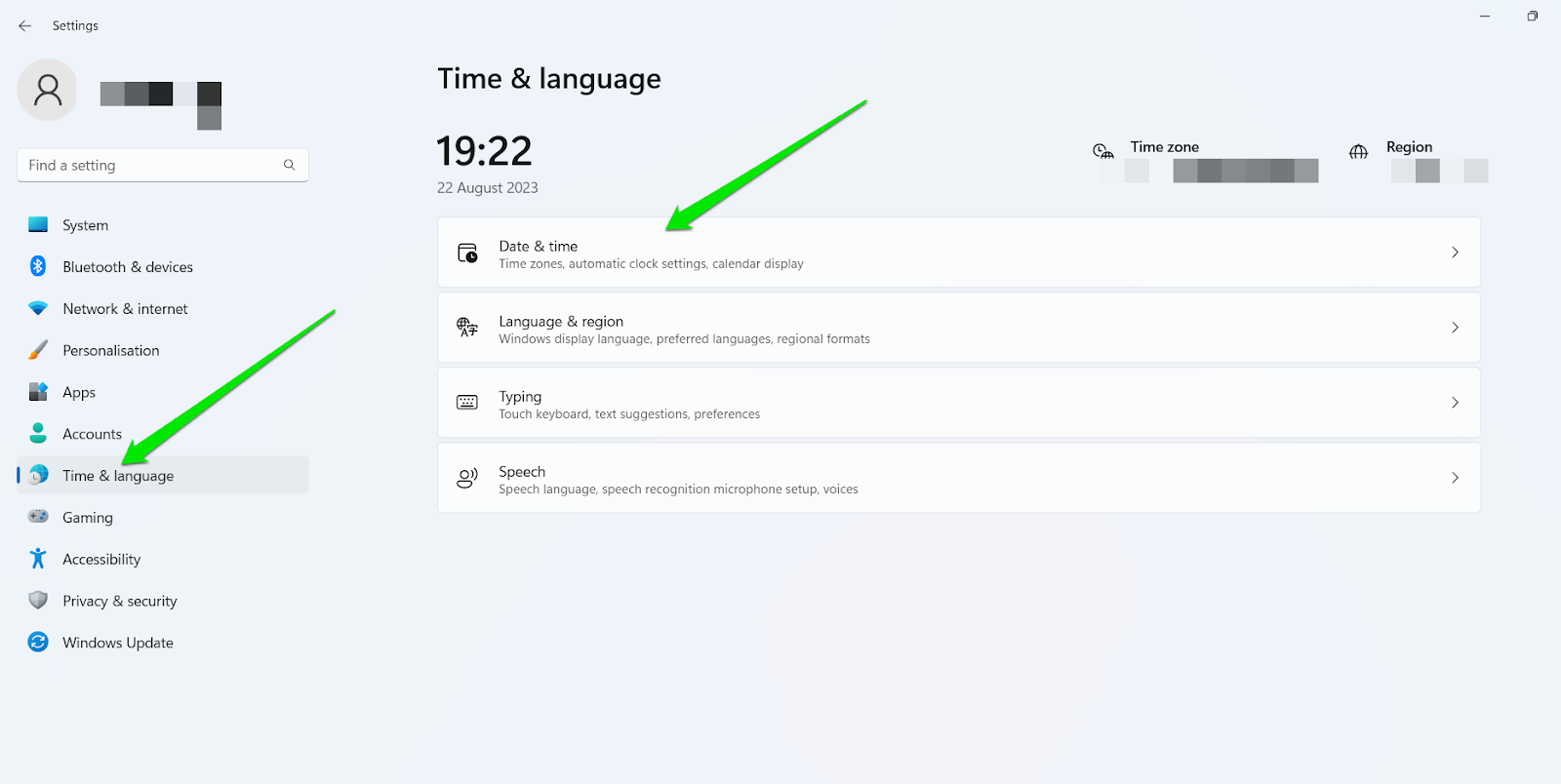
- Toggle on the “Set the time automatically” option.
Solution 2: Changing the TLS Protocol in Windows 10
Perhaps, the issue has something to do with the TLS version that your browser is using. It is worth noting that Windows 10 and earlier versions of the operating system has a central internet protocol setting with options to choose TLS versions.
You should also note that this option worked directly with the new retired Internet Explorer and older version of Microsoft Edge. The new Edge and other browsers such as Chrome have their native protocol policies and use the latest versions of TLS.
You can access Internet Properties to switch to a different TLS version. To do that, follow these instructions:
- Launch the Run dialog box by pressing Windows Key+R on your keyboard.
- Inside the Run dialog box, type “inetcpl.cpl” (no quotes), then click OK.
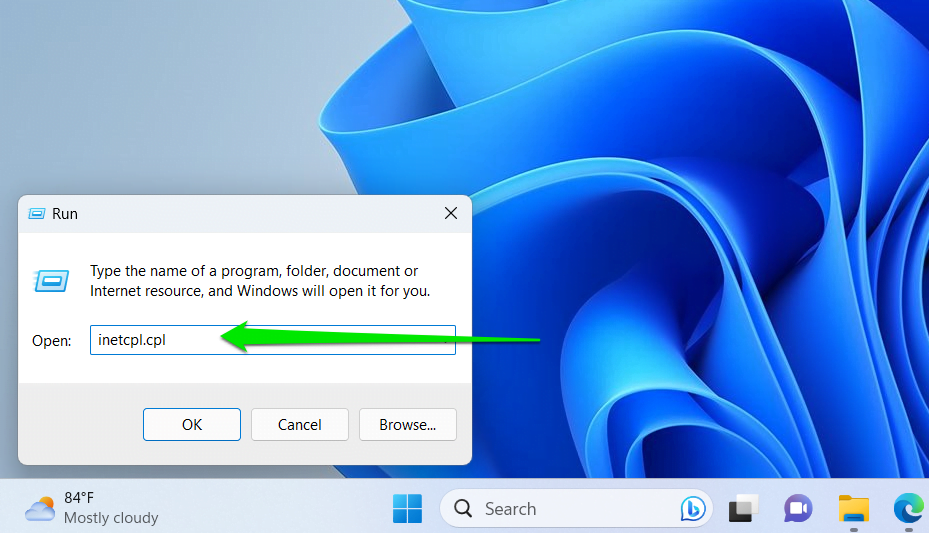
- On the Internet Properties window, go to the Advanced tab.
- Scroll down until you get to the Security section, where you can add or remove TLS protocols.
- If the website you’re trying to access needs TLS 1.2. then you need to select it. You can also select multiple TLS versions.
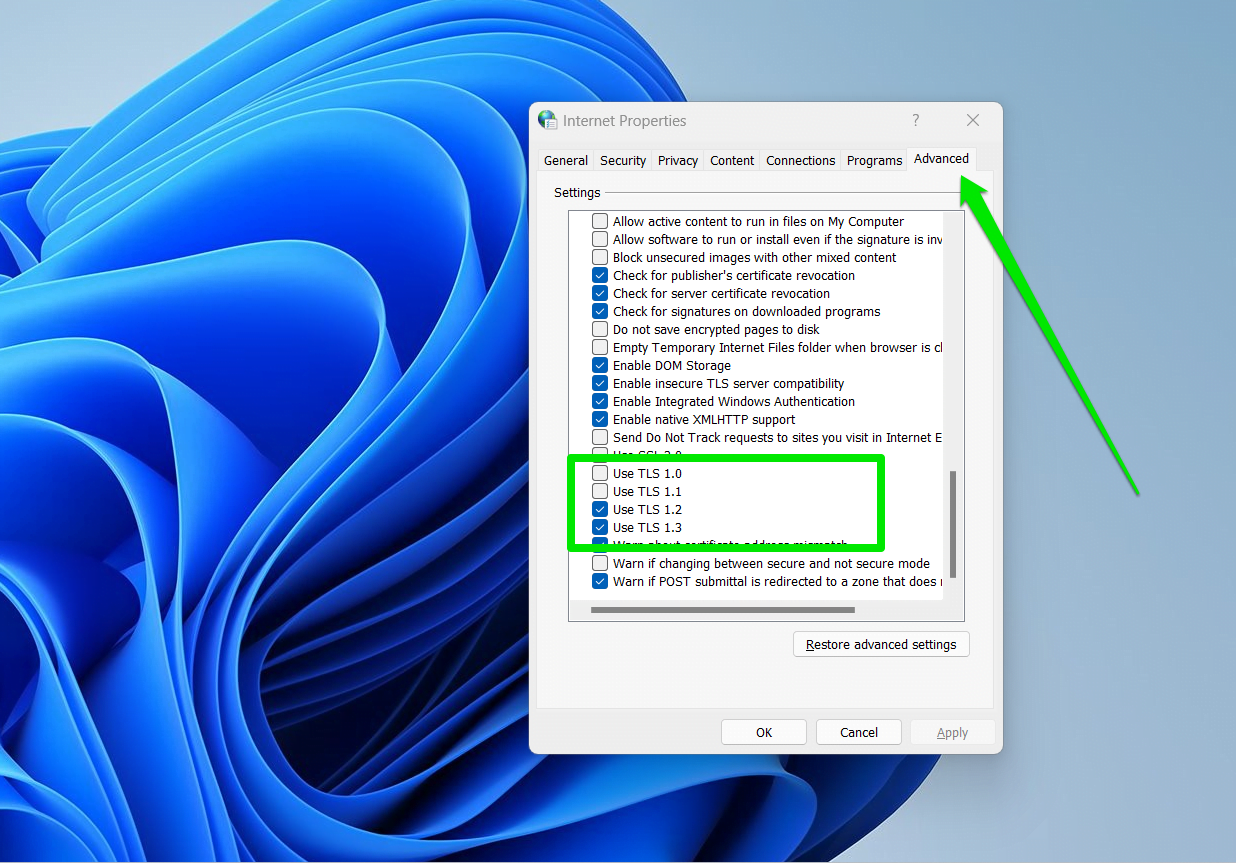
- Click Apply and OK to save the changes you’ve made.
- After changing the TLS version, try accessing the same website again.
Another important thing to remember is that major browsers such as Google Chrome and Firefox have long deprecated TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1. You’ll likely get a safety error or a TLS handshake protocol error message if the website uses any of these protocols.
So, if you want to change the TLS version on Firefox, use the following steps:
- Launch Firefox, then type “about:config” (no quotes) in the address bar.
- Press Enter and click “Accept the risk and continue”
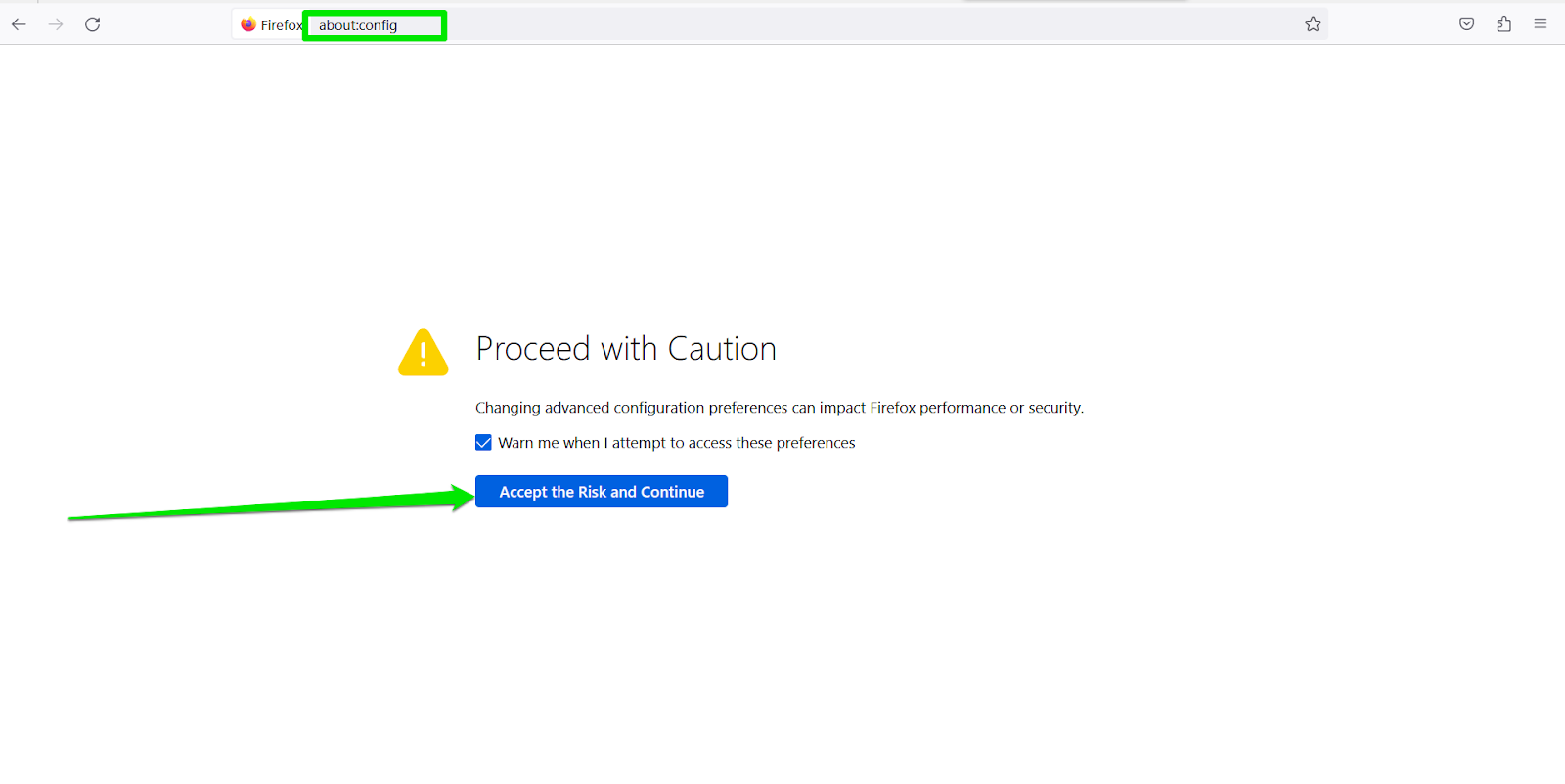
- Next, click the search box and type “TLS” (no quotes).
- Now, look for security.tls.version.min and security.tls.version.max.
- You can force different TLS versions by using the following:
Note: Firefox also deprecated obsolete TLS versions (1.o and 1.1). So, you should ideally force TLS 1.2 and 1.3 if they are not already enabled for some reason.
Force TLS 1 and 1.1 by entering 1 and 2.
Force TLS 1.2 by entering 3.
Force a maximum protocol of TLS (security.tls.version.max) 1.3 by entering 4.
If you absolutely have to visit the website with the deprecated TLS version, you can enable the versions by going to the “security.tls.version.enable-deprecated” option and clicking on the switch button on its right to change its value to True.
Make sure you switch back to false once you finish visiting the website.
Unfortunately, Chrome and Edge have sterner policies when it comes to TLS handshakes, as you cannot change the TLS version. That said, you can allow Chrome to accept handshakes from SHA-1 TLS websites, another deprecated encryption.
Follow these steps:
- Launch Chrome, enter “chrome://flags/” into the address bar and punch the Enter key.
- Once the Experiments page (alongside its warning) displays, go to the search box and type “tls.”
- After the results appear, navigate to “Allow SHA-1 server signatures in TLS” and choose Enabled from its drop-down dialog.
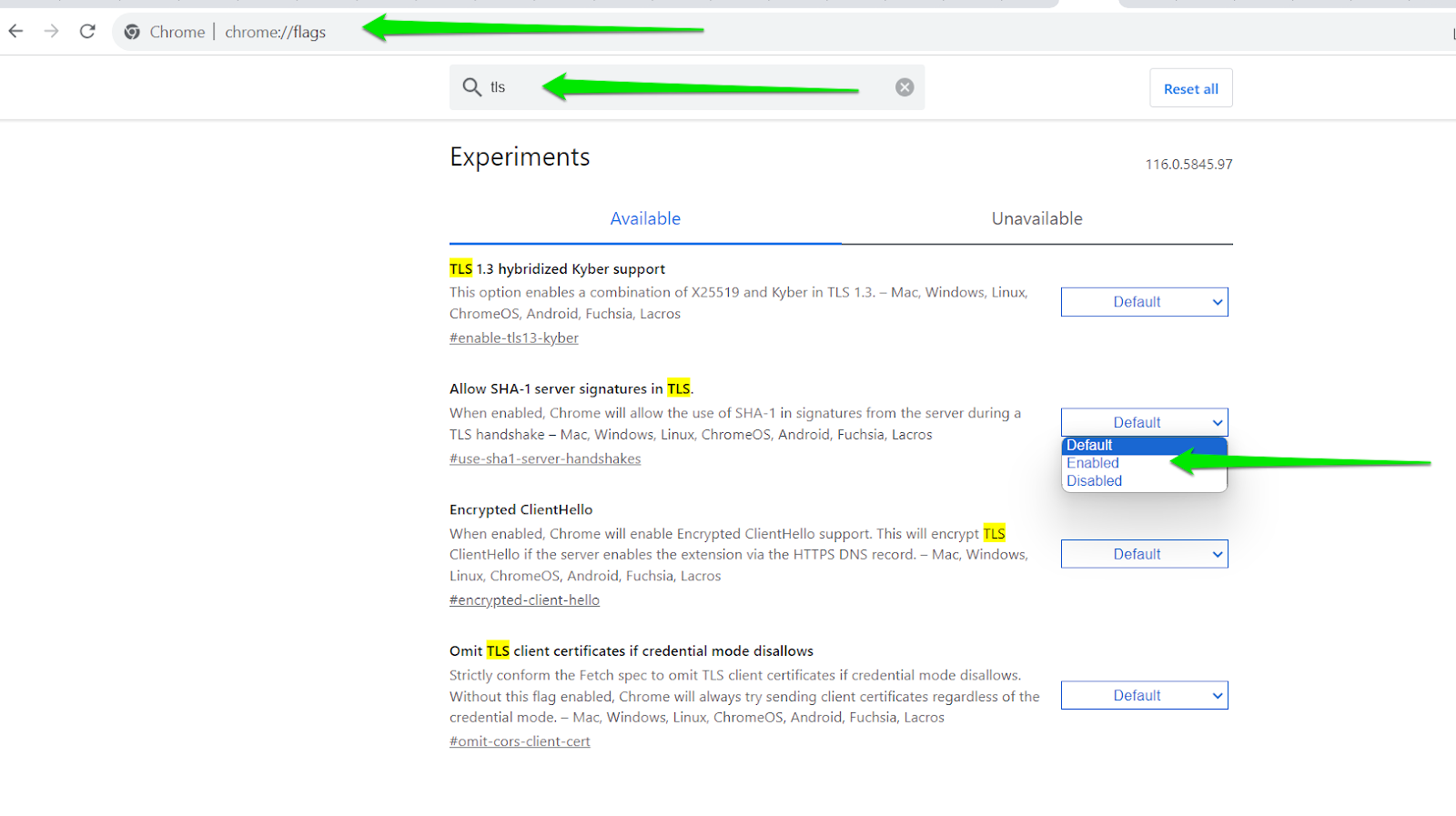
Note: This might be a risky move as most browsers have removed SHA-1 TLS server signatures because they have become increasingly unsafe. So, make sure you personally trust websites you visit before turning on this feature.
We also recommend switching it off once you’re done.
Solution 3: Disabling Interfering Program
If you use a third-party antivirus and firewall application, it might be blocking your connection to the website. Some of these applications have strict policies to block specific websites. So turn off your third-party antivirus/firewall for a while and use the native Windows Security.
If the issue goes away after disabling the antivirus, you can switch to another system protection program that will provide the same level of protection (or even better) without compromising your browsing experience.
Auslogics Anti-Malware is a good pick. It works with a low-profile and does not cause conflicts with your main antivirus suite. That said, it packs powerful features that helps you keep your system safe from even the most sophisticated software attacks.
Another software application or browser extension that may be blocking the TLS handshake is your VPN (Virtual Private Network). These applications are used to reroute network traffic to conceal IP address, improve security, and bypass restrictions.
In some cases, the VPN server may not agree with the website’s server, causing the error to occur. It could be that the website is blocking traffic from the VPN server or the VPN is blocking the website’s protocol.
You can switch VPNs or use another device (without a VPN connection) to access the website to confirm the cause of the problem.
Also Read: How to Choose VPN: Best Free VPN for Windows 10 PC
Solution 4: Deleting the Certificate Database or Browser Profile
Browsers keep a certificate database. For instance, Firefox profiles maintain a cert8.db file. There is one way to know that the TLS handshake failure is related to the local certificate database. You can try deleting the cert8.db file on Firefox. If the error disappears when you restart your computer and browser, then you’ve determined the culprit.
For Edge, the Certificate Manager is responsible for handling the certificates. You can delete the certificates by following these steps:
- Open Edge, then enter “edge://settings/privacy” (no quotes) in the address bar.
- Type “Manage HTTPS” in the settings search bar.
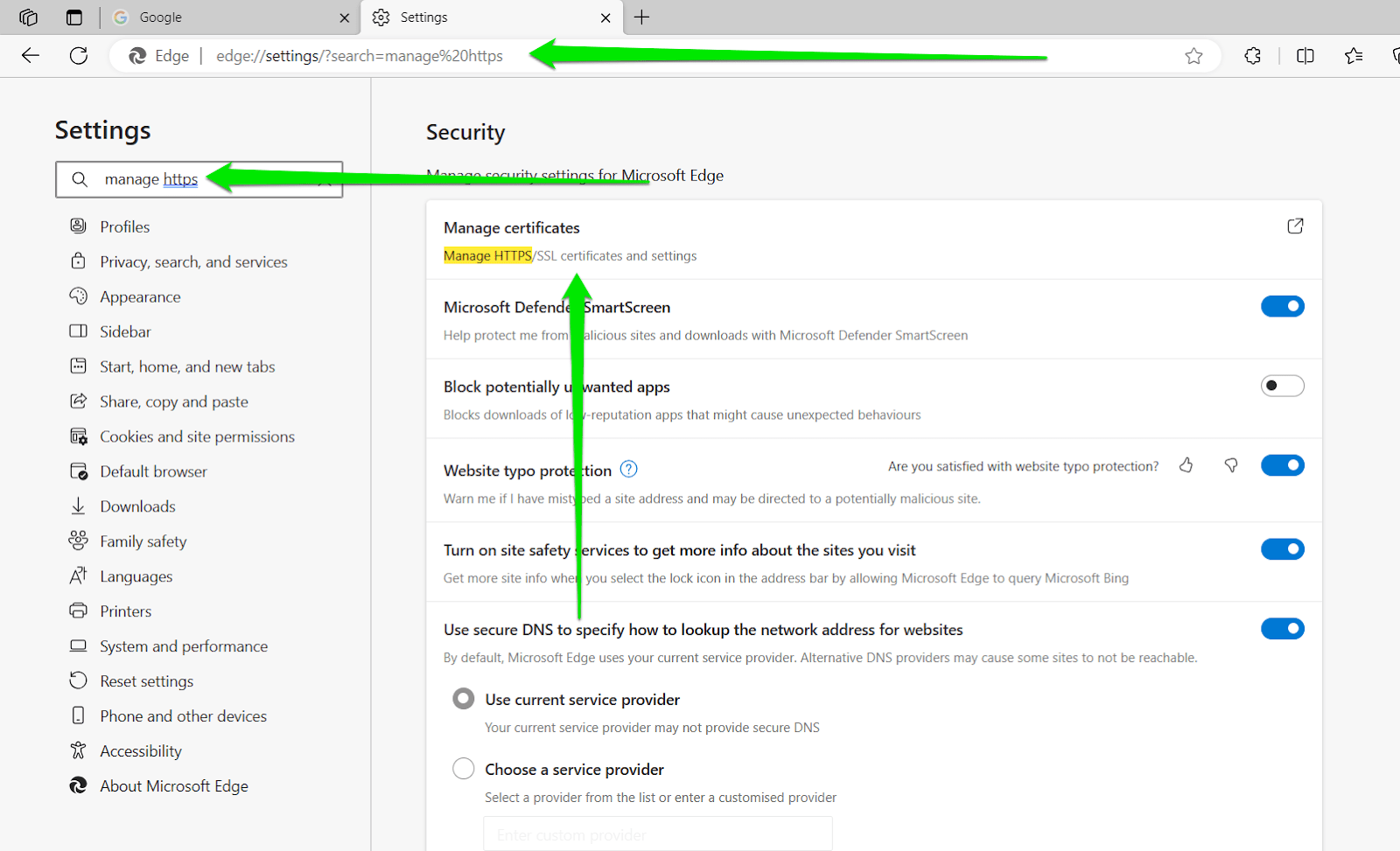
- Click the ‘Manage HTTPS/SSL certificates and settings’ option.
- Now, delete certificates that are expired.
- To delete expired certificates, switch between tabs and check each certificate’s expiry date date under the appropriate column.
- Once you see an expired certificate, click on it once and select Remove. Confirm your option in the dialog that pops up.
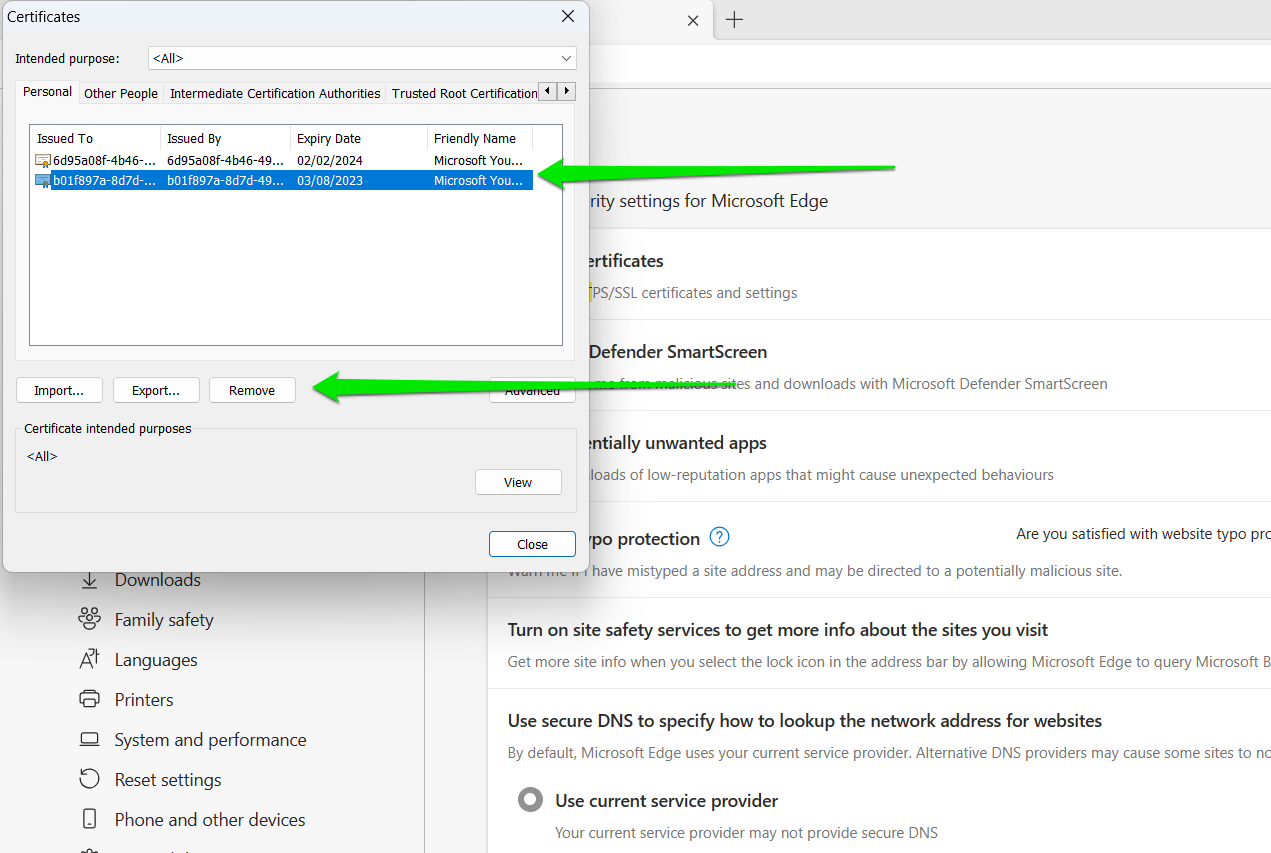
If you’re having trouble finding the certificate database, your best bet is to delete the browser profile. Once you’ve done this, you can try accessing the website again to see if the TLS error is gone.
Deleting a browsing profile permanently removes the user’s browsing data, including passwords, history, and favorites. Each web browser has a different method of deleting profiles.
Follow this step for Microsoft Edge:
- Launch Microsoft Edge and click on the three dots in the top right corner.
- Click on Settings after the menu appears.
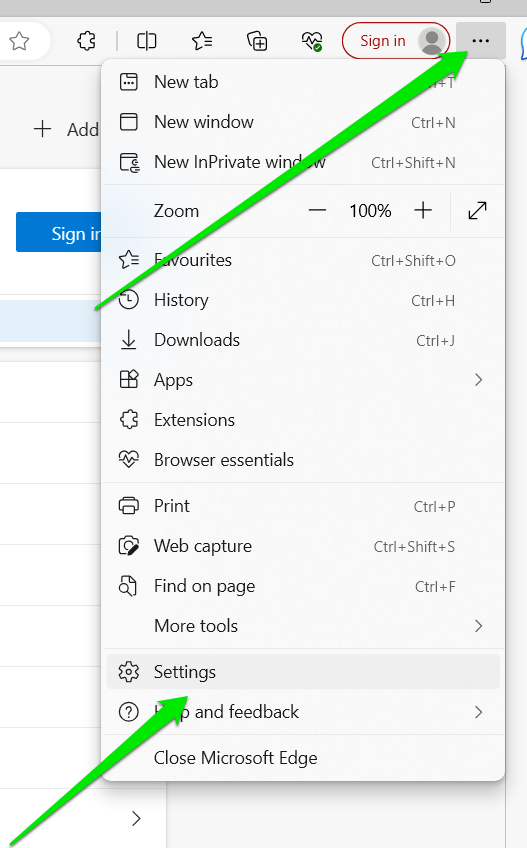
- Select Profiles on the left hand side.
- Go to the Profile on the right and click the three dots.
- Select Remove from the menu.
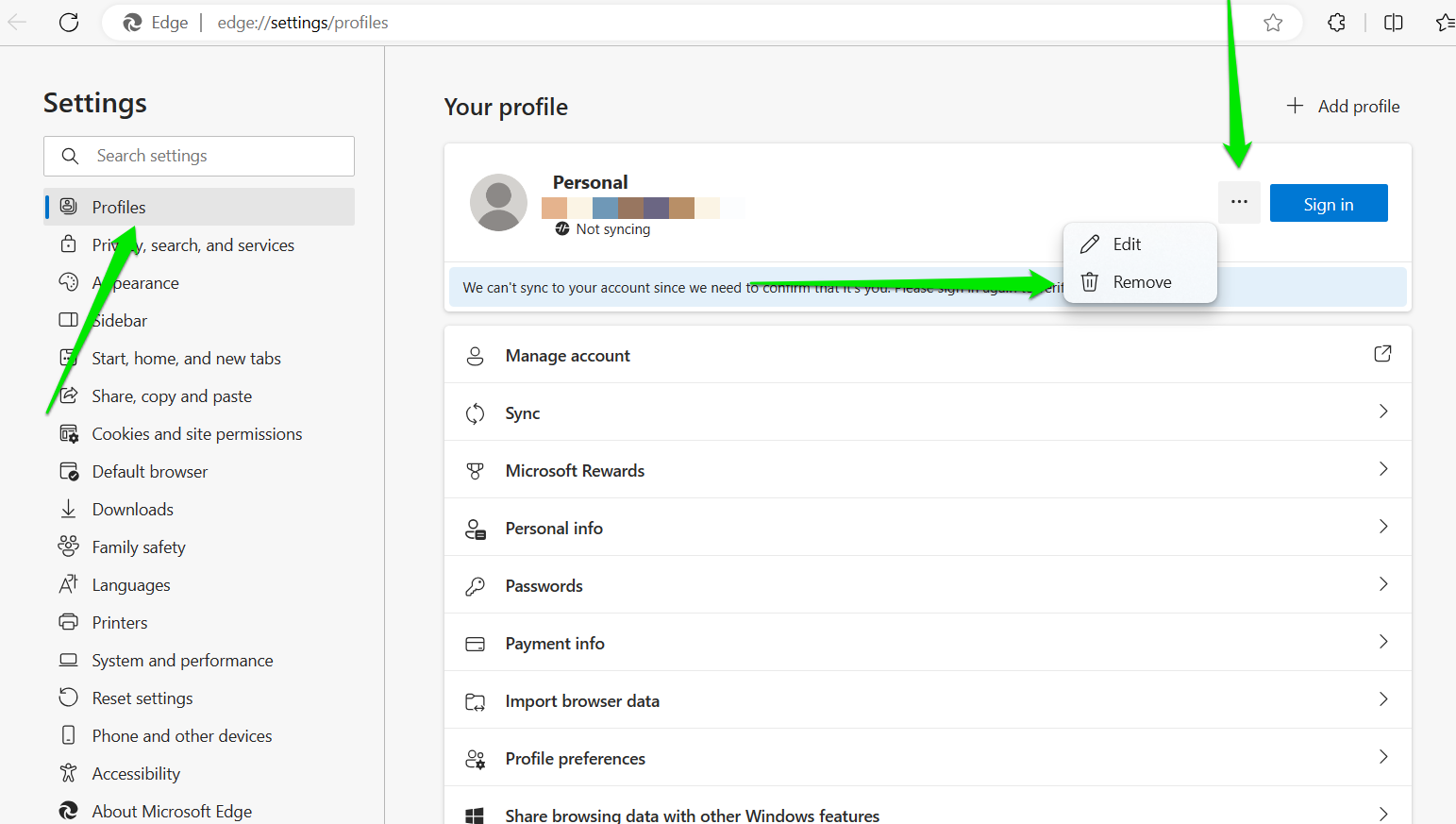
- Click on Remove after the warning pops up.
Follow these steps to remove a Google Chrome Profile:
- Launch Google Chrome and click on the Profile icon in the top-right corner. It’s next to the three dots.
- Once the Profile menu appears, go to Other Profiles towards the bottom and click on the gear icon (Manage Profiles).
- When you see the “Who’s using Chrome” or “Welcome to Chrome Profiles” window, click on the three dots in the box to the profile you want to delete and select Delete.
- Click on Delete to confirm your decision.
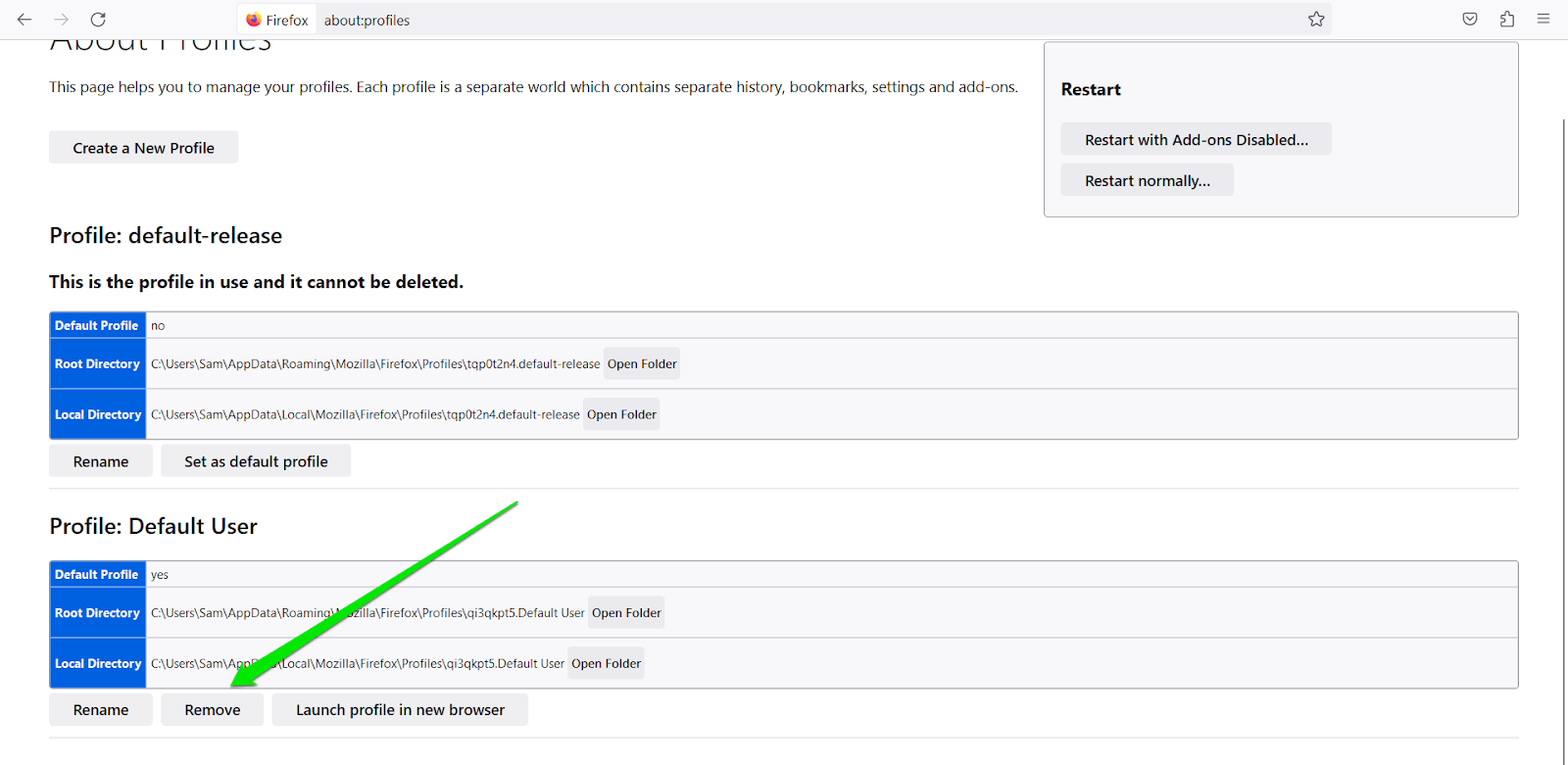
Follow these steps to remove a profile from Firefox:
- Launch Mozilla Firefox, enter “about:profiles” into the address box, and hit Enter.
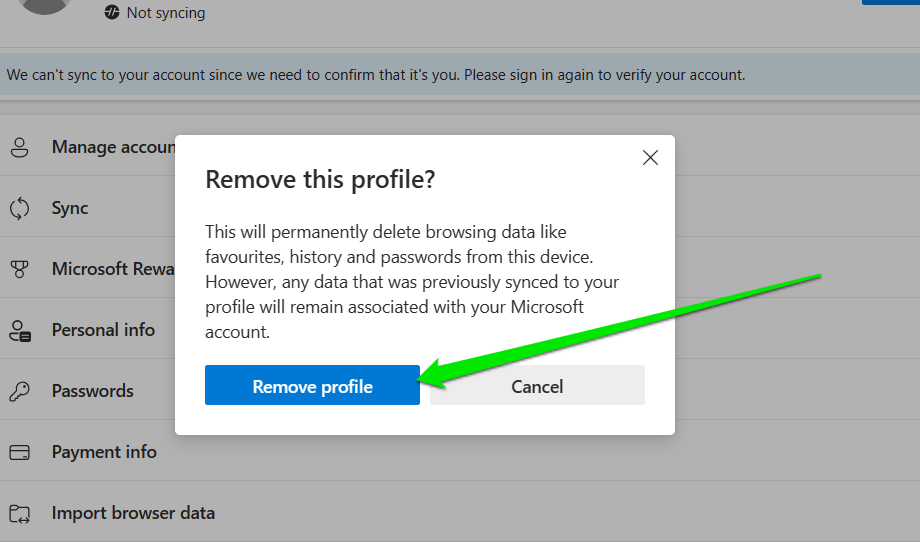
- Click on Remove under the profile you want to get rid of.
- For the purposes of this fix, you’ll be deleting the files related to the profile. So, select Delete Files.
Solution 5: Resetting Your Browser
If none of the fixes we shared is able to resolve the TLS problem, then your last resort is to reset your browser. The best way to do this is to uninstall and reinstall your browser.
That said, it will make sense to reset your browser to default settings before uninstalling it. Some extensions and apps you added might have changed important settings that may be causing the TLS handshake error.
Follow these steps to reset Chrome:
- Launch Chrome and click on the three dots in the top-right corner.
- Click Settings after the menu appears.
- Go to the bottom of the left pane and click Reset Settings.
- Select “Restore settings to their original defaults” and click the Reset Settings button in the warning dialog that pops up.
Follow these steps to reset Mozilla Firefox:
- Launch Firefox and click on the three lines in the top-right corner.
- After the menu appears, select Help.
- Click More Troubleshooting Information.
- Click Refresh Firefox under “Give Firefox a tune up” once the Troubleshooting Information screen appears.
- Click on the Refresh Firefox button to reset the browser.
Follow these steps to reset Microsoft Edge:
- Launch Microsoft Edge and click on the three dots in the top-right area.
- After the menu opens, select Settings.
- Go to the left side of the Settings page and select “Reset Settings.”
- Go to the right and click on “Restore settings to their default values.”
- Click on Reset to confirm and start the action.
Once resetting your browser’s settings, you can try accessing the website again to check if the TLS handshake failure is gone.
If the TLS issue persists, you can now consider uninstalling your browser.
In some cases, the TLS handshake takes longer than normal to complete, causing the connection to fail. This situation is called a “TLS handshake timeout.” When this happens, you’d naturally ask, “How long does a TLS handshake take?”
Well, it should take a few seconds. If it takes longer than a minute or two, then you might have a slow network connection. On the other hand, it’s also possible that your browser is overloaded with extensions, add-ons, and other junk.
When this happens, you must use a reliable PC junk cleaner like Auslogics BoostSpeed. You can use this tool to get rid of unneeded browser files easily. What’s more, BoostSpeed has features that allow you to tweak non-optimal browser settings, ensuring smooth and fast operation.
Which of the solutions helped you fix the TLS handshake issue?
Let us know in the comments below!
FAQ
What is a TLS Handshake?
A TLS handshake is the initial process that takes place when your browser tries to establisha secure connection with a website’s server. The TLS (Transport Layer Security) is commonly used to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity between your computer and the remote server. It is the successor to the earlier SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol.
How to Fix TLS Handshake Failed?
Fixing the TLS Handshake Failed error involves updating your browser, making sure your date and time are correct, and tweaking some browser settings.
How Does a TLS Handshake Work?
The TLS handshake begins with the client (your PC) saying “hello” (called ClientHello in tech terms) to the server (the website). The client suggests ways to communicate securely. The server picks the best way and proves its identity with a certificate (by providing its signature). The client then creates a secret code (an encryption key), shares it with the server, and they both agree on this secret code. This code ensures they can share data privately and securely.
What Causes TLS Handshake Failure?
The TLS error occurs due to a number of possible reasons, including outdated or unsupported TLS protocol versions on either the client or server side, problematic server configuration, incompatible date or time, and mismatched cipher suites.



