Your PC supplies current to its USB ports, which are used to read peripherals such as a mouse, keyboard, camera, smartphone, hard drive, and other storage devices.
However, did you know that the power output of your computer’s USB port determines how fast you can transfer files or charge a connected device? It also affects capabilities for facilitating system backups and large file transmissions.
Moreover, USB voltage output will determine whether your device can only run keyboards, printers, and mice.
Since power is an essential factor in USB usage, you must learn how much your ports are supplying. If it is inadequate, you might not be able to use your USB device on your computer.
Related: How to Fix “USB Device Over Current Status Detected”?
How Many Watts Is a Computer USB Port?
One thing every computer user must know is that not all USB ports are the same. Universal Serial Bus technology has seen a couple of improvements since the inception of USB 1.0 in the 1990s.
Each time a new USB standard is introduced, we witness an increase in data transfer rate and power output. So, how much power can a USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 3.1 port supply?
On a desktop PC or laptop, you’d usually have charging downstream ports (CDPs). However, sometimes, you may find that your PC also has a standard downstream port (SDP).
A charging downstream port, also known as a charge and sync port, can charge your connected device while enabling you to send and receive data. However, standard downstream ports are for data transfers only.
Also read: How to speed up USB 3.0 transfer speed in Windows 10?
- USB 1.0, USB 1.1, and USB 2.0 standard downstream ports are capable of supplying up to 500 mA (milliamperes).
- USB 3.0 standard downstream ports are capable of delivering up to 900 milliamps (mA) of power.
- USB 3.0 charging downstream ports can deliver up to 1,500 milliamps (mA) of power.
How to Check Power Output of a USB Port on Windows 10
that is being used by your connected devices.
You can do so with the help of the Device Manager, but that’s not the only option.
You can use specialized hardware known as a USB voltmeter to check the power supply of a USB port. These devices are quite affordable.
Meanwhile, some third-party software programs can detect the properties of your USB port, including the power output.
Here are your options:
Option 1: Use the device manager to check the power output of your USB ports
Follow the procedure below:
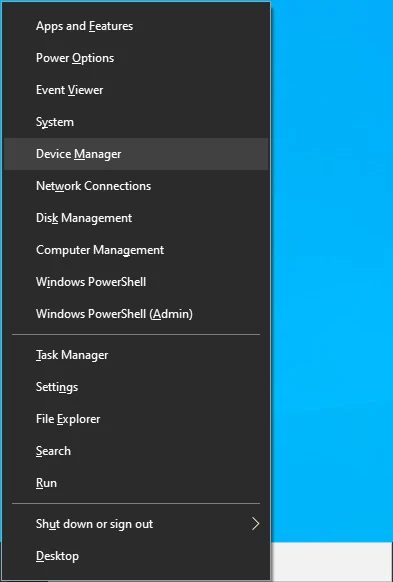
- Open the Device Manager. You can do so by right-clicking on the Start button in the bottom-left corner of your screen or by pressing the
Windows + Xkeyboard combination. Then, click on Device Manager from the Power User menu.
Windows + R keyboard combination. Type Devmgmt.msc into the search field and click OK or press Enter on your keyboard.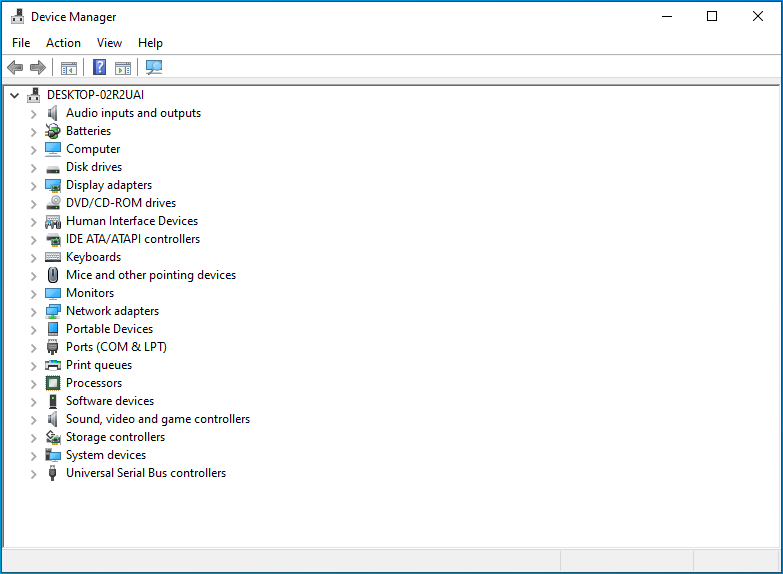
- Once you are in the Device Manager, scroll down and locate Universal Serial Bus controllers. Double-click on the category or click the drop-down arrow on the left-hand side to reveal your USB devices.
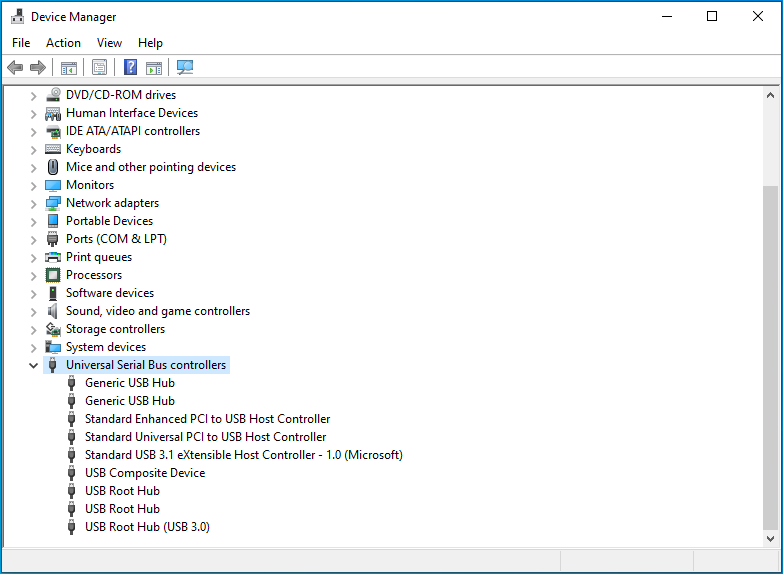
- Right-click on an entry named USB Composite Device, Generic USB Hub, or USB Root Hub. Then, click on Properties in the context menu.
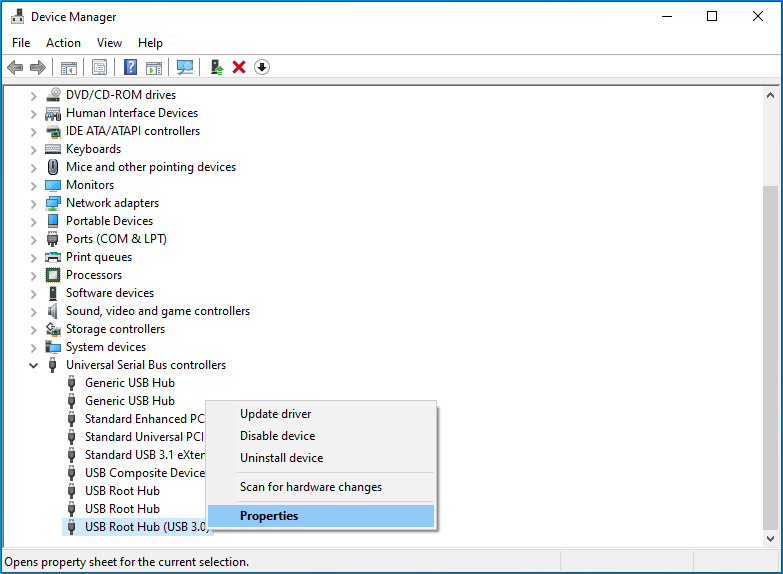
- Switch to the Power Management tab.
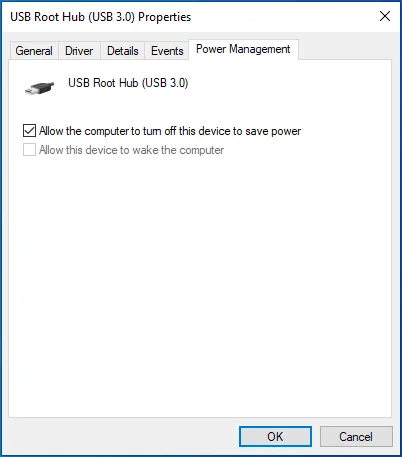
- In the Hub Information field, check the total power available. It could be something like 500 mA per port.
- In the attached devices field, you will see the peripherals that are connected to your computer on the hub and the amount of power they require.
- Repeat Step 3 and Step 4 to find out the capabilities of the other USB hubs.
You can also check the power details of your USB ports. Here’s how to do so:
- Switch to the Details tab.
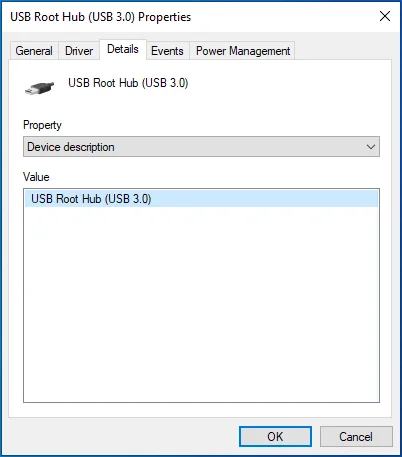
- Expand the Device Description drop-down.
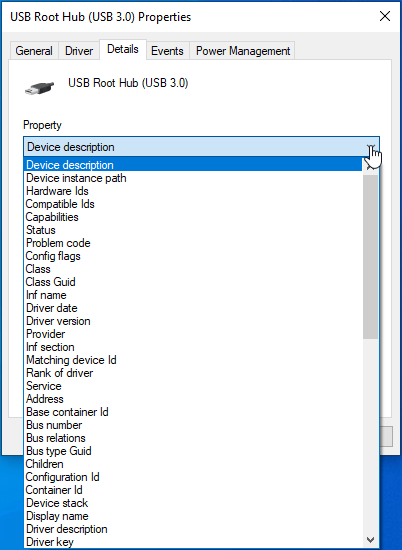
- Locate Power Data in the list of options and click on it.
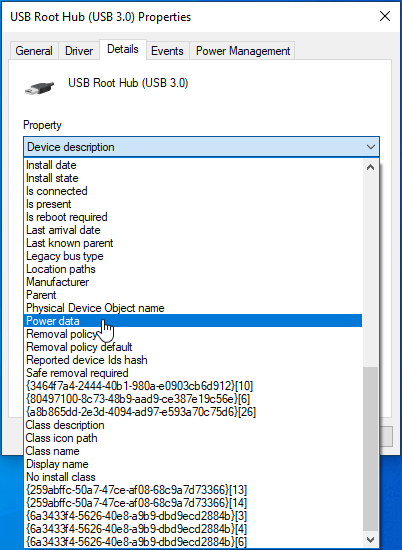
- You will see the power details of the USB port in the Value field. Here’s how to interpret them:
- See what you have under Current Power State.
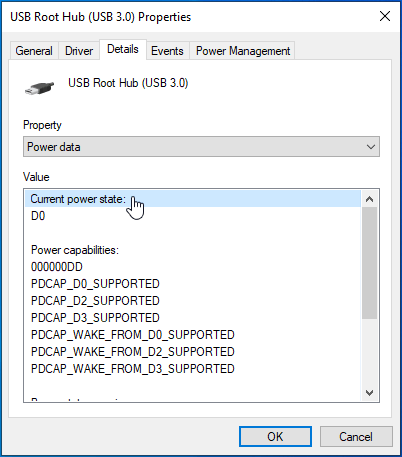
- Look under Power Capabilities. You may see D0 Supported, D2 Supported, or D3 Supported.
- D0 means that the device is fully powered. It is the working state.
- D1 and D2 are intermediate sleep states.
- D3 is the deep sleep state.
When you are done researching the descriptions of your USB ports, you can close the Device Manager.
Option 2: Use A USB voltmeter to measure the power output of your USB ports
You can use a USB voltmeter to measure the power output of your computer’s USB port.
These devices work with your PC, but you can also use them to find out the power of other gadgets, such as your power banks and car chargers. You can easily get one from your local computer store, or you can purchase one online.
Can be useful: How to Fix USB-C Port Not Working on Windows 10?
Option 3: Use a third-party software program to find out your USB properties
If you don’t want to spend money on a power-measuring device, opt for an application that you can easily install on your PC.
Only download and install apps from trusted sources. Some apps could be Trojans that open your system to viruses and other sorts of malware.
They may bundle other optional apps that get installed without your permission. Some of these apps can even change your browser settings, exposing your PC to more threats.
Many third-party apps are available online. They can read the properties of your USB ports and display them to you on a user-friendly interface.
This will protect you against viruses that may steal your personal details, corrupt your files, or even damage your PC.
How to Check USB Power Output on Windows 11
While Windows 11 does have quite a few new tricks up its sleeve, this is not the case when it comes to checking the laptop’s USB power output. You can use any of the methods listed above to check USB output on Windows 11.
How to Check the Power Output of a USB Port in Windows 10: Answered
In this post, we looked at how to find USB output on Windows 10. Knowing the capabilities of your USB ports will help you know the ports that will serve best for the task you want to perform.
We hope you’ve found this article useful. You can share your thoughts in the comments section below. We’d love to hear from you.
FAQ
Power-only connectors may have a lightning bolt or a battery indicator; data-only connections usually have the standard USB symbol. Furthermore, if a device is plugged into a data-only port, it will generally appear as a recognized device on your computer. In contrast, a power-only port will charge the attached device and won’t initiate any data transfer. You can also use Windows 10’s Device Manager. Right-click the Start button, choose “Device Manager,” and then click the “Universal Serial Bus controllers” category to expand it. This is a list of USB ports and controllers. Double-click a port to access its attributes and see details like power output, speed, and others. The maximum power output for USB 2.0 ports can be as low as 0.5 amps or as high as 1.5 amps (for USB 3.0 or newer ports). Some ports, particularly those meant for charging, can produce higher power outputs to charge devices faster. If it does, electricity is being supplied from the USB port. Using a multimeter is an alternative method. After setting the multimeter to measure DC voltage, touch the red probe to the power pin and the black probe to the ground pin of the USB port. When there is a voltage reading, the port is providing electricity.