Whether you have an NVMe SSD or a SATA SSD, solid-state drives are known for their improved speeds and better performance over HDDs.
So if you suspect that your SSD is not performing as it should, it’s a good idea to run a speed test.
Knowing your SSD’s speed is also necessary after installing a new drive, since you need to confirm that the manufacturer’s specs match real-world performance.
Thus, we’ll be looking at 5 methods for finding out your SSD’s read/write speed. We will also discuss what to do if your SSD is slower than the expected speeds.
🛠️ Third-party tools like CrystalDiskMark and BlackMagic Disk Speed Test are trusted utilities for checking sequential and random read and write speeds using various test parameters.
💻 You can also use SSD manufacturer software, Task Manager, File Explorer, and the Command Prompt to check your SSD’s speed.
📊 SSD speed tests provide results in MB/s (megabytes per second) and IOPS (input/output operations per second).
🏆 In some cases, you may receive SSD performance scores.
⚠️ Using the wrong PCIe slot or USB port can impact speed test results.
🚀 If the speed tests reveal that your SSD’s speed is low, you should:
- Check your SSD’s installation and connection
- Update your SSD firmware
- Free up drive space
- Use SSD optimization practices like enabling TRIM
What Is SSD Speed, and Why Is It Important?
SSD speed refers to how quickly your drive can read and write data. It is one of the key metrics for judging drive performance.
Read and write speeds are typically measured in megabytes per second (MB/s). The higher the numbers, the better the SSD performance. This means faster load times, faster processing times, and a more responsive PC.
“SSD speed test” is often an umbrella term for various types of testing, including benchmarks. For the purposes of this article, we’re calculating how much data your SSD can read and write in a given period.
We have a dedicated SSD benchmarking guide where we show you how to use various tools that test SSDs in specific conditions, whether it’s for productivity or gaming. These tools generally provide comparable performance scores rather than only read/write speeds.
❓ Why is SSD speed important?
Booting up the system, running apps, and transferring files all rely on the efficiency of your storage drive in writing and retrieving data.
- Impact on gaming performance: Faster SSD write speed is important in saving game progress, moving game files, and installing new titles. Faster read speeds are even more important, especially when launching and running high-end AAA games.
- Rendering and productivity: Improved SSD read/write speeds make a big difference in multitasking, transferring large files, and implementing heavy workloads like high-resolution video editing.
- Fast boot times: Speedy system startup relies on how fast system files can be accessed from the storage drive. Faster SSD read speed translates to faster boot times. On the other hand, you’ll experience slow Windows startups when your drive’s read performance drops.
- Application performance: Active apps and background processes rely heavily on data access and storage. This includes accessing/storing application files, caching temporary data, and saving user data. Thus, faster SSD speed greatly improves app performance.
- Multitasking: Faster SSD read and write speeds significantly improve multitasking. There’ll be reduced lag when running multiple apps and switching between programs.
❓ What is considered a decent SSD speed?
An acceptable speed for your SSD depends on the drive’s form factor, generation, and the manufacturer’s specification. If you have a SATA SSD, expect maximum speeds of 550 MB/s. NVMe speeds depend on generation. Here’s the breakdown:
| SSD type | Max speed |
|---|---|
| SATA SSD (including M.2 SATA, mini-SATA, and 2.5-inch form factors) | ~ 550 MB/s |
| NVMe SSD: | |
| PCIe Gen 3 x4 | ~ 3,500 MB/s |
| PCIe Gen 4 x4 | ~ 7,000 MB/s |
| PCIe Gen 5 x4 | ~ 14,000 MB/s |
So, before judging your SSD’s speed, determine the type of drive you have and check your manufacturer’s speed claims (go to the section on checking SSD details).
What Is an SSD Speed Test, and What Does It Measure?
SSD speed tests measure the amount of data that can be saved or retrieved in a given amount of time, otherwise known as throughput. It is usually measured in megabytes per second (MB/s), which translates to how many megabytes can be written to or read from the drive every second. There are two types of operations on a storage drive that form the basis for speed measurements:
👉 Sequential operations, where data is read from or written to the drive in continuous, ordered streams. Manufacturers mainly use sequential read/write speeds to promote SSD performance.
Real-world examples of sequential operations include:
- Transferring large files from the drive to another storage location and vice versa
- Installing software from a large installation package
- Extracting compressed files
👉 Random operations, which involve accessing data from multiple areas of the drive, instead of a continuous stream of blocks or pages.
Real-world examples of random operations include:
- Reading and writing system and application files when starting up or running the operating system and individual applications
- Loading browser tabs and cache files
➡️ Units of speed used in speed tests
You’ll discover that sequential and random read/write speeds are not always presented in MB/s when you run speed tests. Sometimes, they could be presented in input/output operations per second (IOPS) as well.
So what’s the difference?
- MB/s: This measures the data size in megabytes that’s moved (read or written) in a second. Read and write speeds have separate MB/s scores.
- IOPS: This is the number of read and write operations that are completed in a second.
➡️ Other terms used in SSD speed tests
You should also take note of these terms, as they’ll appear in various tools:
| Terms | Description | What it tests |
|---|---|---|
| Block size | Size of each data chunk used during testing. | Tests how fast the drive can handle large and small blocks at a time. Transferring files in larger blocks usually leads to faster speeds. Smaller blocks mimic real-world performance better. |
| Queue depth | Number of input/output (I/O) operations queued at once. | Shows drive performance when a specific number of operations are queued. |
| Thread count | Number of CPU threads used during the operation. | Shows the performance of the drive when a specific number of CPU threads are running. The higher the threads, the better the speed. |
SATA and NVMe SSDs have different queue depth limits. A SATA drive has a maximum queue depth of 32, while newer generation PCIe NVMe SSDs go as high as 65,535.
Hard drive speed test tools simulate high and low queue depth scenarios. For example, QD1 shows how a hard drive performs when only one operation is queued up, while QD32 tests mimic high workload scenarios where multiple operations are in the queue.
While the speed tests don’t directly show a drive’s queue depth limit, high QD32 scores indicate higher limits.
What Should I Do Before Running a Speed Test?
Here’s what you should do in preparation for an SSD speed test:
- Check your SSD details
- Close active apps and background processes
- Ensure you’re using the correct PCIe slot or USB port
Check your SSD details
Find out the drive letter, drive type, and product specs.
First, you need to know whether you have a SATA or an NVMe SSD. As mentioned earlier, each of these SSD types has its maximum speeds.
This way, when you run a speed test, you’ll see how your drive compares to the expected speeds.
Here’s how to find out your SSD details using Windows Task Manager:
- Click on the Start icon on your taskbar or press the
Windowskey on your keyboard. - Start typing Task in the search bar, and then click on Task Manager from the search results.
- Switch to the Performance tab in the left pane.
You’ll now see the type of SSD you have, whether NVMe or SATA. If you have more than one drive on your PC, they will also show up here, along with their drive letters.
For NVMe drives, it’s important to know the drive’s exact specs. This should include:
- The PCIe generation
- The drive’s advertised speeds
If it’s an SSD you purchased separately, you can get the necessary details by reading the information printed on the packaging or on the SSD’s body. Otherwise, continue with the following steps:
- Still in the Task Manager window, select the drive and write down the name as displayed in the top-right corner.
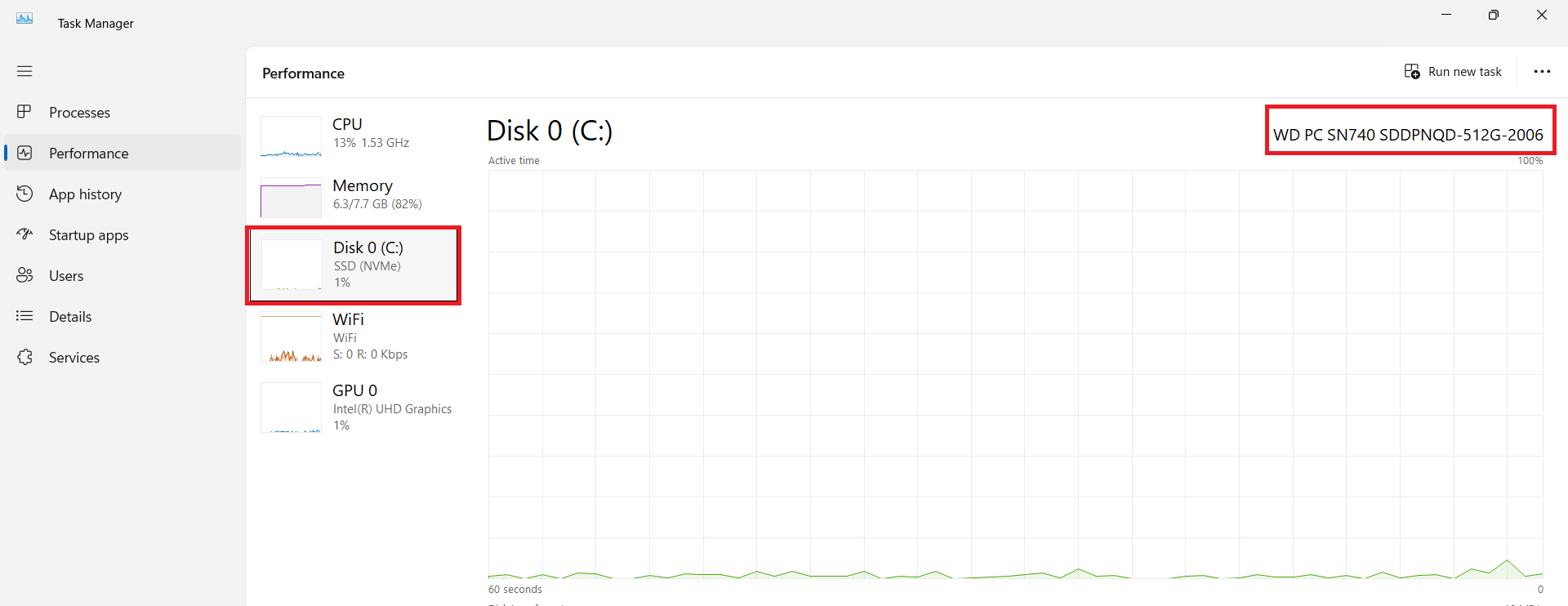
- Open your browser, type in the SSD name, and run a search to gather detailed information about the drive.
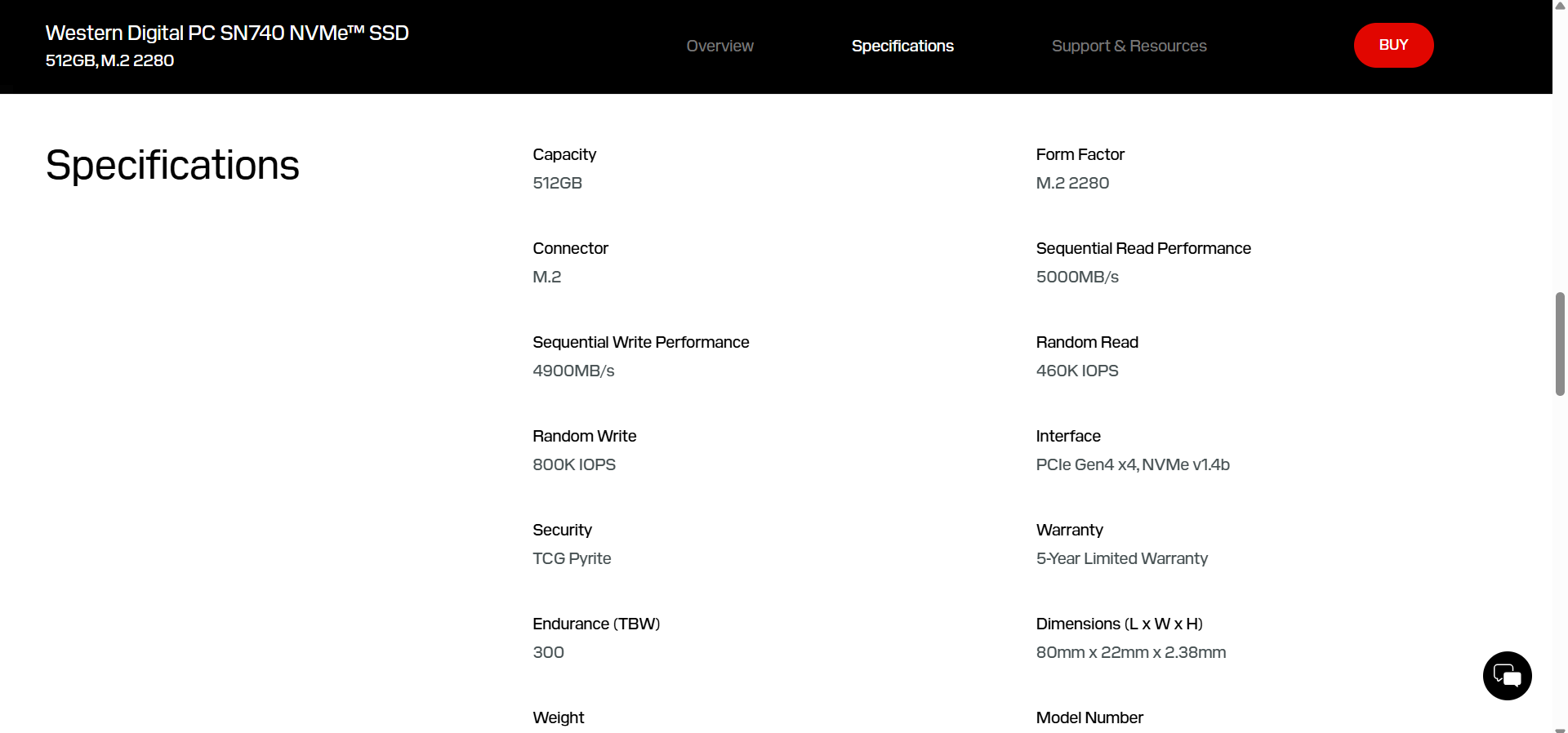
- In most cases, you should see a link to the official product page. Click the link and locate the drive’s official specifications.
Close active apps and unnecessary background processes
To reduce the strain on your drive and also get more accurate results, it’s recommended to close all active applications before commencing with the SSD speed test. You should also close background processes that may be hogging system resources. Otherwise, the results could be skewed when multiple apps are accessing the drive during the test.
Here’s how to close active processes using Task Manager:
- Right-click on your taskbar and click on Task Manager in the context menu.
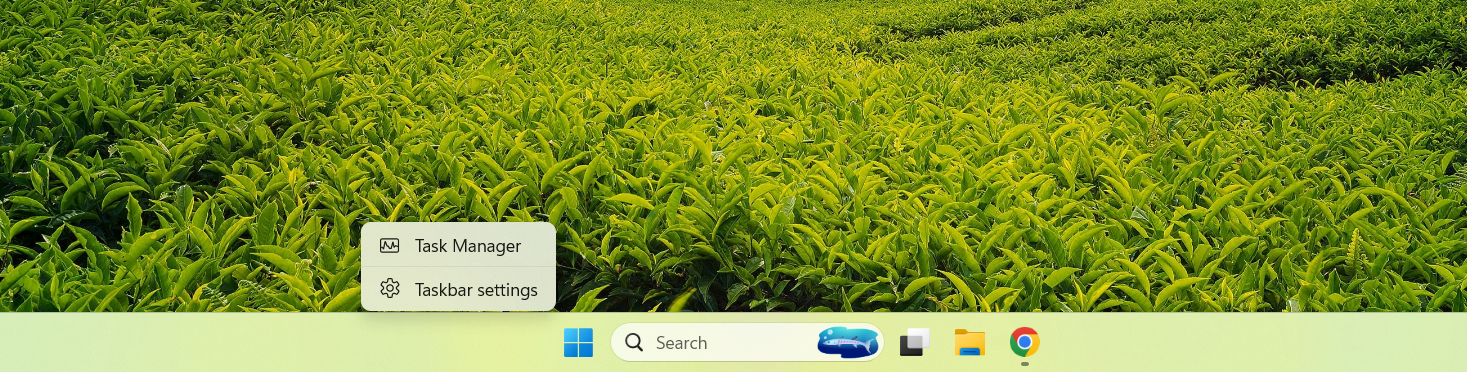
- On the Task Manager window, see that the Processes tab is highlighted in the left pane.
- Right-click on each process under Apps, and then click on End task in the context menu.
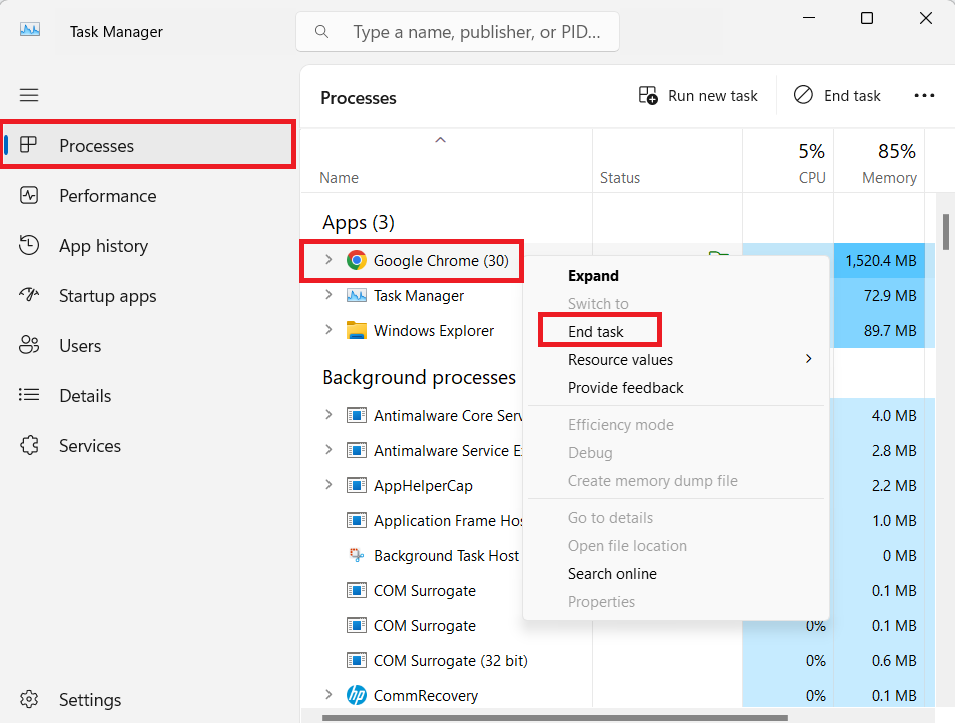
- Also, under Background processes, locate your installed apps, right-click on them and click on End task.
Insert your NVMe SSD into a suitable PCIe slot or USB port
A PCIe 5 SSD will work in a PCIe 4 slot in a desktop motherboard, but its speed will be truncated. The same applies to older generations. So, read your motherboard’s manual if you’re unsure about its PCIe generations and placements.
How to Run SSD Speed Tests
There are various ways of finding out your SSD speed on Windows. And they are as follows:
- Use third-party tools to run speed tests (CrystalDiskMark and Blackmagic Disk Speed Test)
- Use SSD manufacturer software to run speed tests
- Monitor live speeds in Task Manager
- Determine sustained speeds when transferring files
- Use CMD to run SSD speed tests
| SSD speed test methods | Speed metrics | Best use case |
|---|---|---|
| CrystalDiskMark |
|
Detailed benchmarking for high and normal workloads |
| Blackmagic Disk Speed Test | Sequential read/write speeds only in MB/s | Determining SSD suitability for various video editing and rendering purposes |
| SSD manufacturer software (Samsung Magician) |
|
Simple SSD health tests with custom controls |
| Task Manager |
|
|
| File Explorer | File copy speed only | Determining realistic transfer speeds in real-world scenarios when copying and moving files |
| Command Prompt (Admin) |
|
|
![IMG]() Using third-party tools
Using third-party tools

Free third-party tools like CrystalDiskMark and Blackmagic Disk Speed Test offer industry-standard speed test results you can trust.
These tools are easy to use. They also provide more in-depth results than your SSD’s dedicated software program or the Windows native Command Prompt.
I’ll show you how to use each program.
CrystalDiskMark
CrystalDiskMark remains one of the most popular open-source benchmarking speed test tools suitable for both beginners and power users. It is available for free, and it provides an accurate SSD speed measurement.
Here’s how to download CrystalDiskMark on Windows:
- Visit the CrystalDiskMark SourceForge page.
- Click the big green Download button to download the CrystalDiskMark ZIP file.

- Go to the download location and extract the contents of the ZIP file.
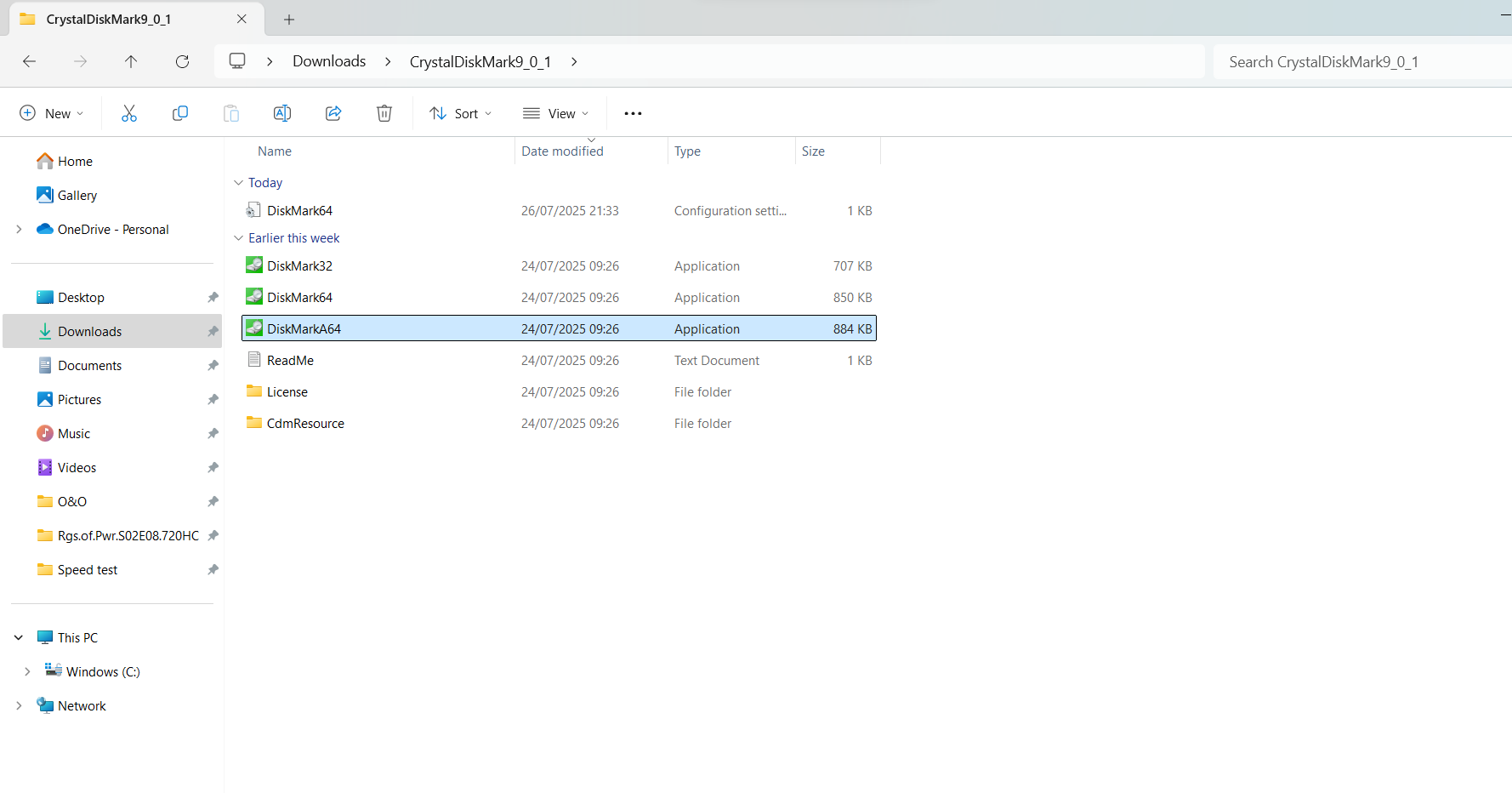
The CrystalDiskMark portable program doesn’t require installation. After extracting the contents of the downloaded ZIP file, you can launch the app by double-clicking on DiskMark64 for 64-bit Windows versions and on DiskMark32 for 32-bit Windows versions.
Here’s how to run the SSD speed test:
- Launch CrystalDiskMark.
- Select the SSD you want to test.
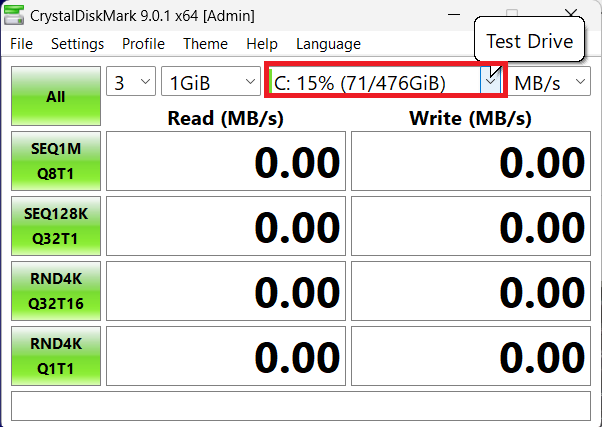
You can also specify the file size (in megabytes or gigabytes) that the tool will write to your drive during the test.
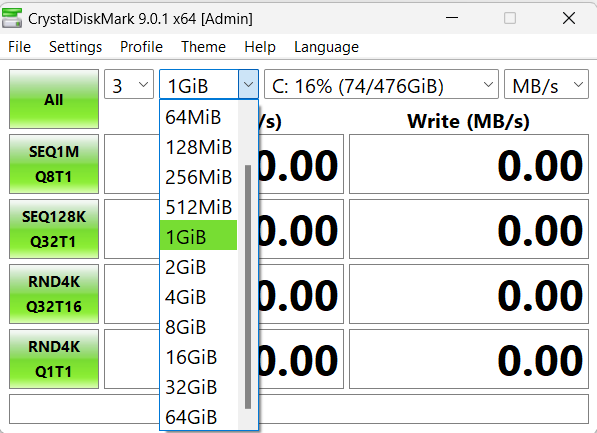
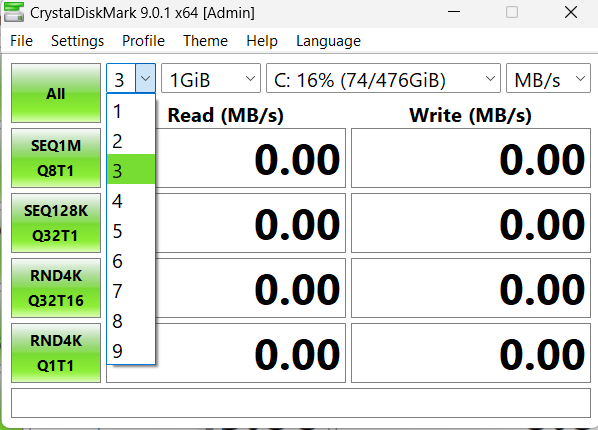
- The next parameter is the number of passes, which is the number of times the test will run. You can increase it to achieve higher test accuracy.
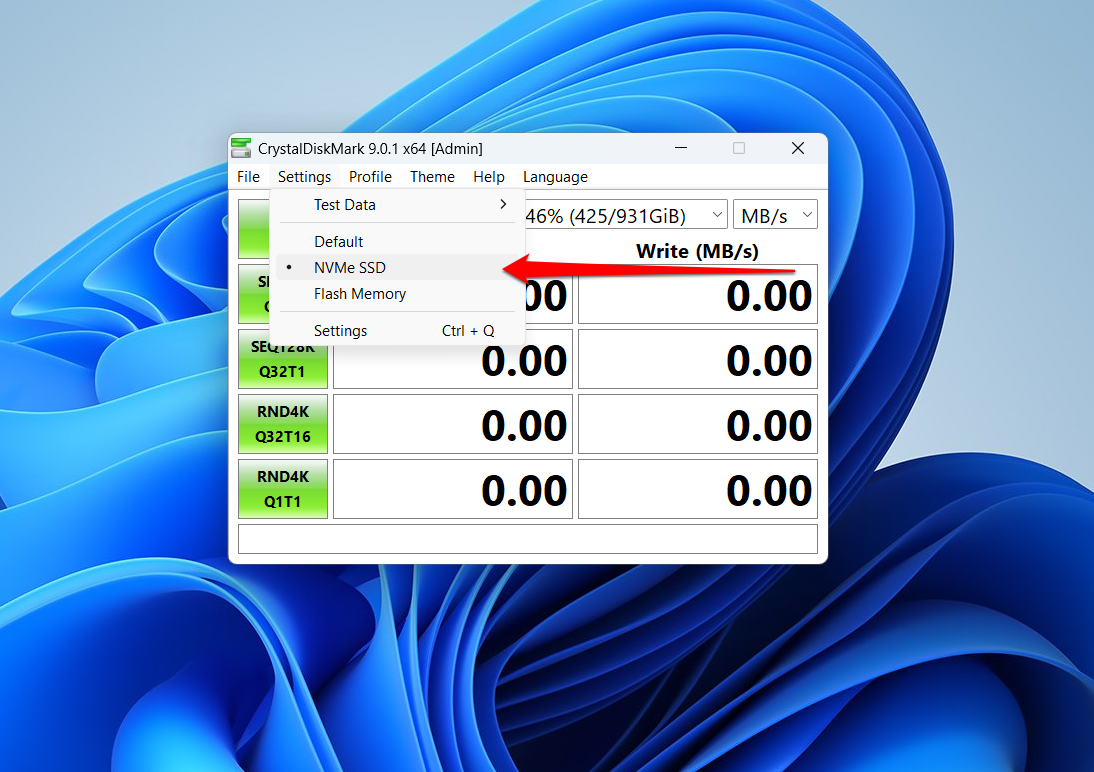
- After that, click Settings at the top of the window and select NVMe SSD (if your SSD is an NVMe SSD).
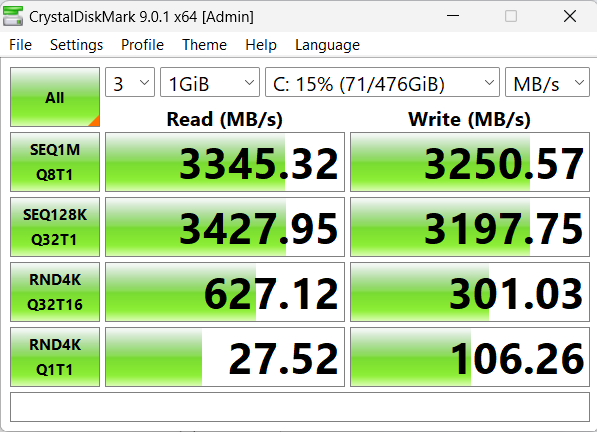
- Now, click the All button to start the test.
- Once the test is complete, you’ll see the sequential and random read and write speeds of your SSD.
What do the CrystalDiskMark results mean for my SSD speed?
Here’s a short glossary to help you understand what the numbers mean in CrystalDiskMark:
| Test parameter | Attribute | How it appears in CrystalDiskMark |
|---|---|---|
| Sequential | Test type (continuous data blocks/chunks) | SEQ |
| Random | Test type (scattered data chunks) | RND |
| Block size | Size of each chunk of data (file fragment) | 1M, 128K, 4K, etc. |
| Queue depth | Number of queued operations | Q1, Q8, Q32, etc. |
| Thread count | Number of parallel CPU threads | T1, T5, T16, etc. |
➡️ SEQ1M Q8T1:
Indicates a sequential test using a 1 MB block size, eight queues, and one thread. This type of test represents the highest theoretical speeds for your SSD. They are closest to the speeds manufacturers advertise for SSDs.
For example, the SSD being tested here is a 500 GB Western Digital SN740 SSD. It is a Gen 4 PCIe NVMe SSD with advertised sequential read and write speeds of up to 5,000 MB/s and 4,000 MB/s, respectively.
So, if the numbers you get are close enough, it means that your drive is performing well.
However, if the numbers are half of the drive’s advertised speeds or lower, it means that something is wrong.
Especially if the SSD is new.
➡️ SEQ128K Q32T1:
The sequential 128-kilobyte read and write speeds, with a queue depth of 32, are better real-world representations of your SSD’s sequential speeds. Therefore, they might be lower than the SEQ1M speeds, but not by much.
➡️ RND4K Q32T16:
Random read and write tests are usually implemented with 4 KB blocks to properly represent real-world use. The first test uses a queue depth of 32 and 16 CPU threads, which produces better numbers.
➡️ RND4K Q1T1:
The second random read/write test shows smaller numbers since it uses a lower queue depth (Q1) and CPU thread (T1).
Using different profiles
You can change test parameters to view your SSD’s performance in different use cases. Click Profile at the top of the window and select any of the following:
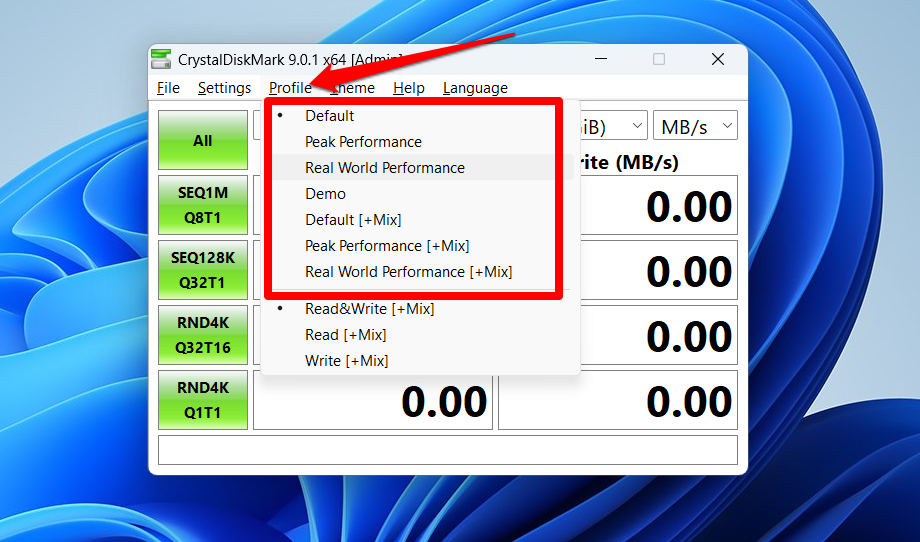
- Peak performance: For heavy workloads like gaming, 3D animation, simulation, and video rendering.
- Real-world performance: Mimics everyday storage use cases.
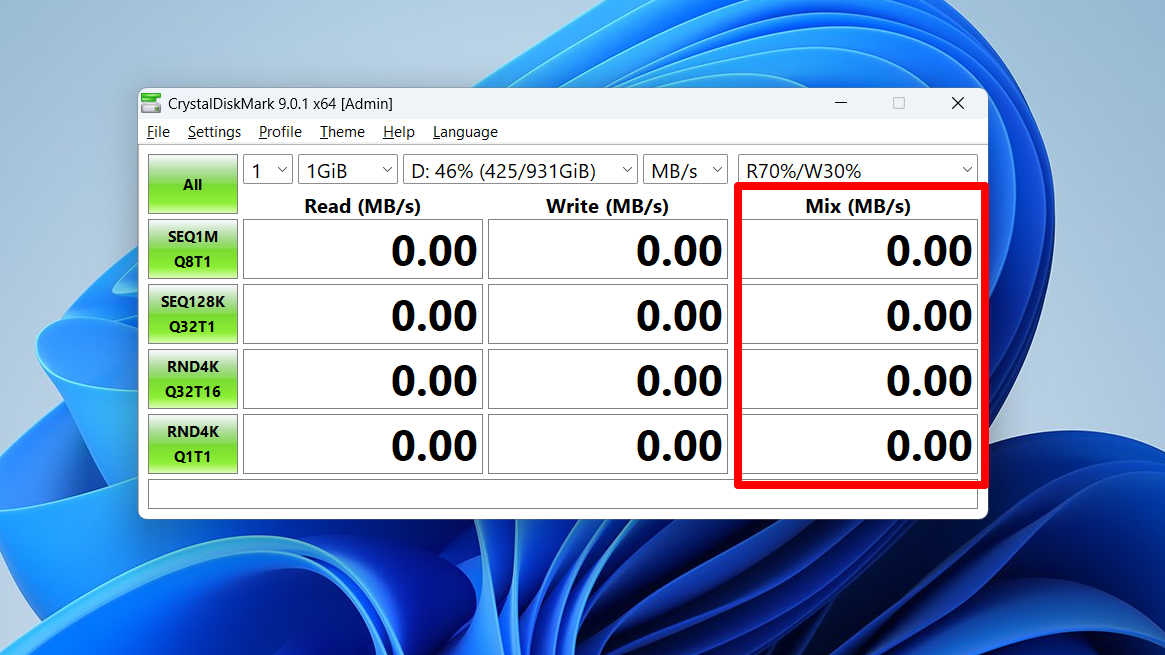
- Mix: Includes a third performance measurement that indicates a mixture of read/write performance per second. It is available for every profile.
Customized profiles
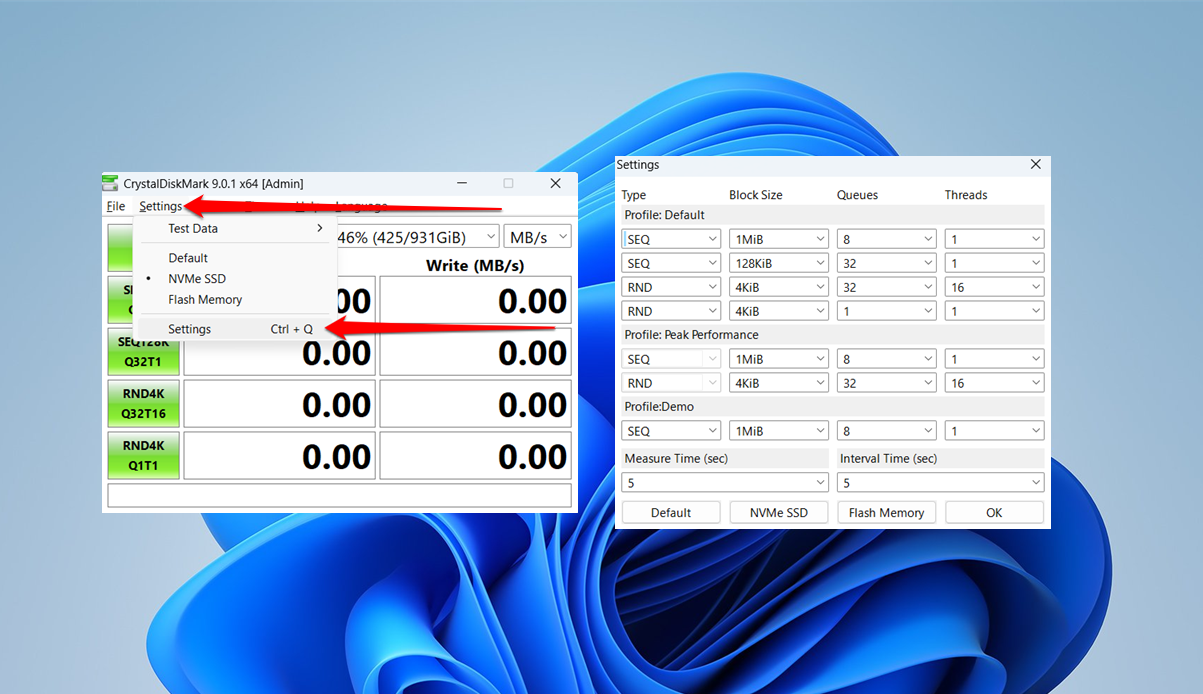
Users can also click Settings in the menu bar and select Settings again or press Ctrl + Q and choose specific test parameters.
Saving the test result
Once your test is complete, you can save the results for future reference. Go to File and choose any option.
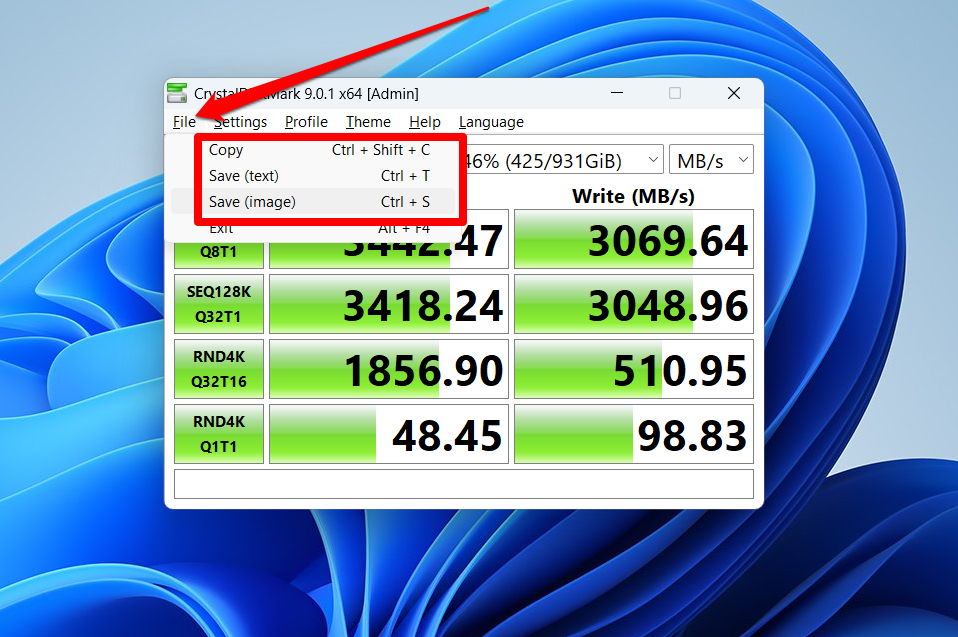
- The Copy option (press
Ctrl + Shift + C) allows you to copy the results in text format and paste them into any text editor. - The Save (text) option (press
Ctrl + T) allows you to save the results as a text (TXT) file, which you can later open in Notepad, Word, or Docs. - The Save (image) option (press
Ctrl + S) saves the result as an image. You can choose between JPG, PNG, and BMP formats.
Blackmagic Disk Speed Test
Blackmagic Disk Speed Test is a tool that video professionals would appreciate. It simulates video editing workloads to find out how your drive will perform during such processes. It tells which video-related operations your SSD can run and how fast it will run them. The tool accompanies the Blackmagic Desktop Video software program. Here’s how to download and launch it:
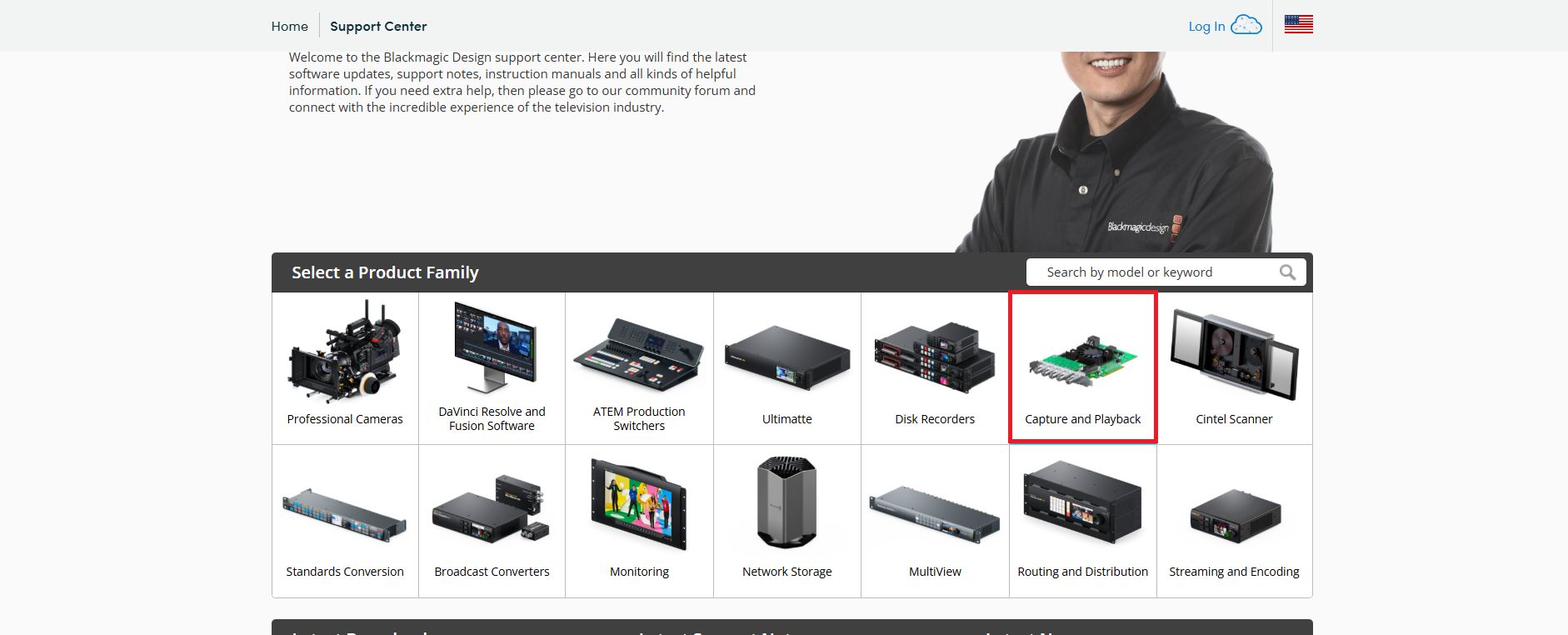
- Go to the official Blackmagic support page.
- Select Capture and Playback under the Select a Product Family category.
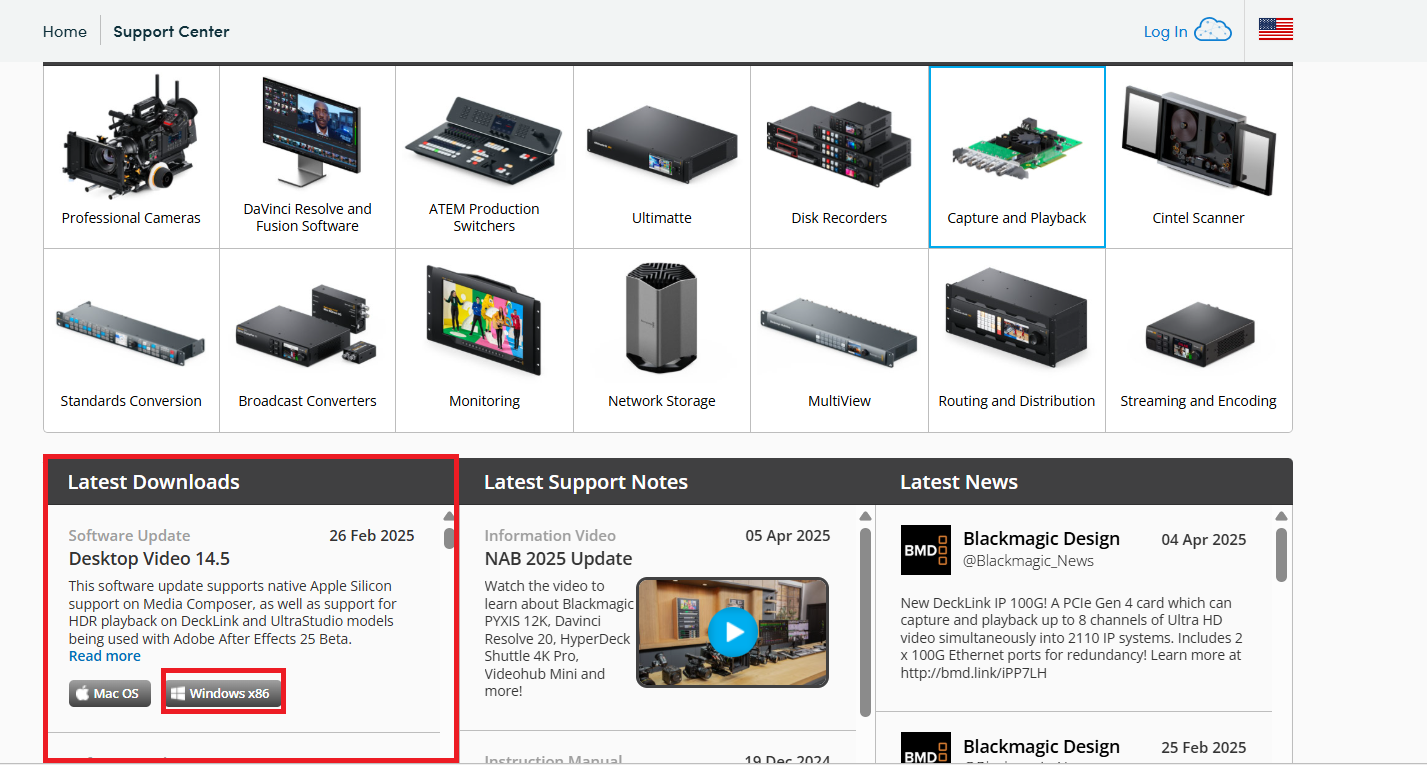
- Scroll down to the Latest Downloads section.
- Click the Windows x86 button on the latest version of Desktop Video.
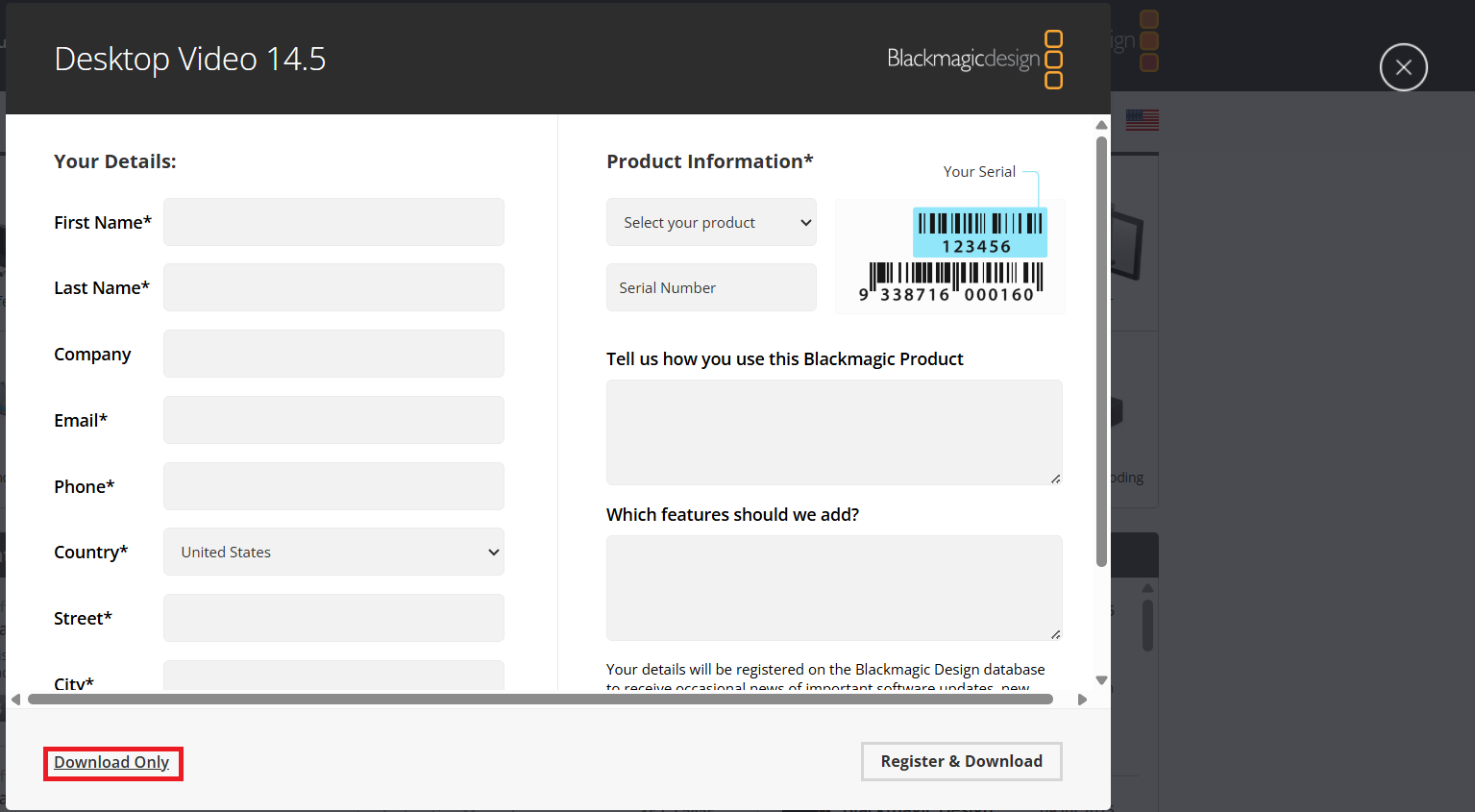
- Select the Download Only option in the registration pop-up to proceed directly with the download if you don’t wish to register.
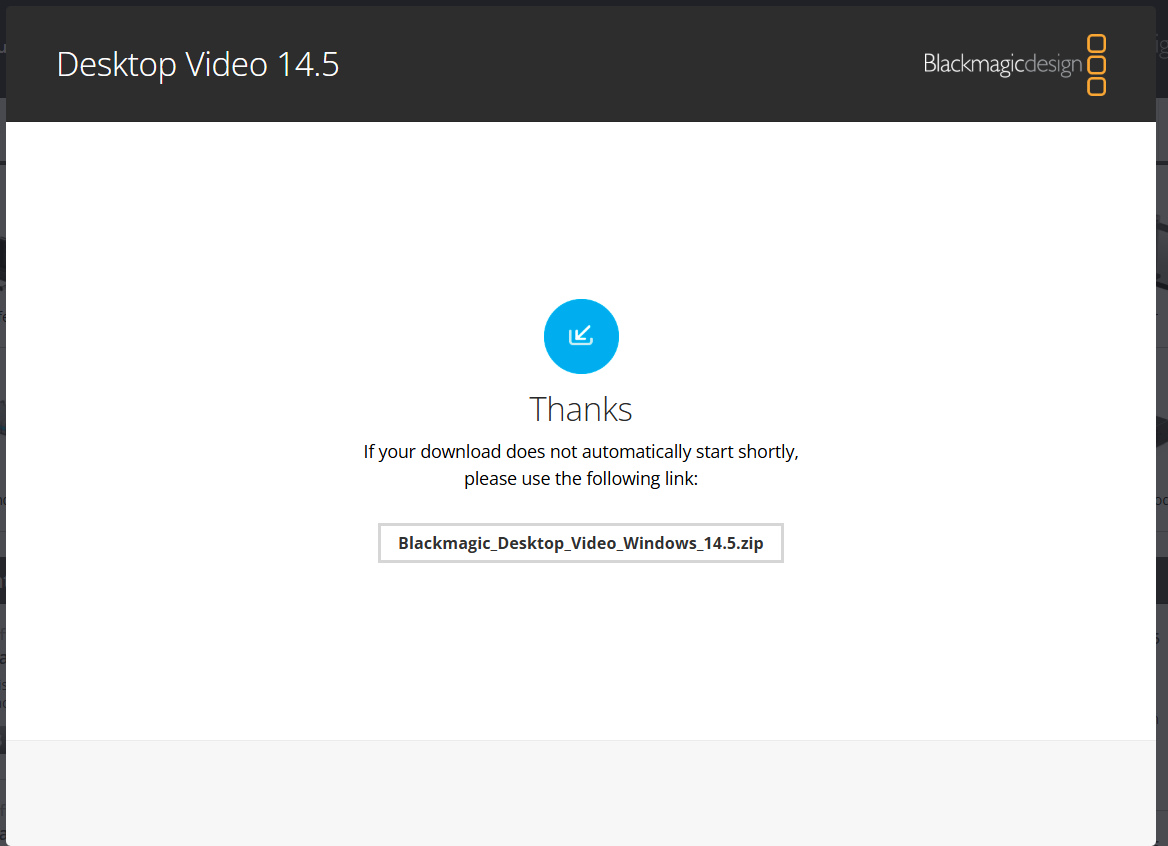
- Your download should now start automatically. Or you can click the link on the Thanks pop-up to start it.
- Restart your PC when prompted.
Here’s how to run the SSD speed test:
- Open the Start menu and type Blackmagic in the search bar.
- Switch to the Apps tab.
- You’ll now see the Blackmagic Speed Test app under the Apps category.
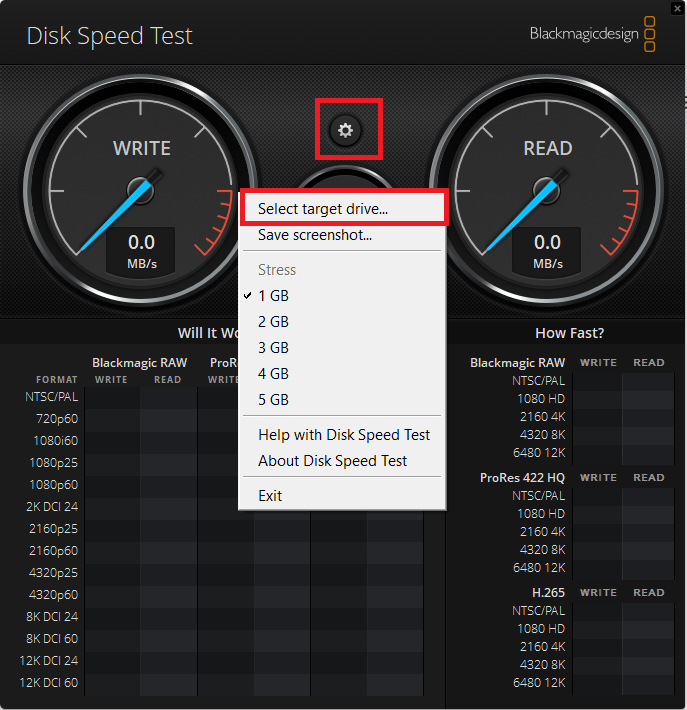
- Once the app opens, click on the Settings icon.
- Click the Select target drive option to choose the drive you’d like to test. You can also select the test file size here.
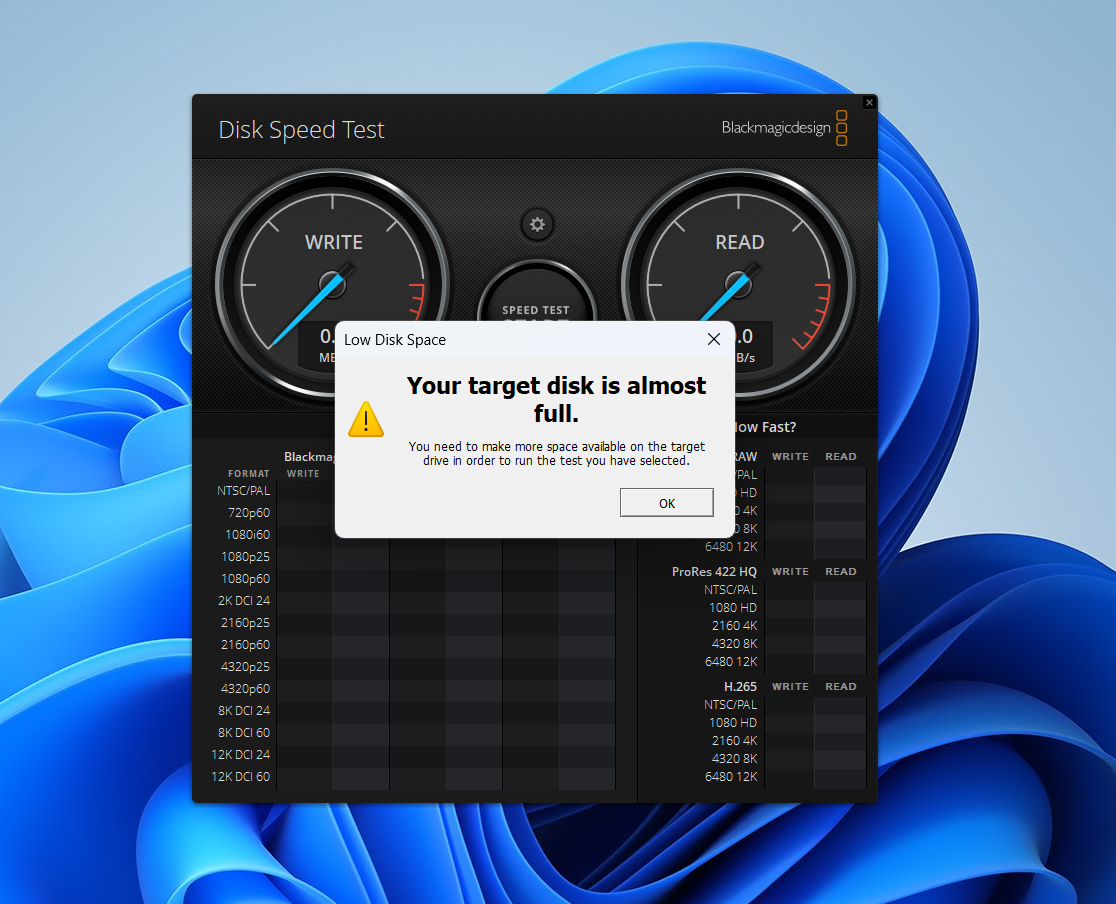
- You can choose any folder location on the drive where you have permission. If the drive is filled up, you’ll receive a warning instead.
- Click the Speed Test Start button after selecting the drive.
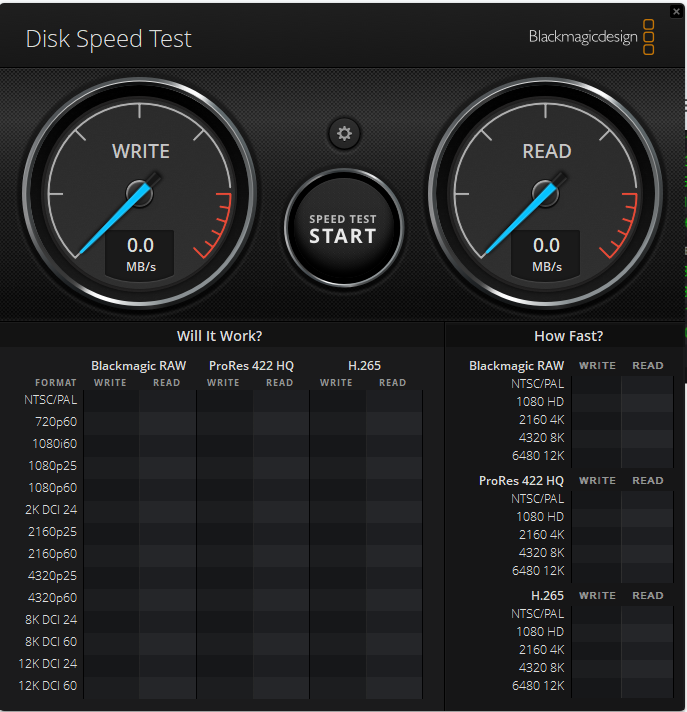
- The app will now continuously evaluate your drive.
- Click the Speed Test Start button to stop the test when you’re satisfied with the results.
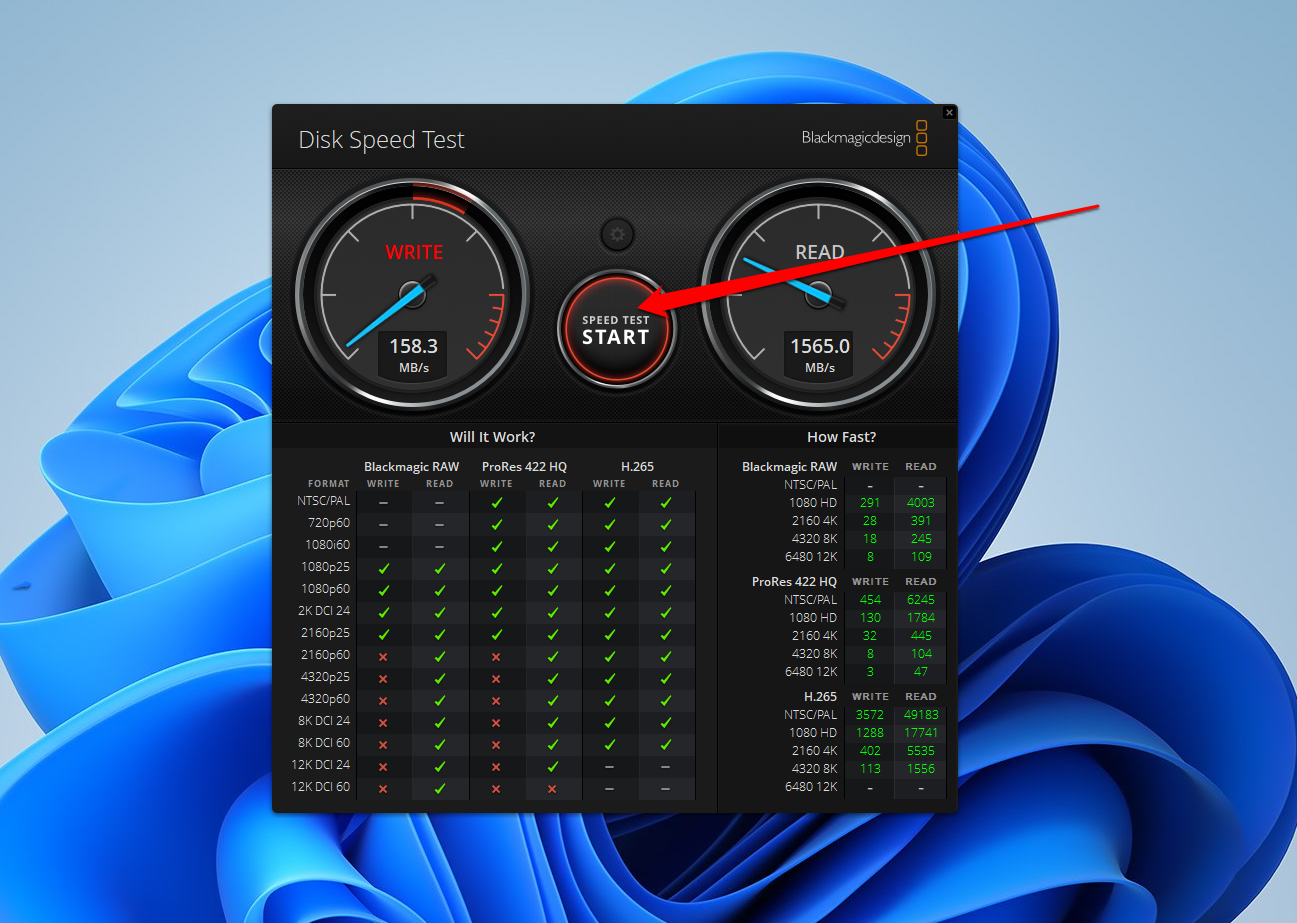
- Under the Will It Work? category, you can see the video resolutions that your SSD can comfortably handle during editing.
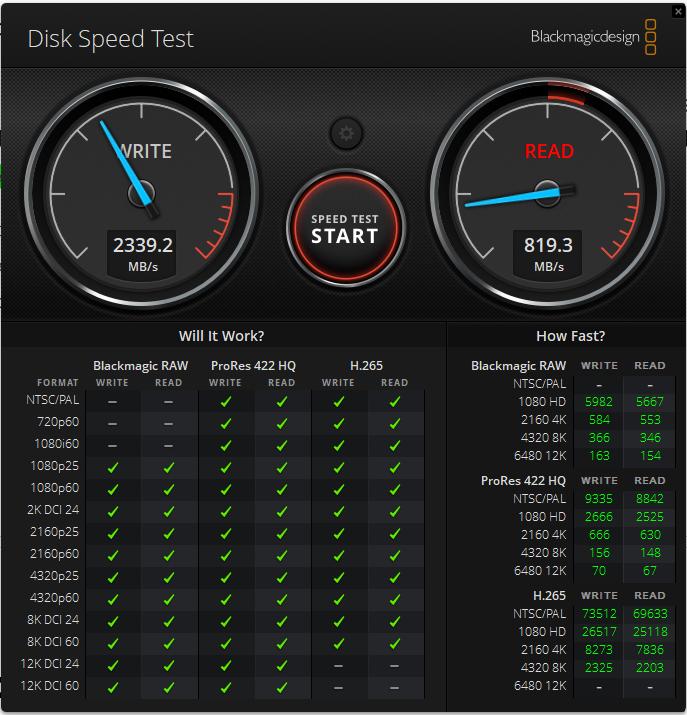
- And under the How Fast? category, you will see the read and write speeds for each video resolution.
![IMG]() Using SSD manufacturer software
Using SSD manufacturer software

SSD manufacturers like Western Digital and Samsung provide dedicated software programs that you can use to manage and monitor SSD performance. Some, like Samsung Magician, provide speed testing capabilities. We’ll show how to use Samsung Magician to test the read/write speed of your Samsung drives:
- Download and install the latest version of Samsung Magician from the official Samsung Semiconductor website.
- Launch the app. It will automatically detect your Samsung SSD.
- If you don’t use a Samsung SSD, you can select your drive in the top corner.
- On the left pane, select Performance Benchmark.
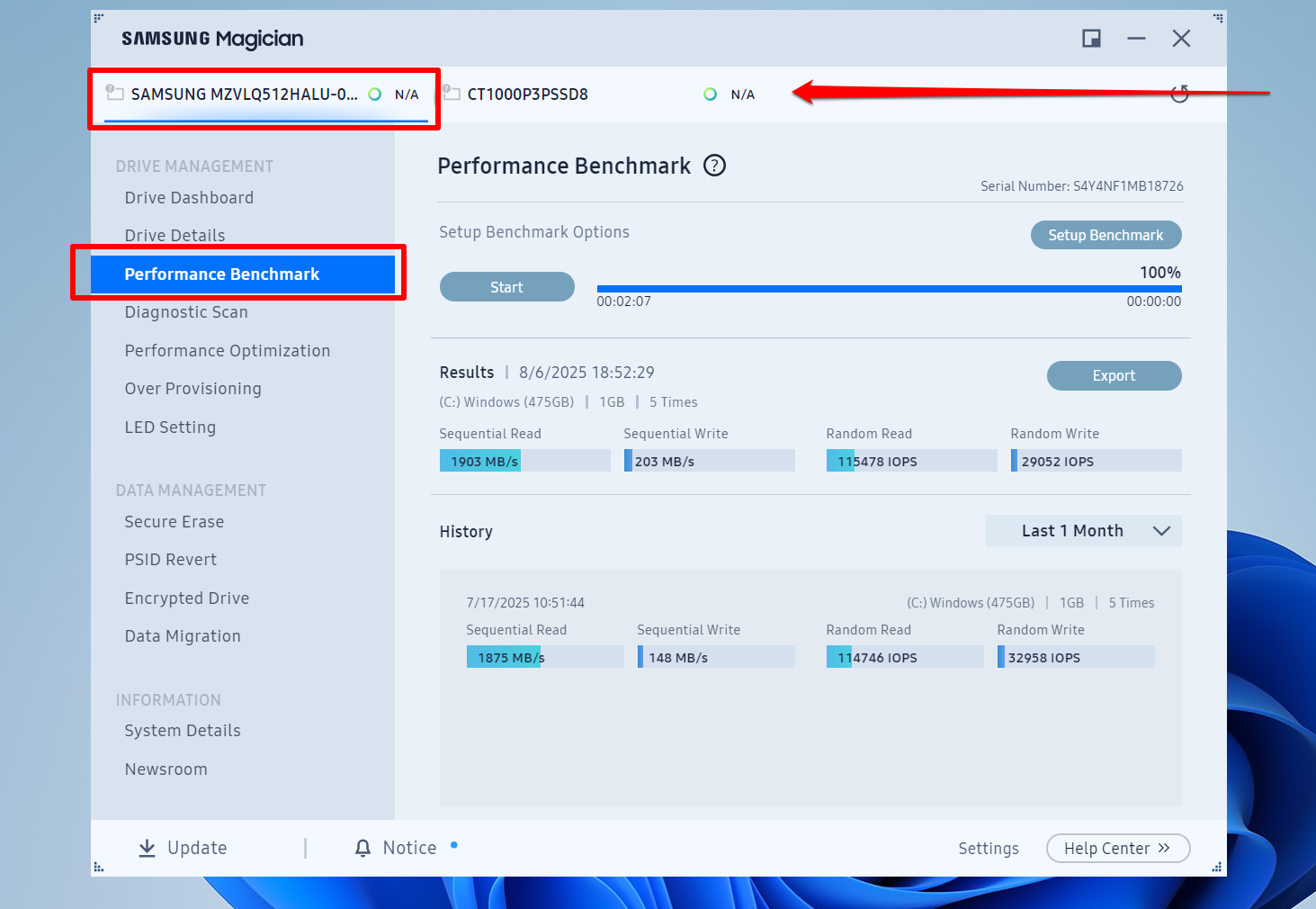
- By default, the sequential tests use 128 KB block sizes and 1 CPU thread, while the read tests use 4 KB block sizes and 4 CPU threads. Both tests use a queue depth of 32 and a 1 GB file. You can click the Setup Benchmark button to set specific test parameters. Once the setup window opens, scroll down to see more options to adjust.
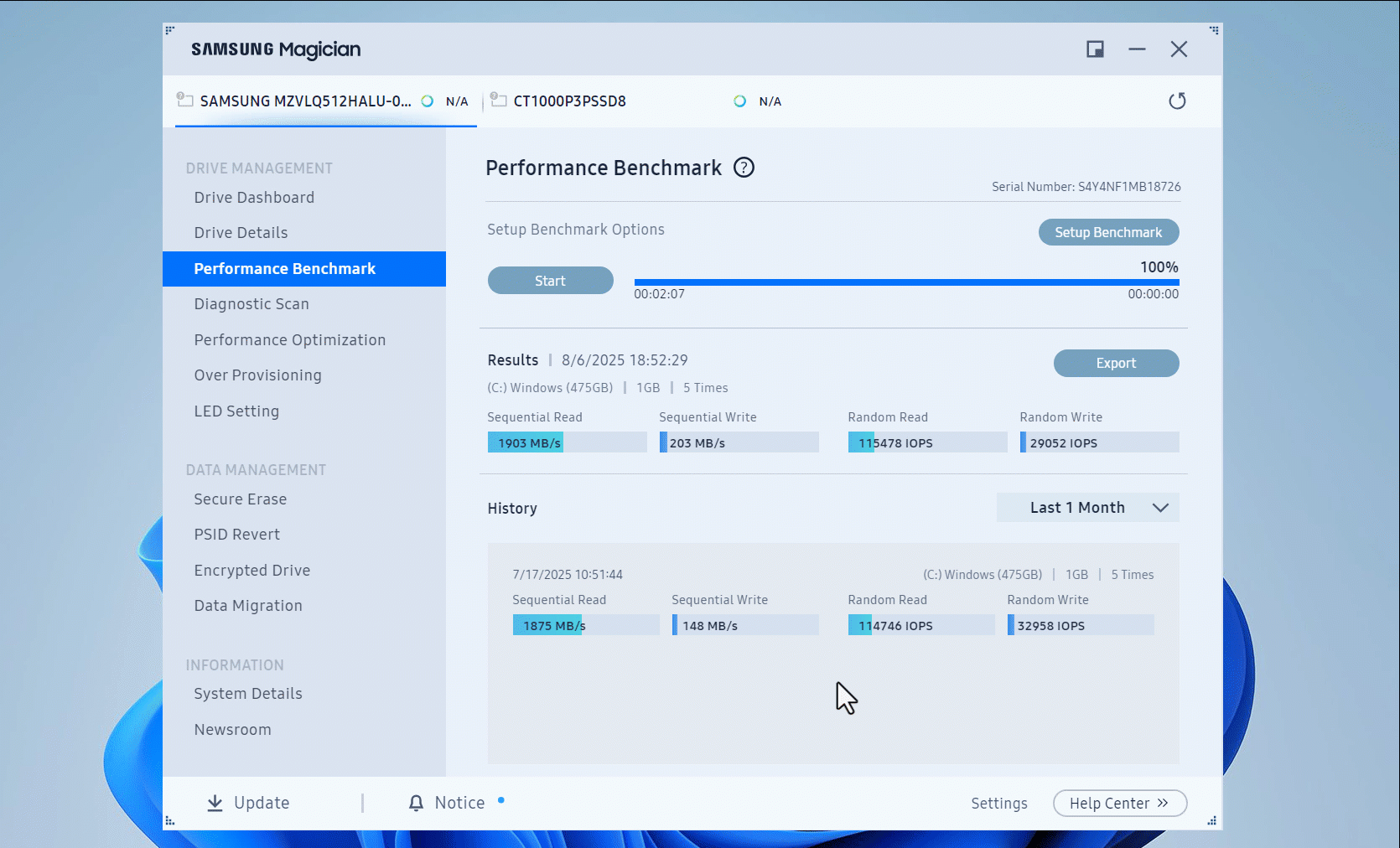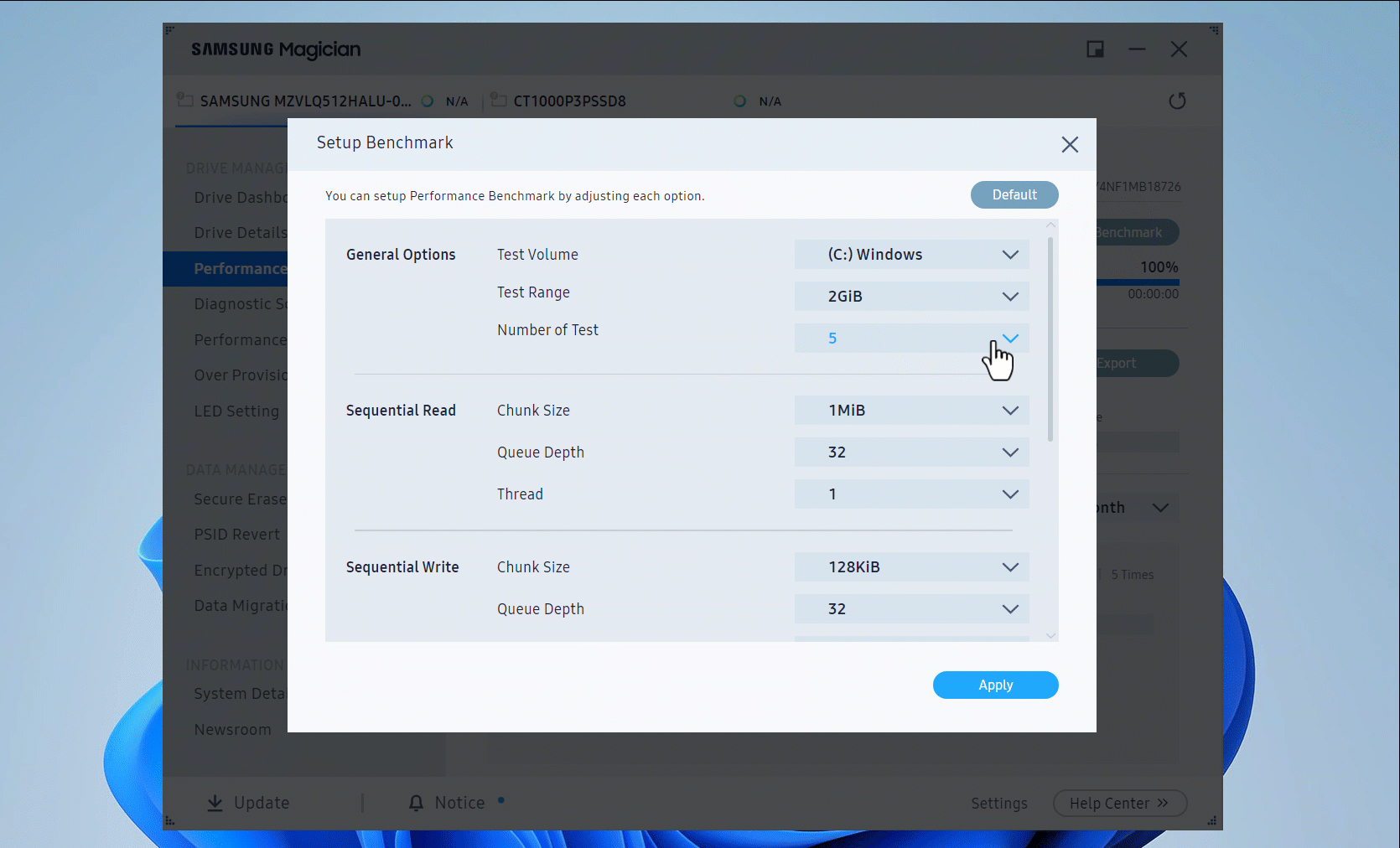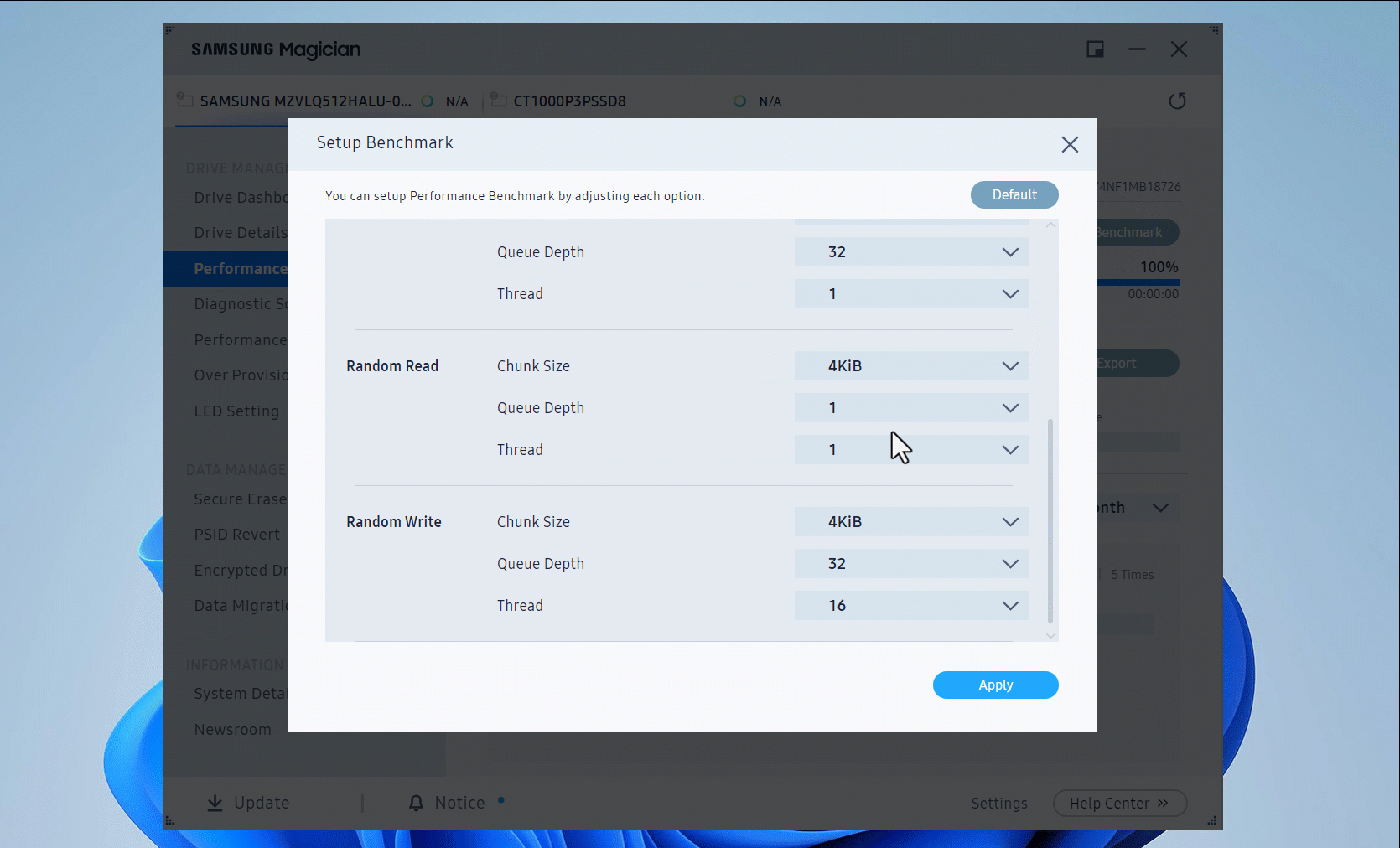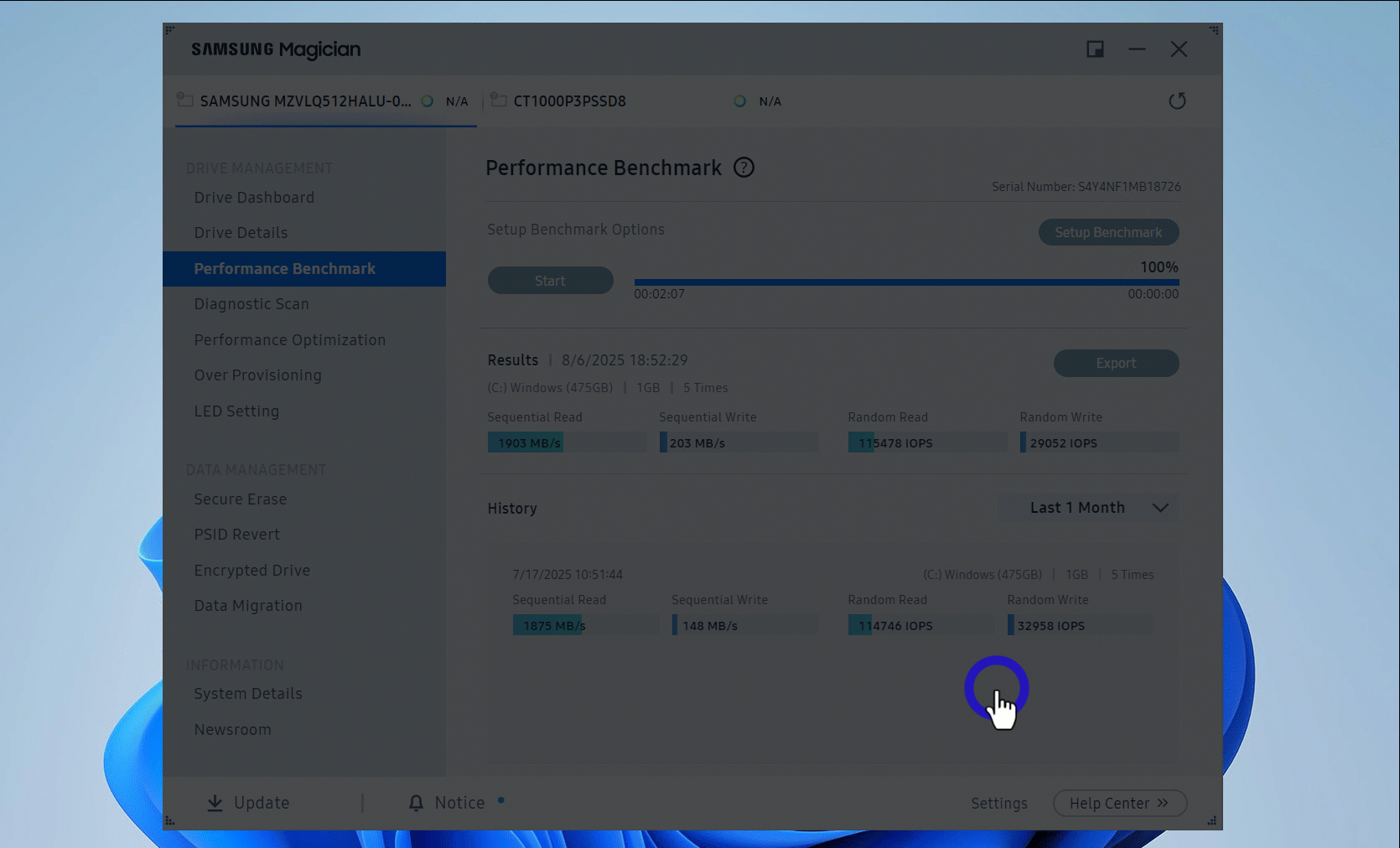
- Click the Start button to begin the speed test.
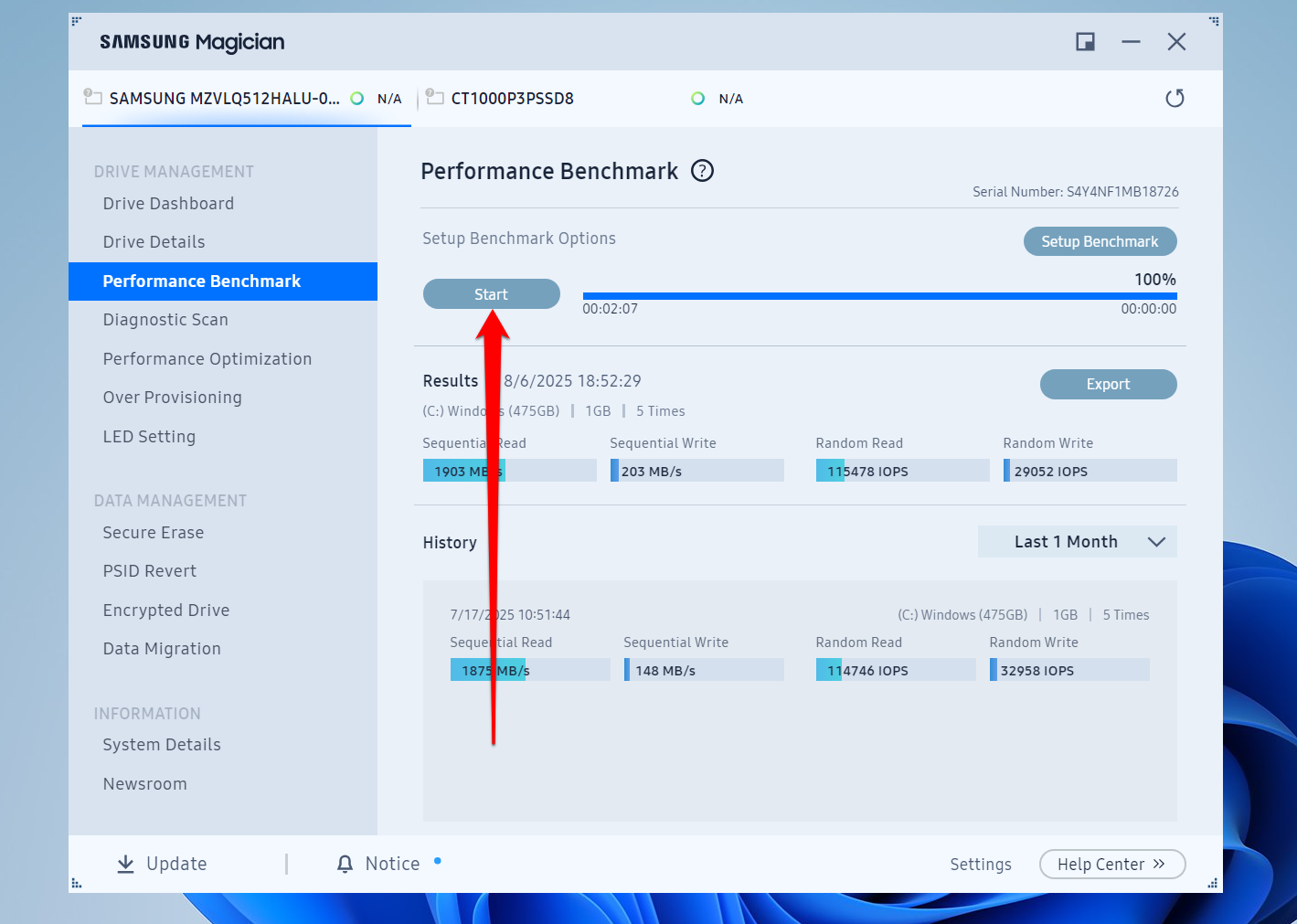
- After the process is complete, you will be presented with the sequential read and write speeds in MB/s. The random read and write speeds will be measured in IOPS.
- You can also export the results as a PNG image using the Export option.
![IMG]() Viewing SSD speed in Task Manager
Viewing SSD speed in Task Manager

This method involves viewing real-time read/write speeds based on your computer’s current activities. However, closing down most background processes and foreground applications allows you to see speeds when copying, moving, and extracting files.
You get to only see read/write speeds without specifications about sequential and random access operations.
However, when transferring files or running speed tests, you’ll find similar results if you open the Task Manager window next to your speed test tool like I did here:
Here’s how to check speeds in Task Manager:
- Press the
Windowskey on your keyboard to open the Start menu. - Start typing Task Manager and click on the option when it comes up in the search.

- Switch to the Performance tab.
- Select the drive you want to view.
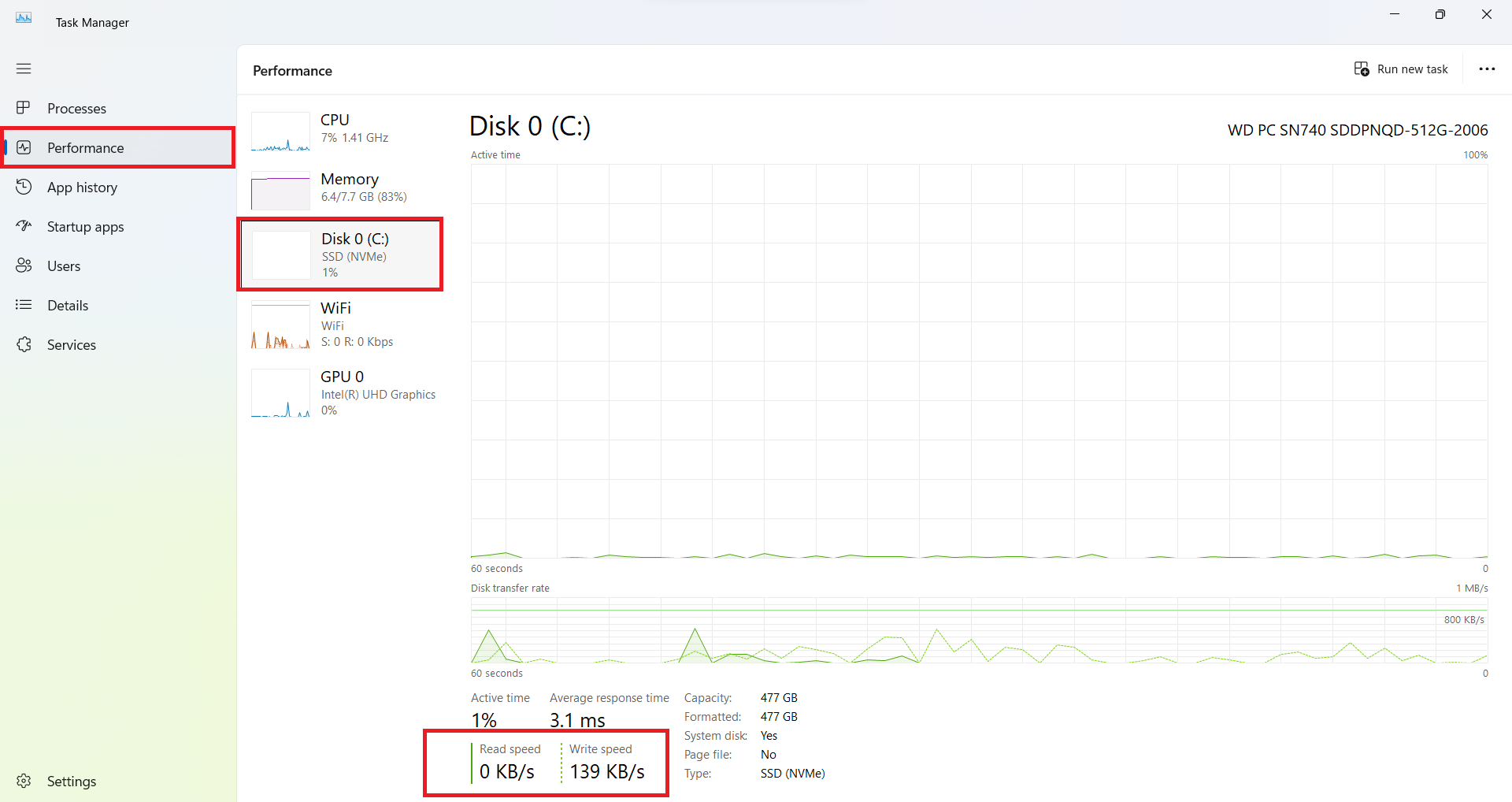
- You will now see the real-time read speed and write speed of your selected drive.
![IMG]() Copying large files to measure speed levels in File Explorer
Copying large files to measure speed levels in File Explorer

Speed test tools measure read and write speeds in simulated environments. Will you see the same results in real life? You can find out by copying data within your drive and checking how fast it moves. You can also measure how fast you can copy and move files from one drive to the other. Additionally, this method can be paired with Task Manager to show you real-time speeds.
Don’t expect the same numbers you see in CrystalDiskMark and other test tools. Transfer rates are almost always determined by the slowest read/write speed in the transfer chain.
For example, if a drive writes files slower than your SSD can read data, you won’t see your actual SSD read speed in File Explorer’s progress window. Also, results will be limited to the source drive’s read speed if it is slower than your SSD’s write speed.
Now, let’s discover your SSD’s transfer speed using File Explorer:
- Click the
Windows + Ehotkey to open File Explorer. - Open your SSD drive under This PC and select a couple of files. Each file should be at least 5 GB in size.
- Copy the files to another folder within the drive. You can also try transferring to another drive to see how the speeds compare.
While the transfer is in progress, you can view the live read and write speeds via Task Manager. You can leverage Windows’ split screen as shown below:
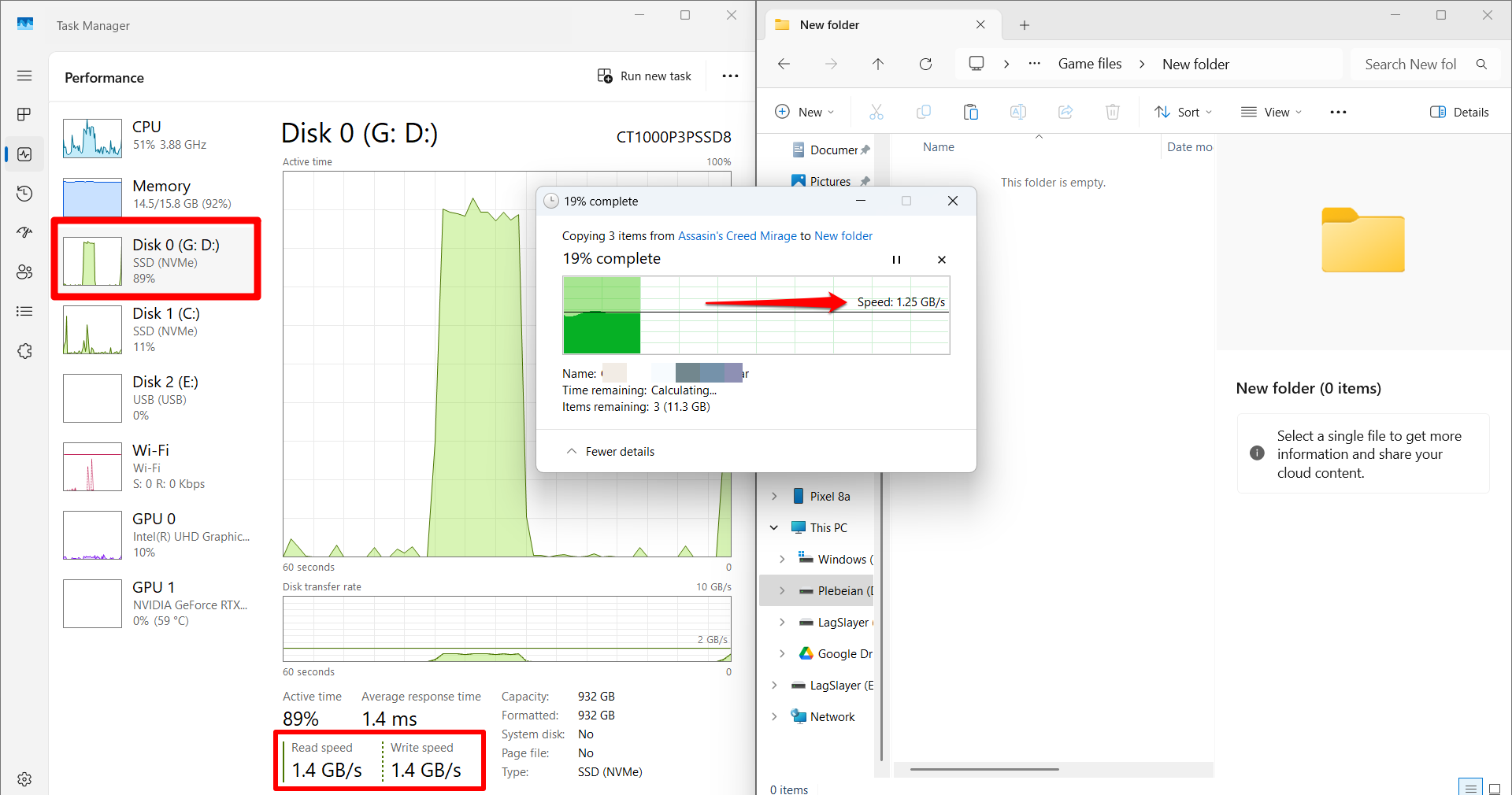
![IMG]() Using the elevated Command Prompt
Using the elevated Command Prompt

Apart from the basic methods of checking your SSD speed through Task Manager and File Explorer, Windows allows you to run a speed test using the elevated Command Prompt. The test will show your SSD’s random and sequential read/write speeds. Here’s how to get it done:
- Click on the Start icon on your taskbar.
- Type CMD into the search bar.
- Click on Run as administrator.
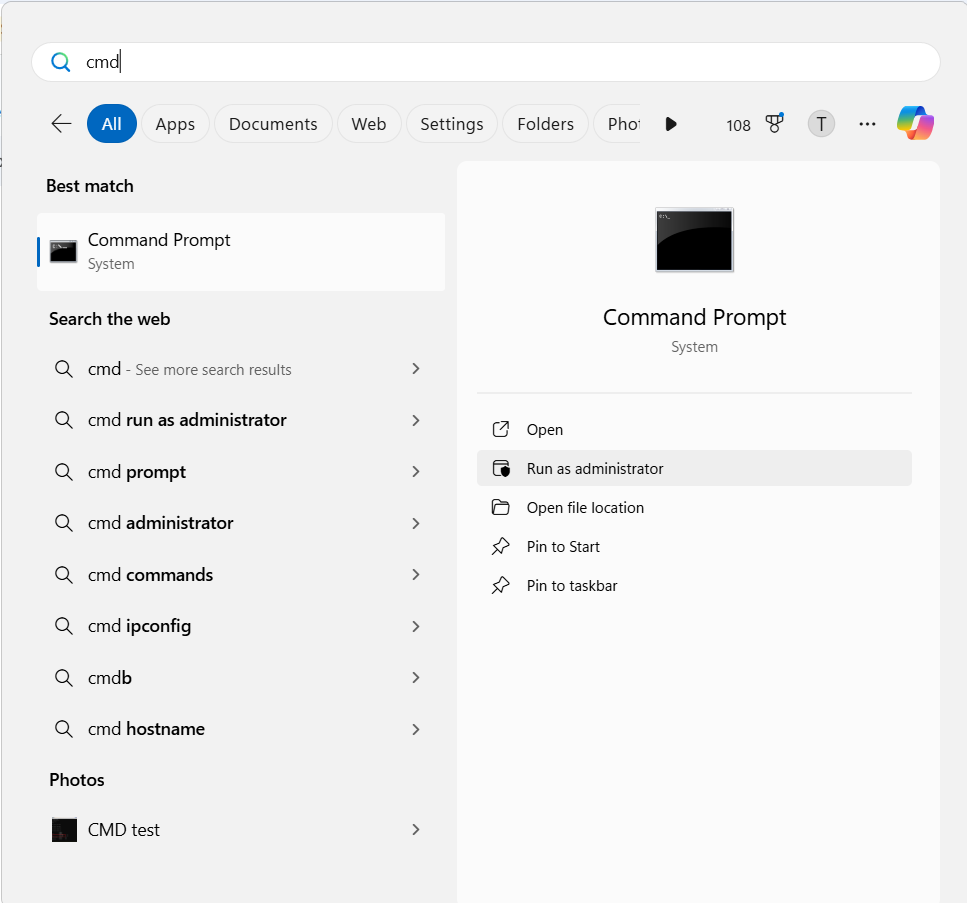
- To continue, click the Yes button on the User Account Control prompt.
- Once the elevated Command Prompt window opens, type in the following command and press
Enteron your keyboard to start the speed test:
winsat disk -drive DriveLetter
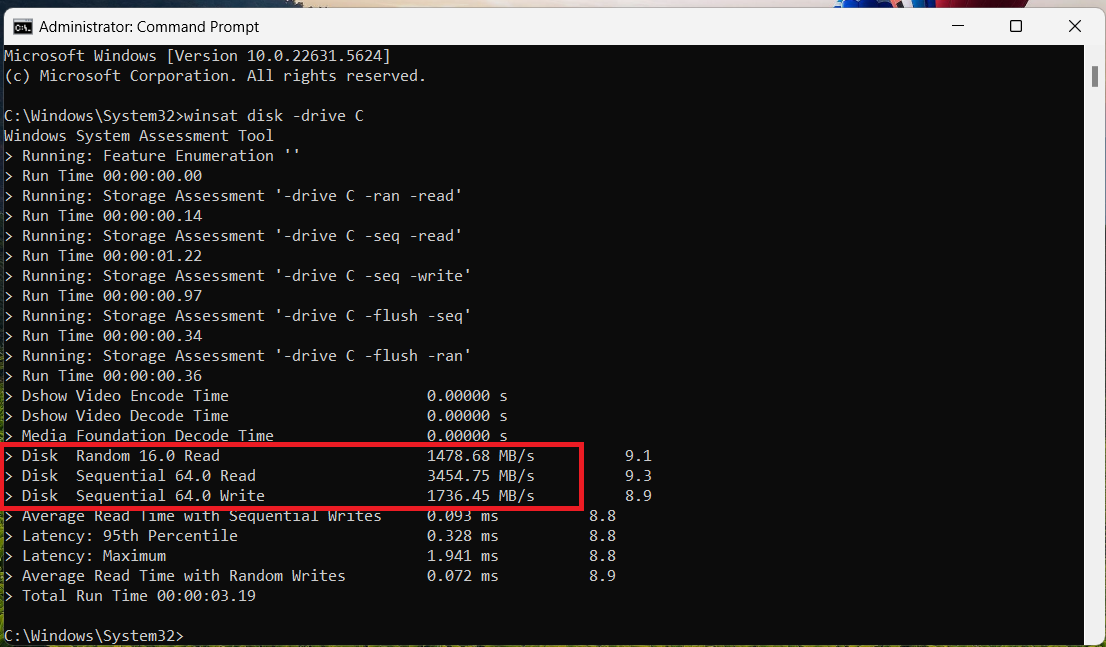
Using the above default command, WinSAT will not test your SSD’s random write speed. This is to guard against potential wear. However, you can use separate commands to test your random write speed:
winsat disk -ran -write -drive DriveLetter
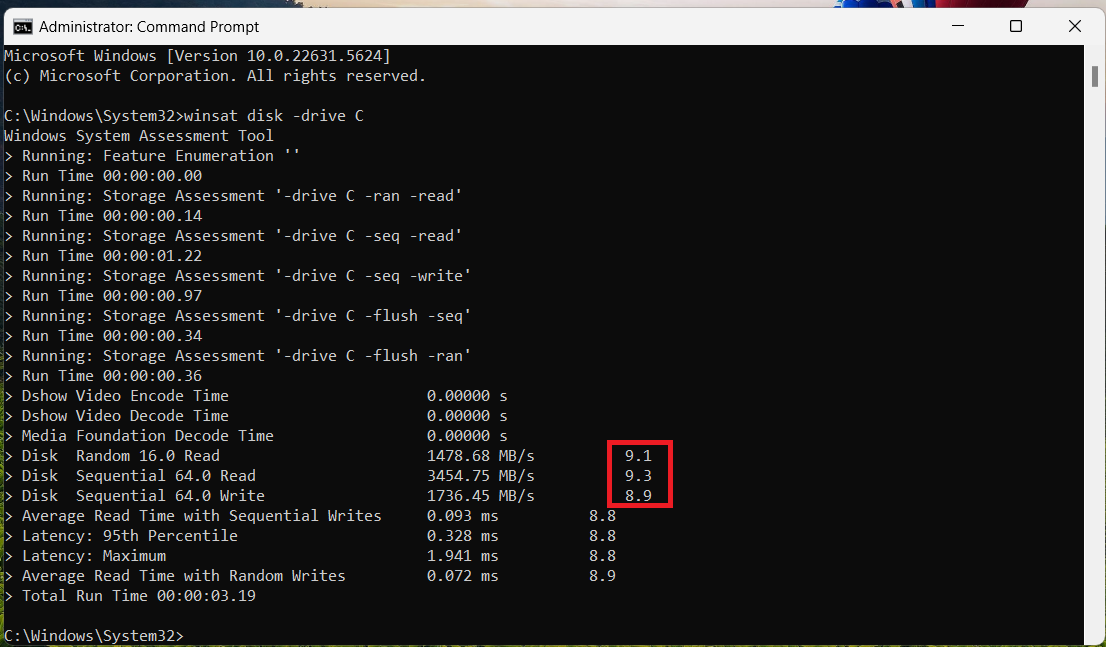
- 8.0–9.9: Very high performance
- 6.0–7.9: High performance
- 5.0–5.9: Moderate performance
- 3.0–4.9: Basic performance
- 1.0–2.9: Low performance
My SSD Speed Is Low. What Should I Do?
Congratulations! Now you know your SSD’s read and write speed.
However, if it is not close enough to the expected maximum speeds, the following solutions can help turn things around and make the drive faster:
Follow the installation instructions
Always follow the drive or motherboard manufacturer’s instructions when installing your SSD. Some drives and boards may have protective film or plastics that you must pull off to ensure proper connection and heat dissipation. In some cases, you may have to follow specific SSD heatsink installation processes.
Update firmware
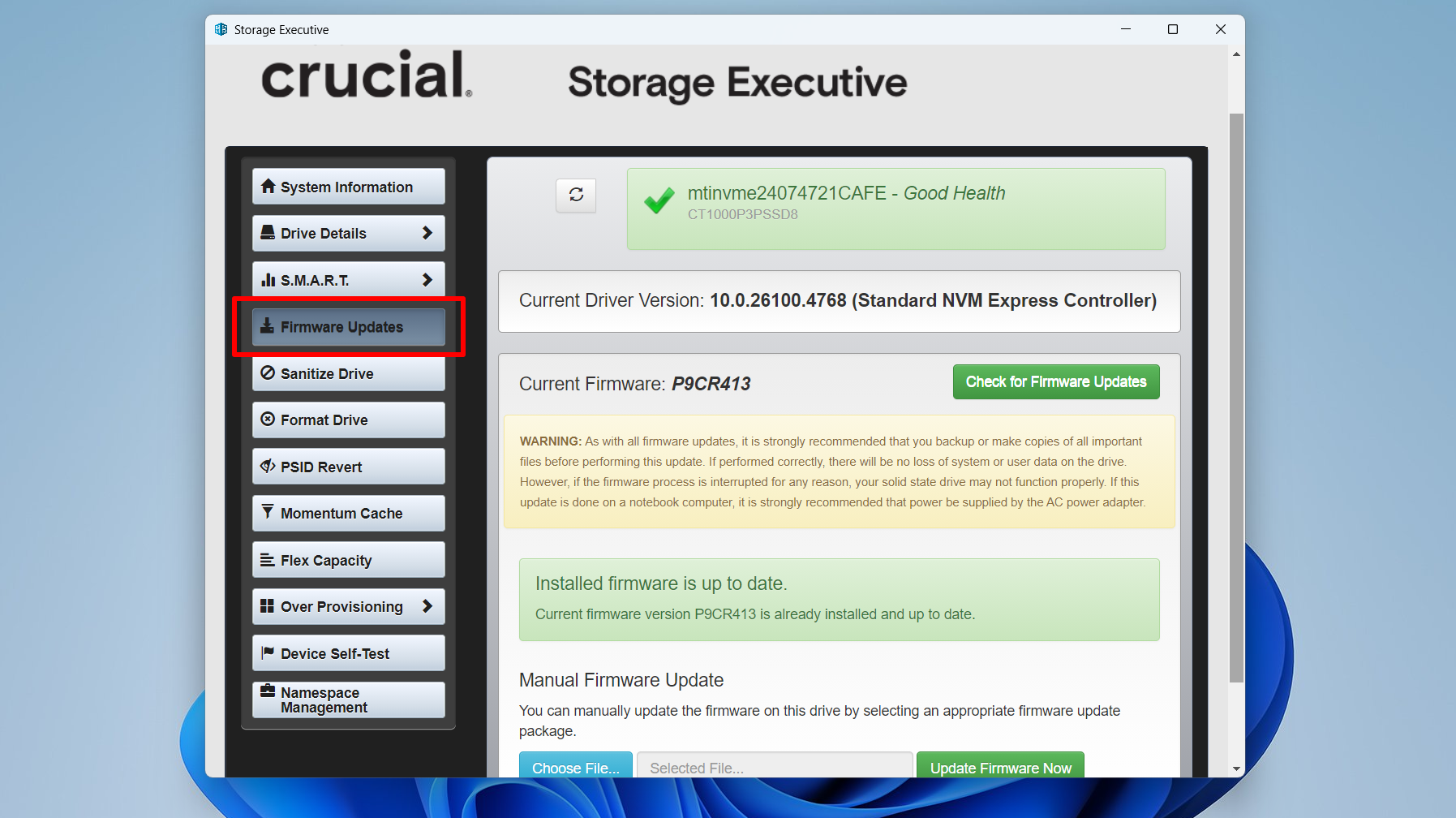
The SSD firmware is a low-level software program that essentially operates the drive. An outdated firmware can impact speed and cause other problems. You can use your drive manufacturer’s dedicated program to install its latest firmware.
For example, if you use a Crucial SSD, you can install Crucial Storage Executive, while Samsung Magician works for modern Samsung SSDs.
Free space management
Lack of free storage space could be the reason for the slow speeds. It’s important to leave at least 10–20% of free space to facilitate automatic SSD optimization processes like garbage collection and wear leveling.
Run SSD optimization
Low speeds could also result from suboptimal system settings and inefficient SSD management. You can follow our SSD optimization guide to learn about the best practices that can speed up your drive and maintain its health.
SSD Speed Tests: What to Remember
SSD speed tests may not match the manufacturer’s marketing claims, but they are a good place to start if you want to confirm your drive’s capabilities. Ensure you enable the right conditions before running the test and stick to tests that suit your use case.
For example, if you want to see how your drive fares under heavy workloads, you can use CrystalDiskMark’s Peak Performance profile. Video editors can rely on Blackmagic’s Disk Speed Test, while everyday users can use their manufacturer’s SSD utility.
You should also remember to provide your SSD with the best conditions by running regular optimizations.
We hope you’ve benefited from this guide. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d like to hear from you!
FAQ
This depends on the type of SSD you have.
SATA SSDs achieve a maximum read/write speed of 550 MB/s.
PCIe NVMe SSDs have higher speeds, depending on the generation:
- Gen 3 SSDs can reach speeds of up to 3,500 MB/s.
- Gen 4 speeds reach up to 7,000 MB/s.
- And Gen 5 goes as high as 14,000 MB/s.
Furthermore, apart from showing your drive’s read and write speeds, the Windows System Assessment Tool (WinSAT), which can be run from the Command Prompt, also uses a scoring system to grade the performance of your SSD from 1.0 (lowest) to 9.9 (highest), as follows:
- 8.0–9.9: Very high performance
- 6.0–7.9: High performance
- 5.0–5.9: Moderate performance
- 3.0–4.9: Basic performance
- 1.0–2.9: Low performance
