- What Is Disk Defragmentation?
- Do I Need Disk Defragmentation?
- What Are the Tools for Defragging Hard Drives?
- How to Defragment a Hard Drive
- How Does Disk Defrag Affect My Computer’s Performance?
- Are There Disadvantages to Disk Defragmentation?
- What Defragging Does Not Do: Myths About Disk Defrag
- Make the Most of Defragmentation: What to Remember
- FAQ
Windows users still ask, “What is defragging?” in 2025, partly because HDDs are no longer the major players in modern storage.
But these drives occupy a critical role as backup devices, one that requires every drive to be in tip-top shape.
Defragmentation (or defragging) is one of the techniques you need to achieve that, especially if you write and delete files frequently.
It helps ensure that hard disks can access files as fast as possible and speeds up the write process.
At the same time, many users still have concerns and reservations about defragging hard drives, asking questions like “When should I defrag?” “Which tools should I use?” “How often should I defragment my hard drive?” and “Which drive should I defragment?”
Stick around to find answers to these questions—and more.
🔄 Defragmentation lines up pieces of individual files closer together on hard disk drives.
🧩 It is deployed when file fragments are scattered across a hard disk (fragmentation).
🐌 The system slows down when a drive is badly fragmented.
⚙️ You can run defragmentation using Windows’ built-in disk defragmenter and third-party tools.
🚫 Do not defragment an SSD, as it can reduce the drive’s lifespan.
⌛ These programs can also help you run scheduled defragmentation.
⚡ Once a drive is defragged, it runs faster and improves overall system performance.
What Is Disk Defragmentation?
Defragmentation is a process that Windows uses to reorganize file fragments on hard disks to allow faster read access and improve drive performance. The rearrangement brings pieces of files scattered across the drive’s surface closer to undo the effects of fragmentation.
I’ll explain what fragmentation is and how it affects your computer to help you understand defragmentation better.
How do hard disk drives work, and what causes fragmentation?
Let’s start with how data is written to and read from hard disk drives.
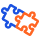
Within every hard disk drive, there is at least one read/write head (attached to a mechanical arm) and a spinning disk. Whenever you save or copy a new file to the HDD, the R/W head writes the data to sectors on the hard drive, arranged in a concentric pattern. These sectors are the drive’s basic storage units, and each can only contain 512 bytes.

The drive breaks up files into pieces of 512 bytes and writes these fragments sequentially across multiple sectors. Whenever the drive needs to read a file, it must locate every fragment. File access is faster when fragments are close to each other.
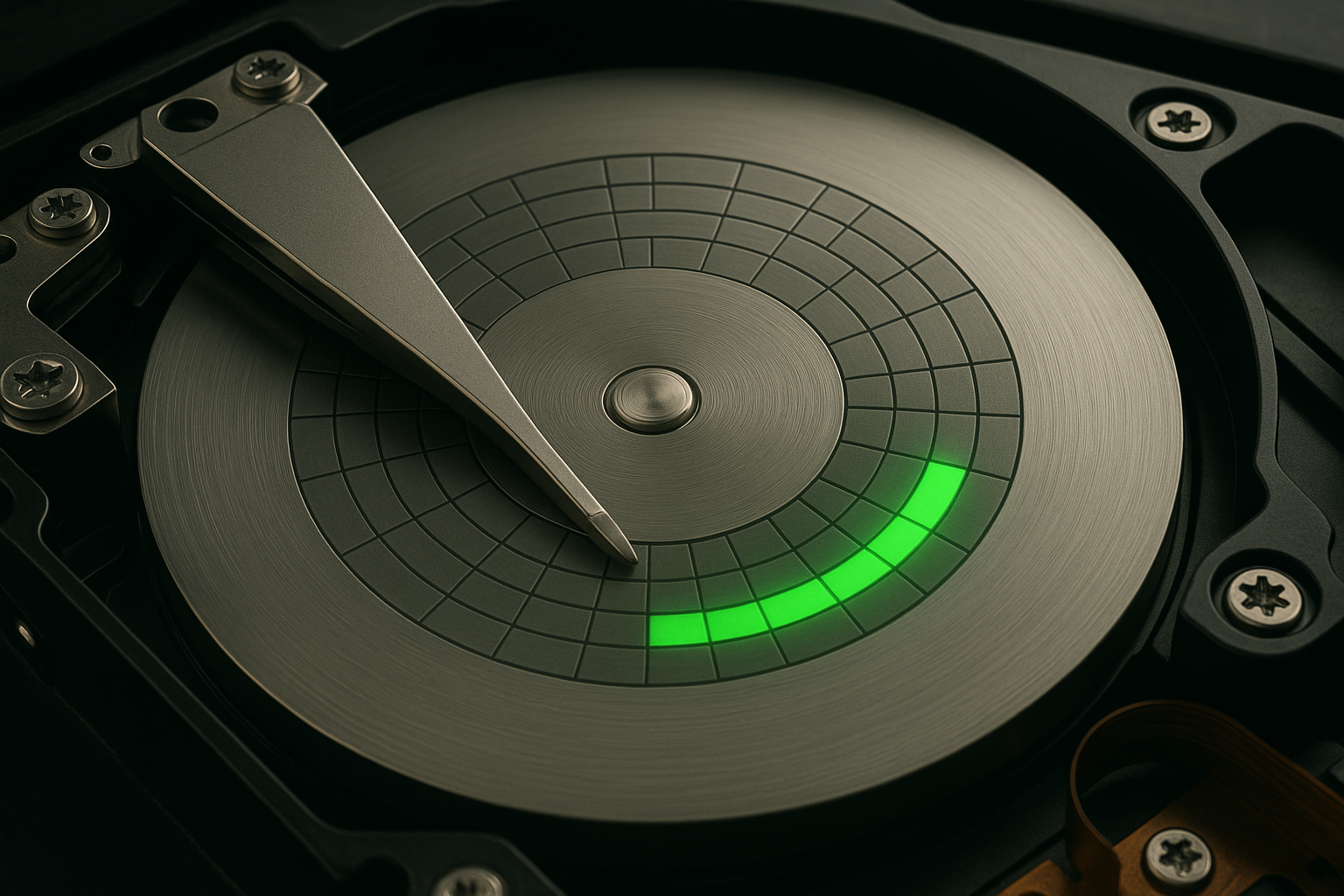
If the drive is filled up, other files may be saved to the reserved MFT space, causing MFT files to be fragmented and scattered across the disk.

Whenever you delete files for the first time, the spaces they originally occupied will become empty. The hard drive will then overwrite those empty spaces with new files.
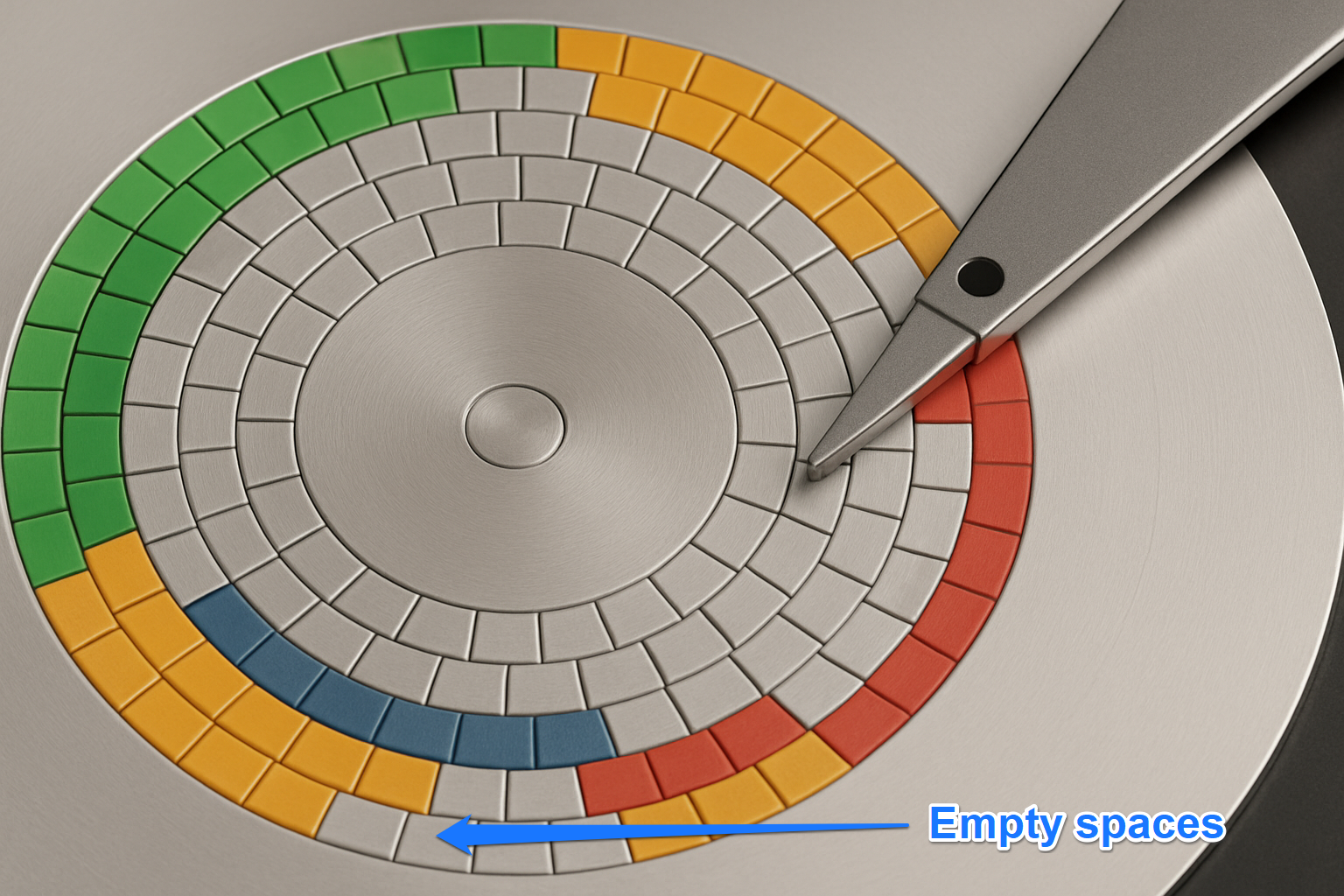
If the new files you’re saving are significantly larger than the leftover empty spaces, the R/W head will first fill up those empty spaces and then write the rest of the file fragments to other sectors on the drive.
As you continue to delete files and create or copy new ones, file fragments continue to scatter across the disk. As a result, it takes the HDD head longer to read files since it must locate every fragment.
The following are the effects of fragmentation:
- Slow read and write times: The drive takes more time to read files since they’re farther away. Write times also take longer because the drive has to fill up empty spaces on distant sides of the disk.
- Reduced system performance: Because the drive head takes time to locate file fragments, most system processes that rely on files on the drive will experience a slowdown. Depending on your drive’s role, this could mean slow boot times, longer application load times, and File Explorer lags.
- Inefficient virtual memory: Most times, Windows creates a paging file (also called a swap file) on the hard drive to extend the system memory. This file can also fall victim to fragmentation and cause all sorts of issues because it will take the drive longer to supply data to the RAM.
- Shorter drive lifespan: The mechanical arm will be more prone to wear since it has to work harder to read and write files.

Disk defrag commands tell the HDD head to locate each file’s fragments and bring them closer together. That way, it can read files faster since it doesn’t have to cover a long distance to locate sectors on different ends of the disk.

Other things a defragmentation session can help you do include:
- Consolidate free space: When file fragments are arranged closer together, new files can be written sequentially.
- Optimize Windows: Operating system files will be consolidated to allow Windows to boot faster.
- Fine-tune your file system: In cases where MFT files are fragmented and scattered, defragmentation can remove regular files from the reserved zone and return the MFT files to be saved contiguously. This process allows the file system to work more efficiently and reduces the time the drive head has to read MFT files before locating system and user files.
- Prolonged drive lifespan: With file fragments reorganized to be closer, the HDD head movement will reduce, which decreases long-term wear and tear and reduces power consumption and heat.
Do I Need Disk Defragmentation?
Yes, if you use a hard disk drive. However, defragmentation shouldn’t be a regular thing. Disk defrag tools, like the built-in Defragment and Optimize Drives program, can tell when your hard disk drive is fragmented. But what are the signs that you should check for fragmentation? Check for fragmentation if:
- Your computer is slow
- It takes longer to copy and move files from one folder to another or from the affected drive to another storage device
- Your system takes longer to boot
You don’t need disk defragmentation if:
- You use an SSD
- Your drive is fast, and fragmentation is below 10%
No. Do not defragment your SSD. Solid-state drives operate in ways that make defragmentation meaningless and potentially harmful. They use flash memory, which means there are no moving parts required to manually reach for and fetch data. Instead, data is accessed instantly, regardless of where it is.
SSD optimization involves different techniques, such as TRIM and write-caching, not defragmentation. Instead, the disk defrag process can hurt your SSD’s health, since it involves heavy write operations.
How often should I defrag my hard disk drive?
There is no general schedule for defragmenting hard disk drives. It depends on how frequently you write, overwrite, move, and delete files. If you perform these actions less frequently, you wouldn’t have to defragment often.
Here are my recommendations for different use cases:
| Use case (HDDs only) | Description | Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Light home use | Occasional document editing, web browsing, media playback | Once every 1 to 3 months |
| Moderate use (professional and office use) | Regular file operations, productivity apps, spreadsheets, etc. | Every month |
| Heavy use (video editing, gaming, etc.) | Frequent large file transfers, editing, saving, and deleting files | Every 1 to 2 weeks |
| File servers (HDD-based NAS systems) | Constant file access by multiple users | Weekly or daily, depending on number of users and activity |
| Backups | Periodic backups, archiving, and file copies | After major backups and large data changes |
What Are the Tools for Defragging Hard Drives?
Windows has a dedicated defragmenter, but there are competent third-party options that you can use. While each tool provides primary defragging capabilities, there are differences between third-party programs and Microsoft Drive Optimizer that you should read about to make a long-term decision about which tool to use.
Most third-party tools provide granular control, more features, and access to fragmented files. In most cases, you get to see a visual representation of file fragments to understand the level of fragmentation on a drive
Here’s a short list of effective disk defragmenters to consider and what they offer:
| Feature | Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Auslogics Disk Defrag | O&O Defrag | Defraggler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free version availability | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ (only trial version) | ✅ |
| Analyze and defrag | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| File/folder defragmentation | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| SSD detection | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Customizable algorithms | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Visual representation of fragmentation | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Disk health/SMART monitoring | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Custom defrag scheduling | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
How to Defragment a Hard Drive
I’ll show you basic steps on how to defragment your hard drive using Windows’ built-in tool and a third-party program.
The process starts with analyzing the drive to check for fragmentation. As I mentioned earlier, anything under 10% is fine.
However, if the drive is frequently used and is fragmented over 10%, consider defragmenting it. Ensure you defrag hard disks with fragmentation levels above 20%.
If you want to learn how to run advanced defrag processes, follow our complete step-by-step guide on defragmentation.
Let’s start with the native disk defragmenter:
- Open the Start menu and type defrag.
- Click Defragment and Optimize Drives in the search results.
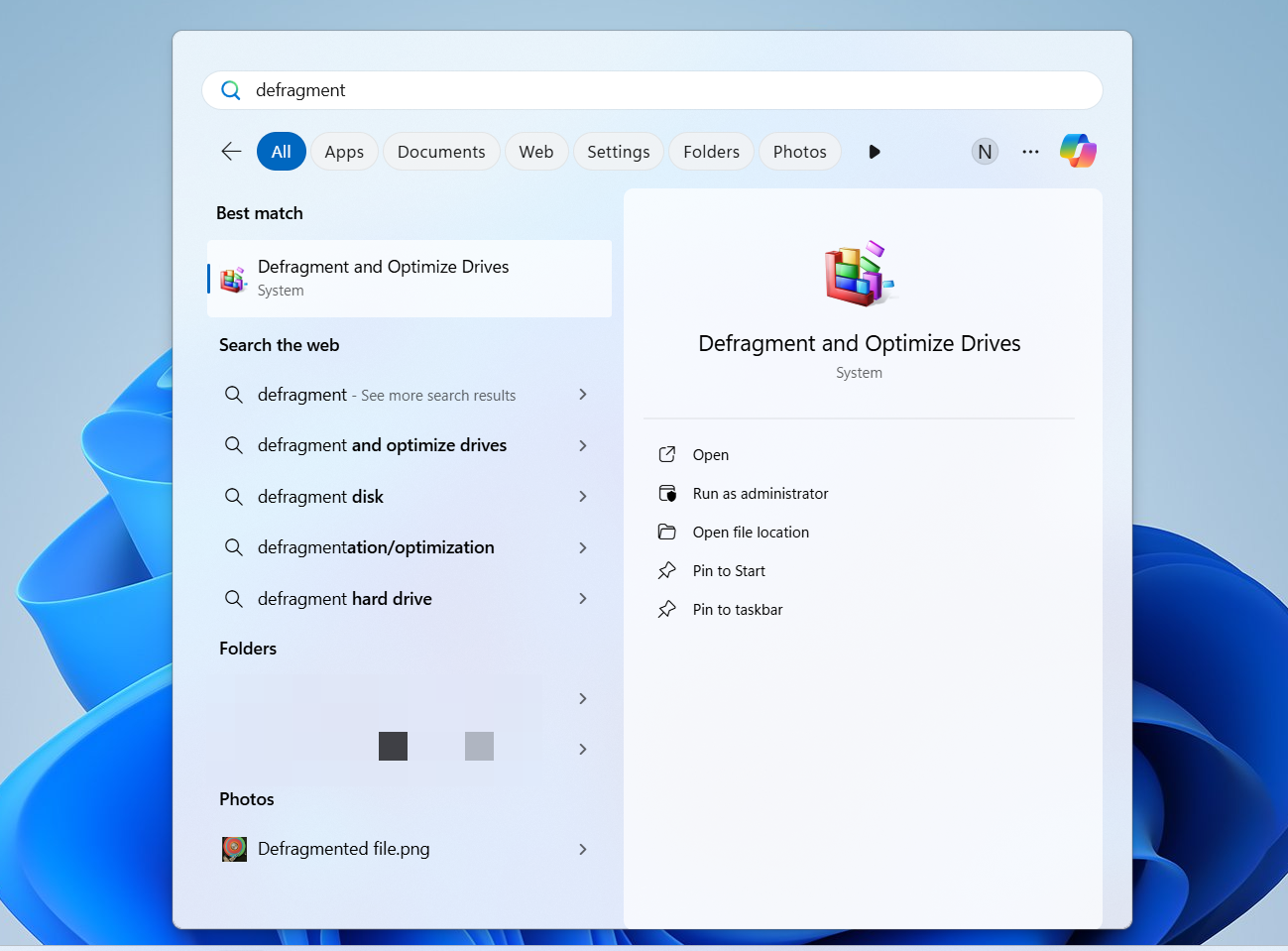
- Select the drive you want to defragment and click Analyze to check the hard disk’s level of defragmentation.
- If you want to defragment the hard drive, click the Optimize button.
- The tool will now start defragmenting your hard drive, and you should see the progress under Status.
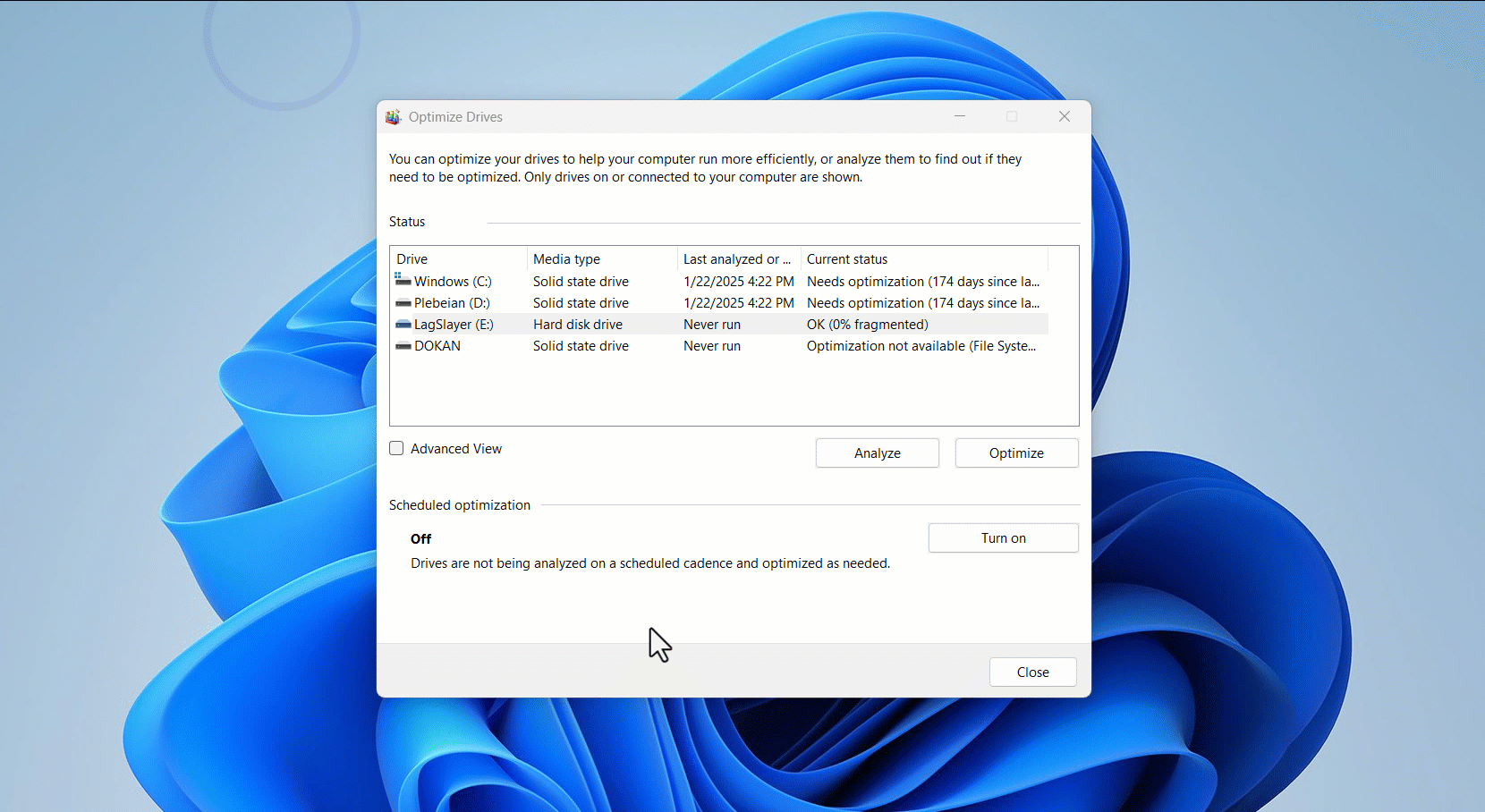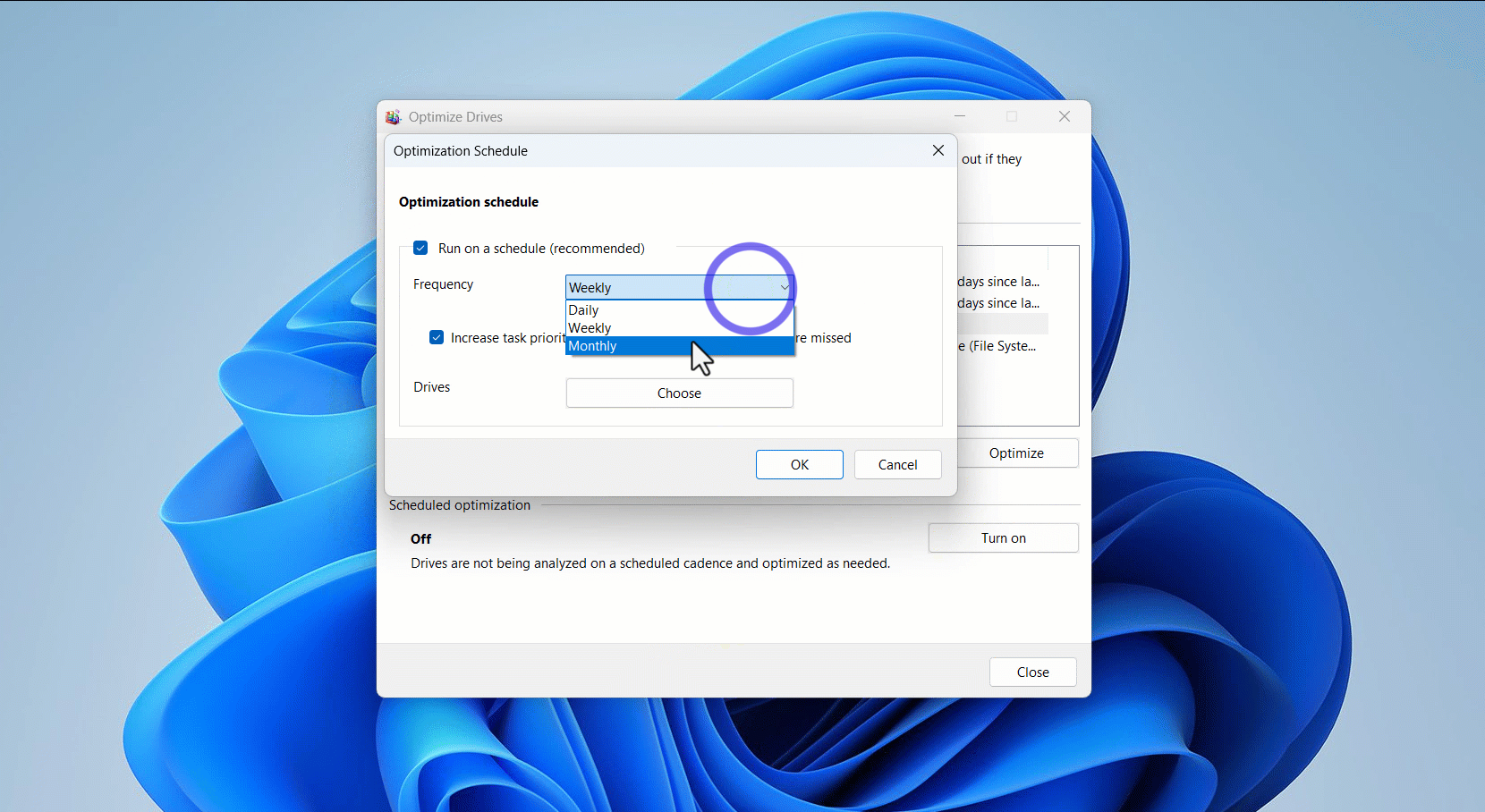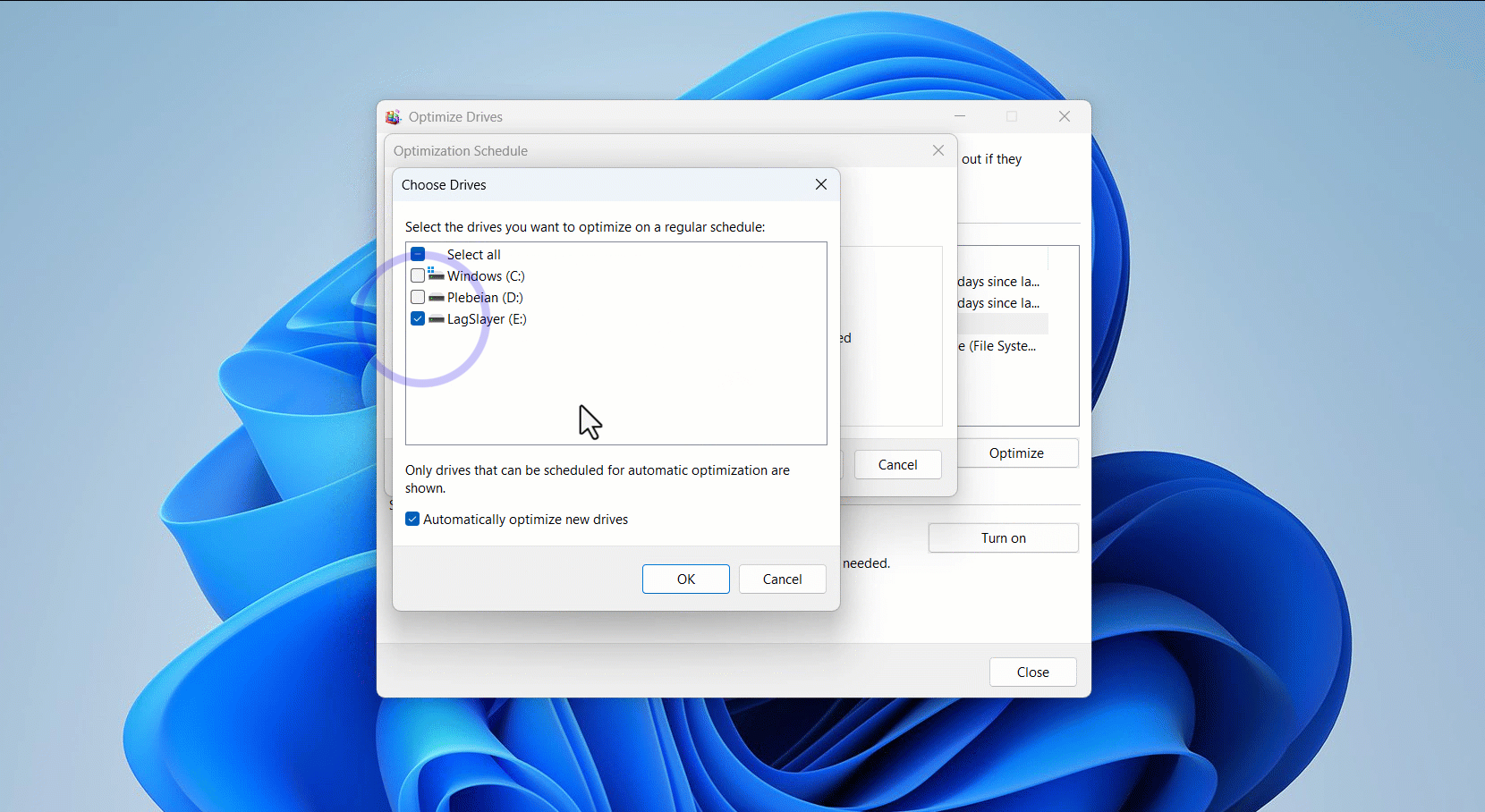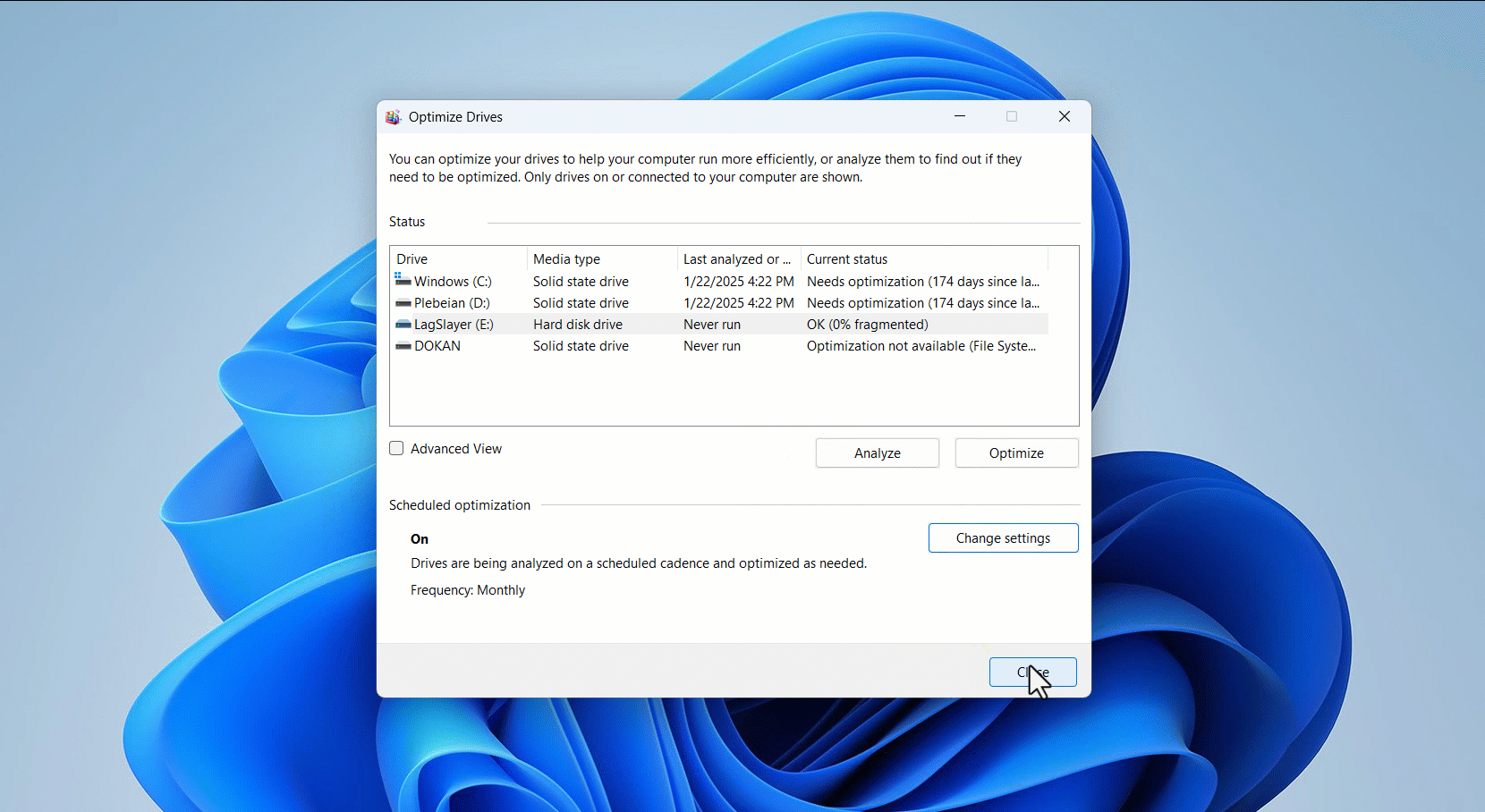
To schedule automatic defragmentation, click the Turn on button under Scheduled optimization, check the box beside Run on a schedule (recommended), select an option next to Frequency (monthly, weekly, or daily), and click the OK button.
- You can also click the Choose button next to Drive to exclude any drive you want.
How to defragment a hard drive using Auslogics Disk Defrag:
- Download and launch Auslogics Disk Defrag.
- Once the tool opens, click the drop-down button beside the Defrag & Optimize button and select Analyze.
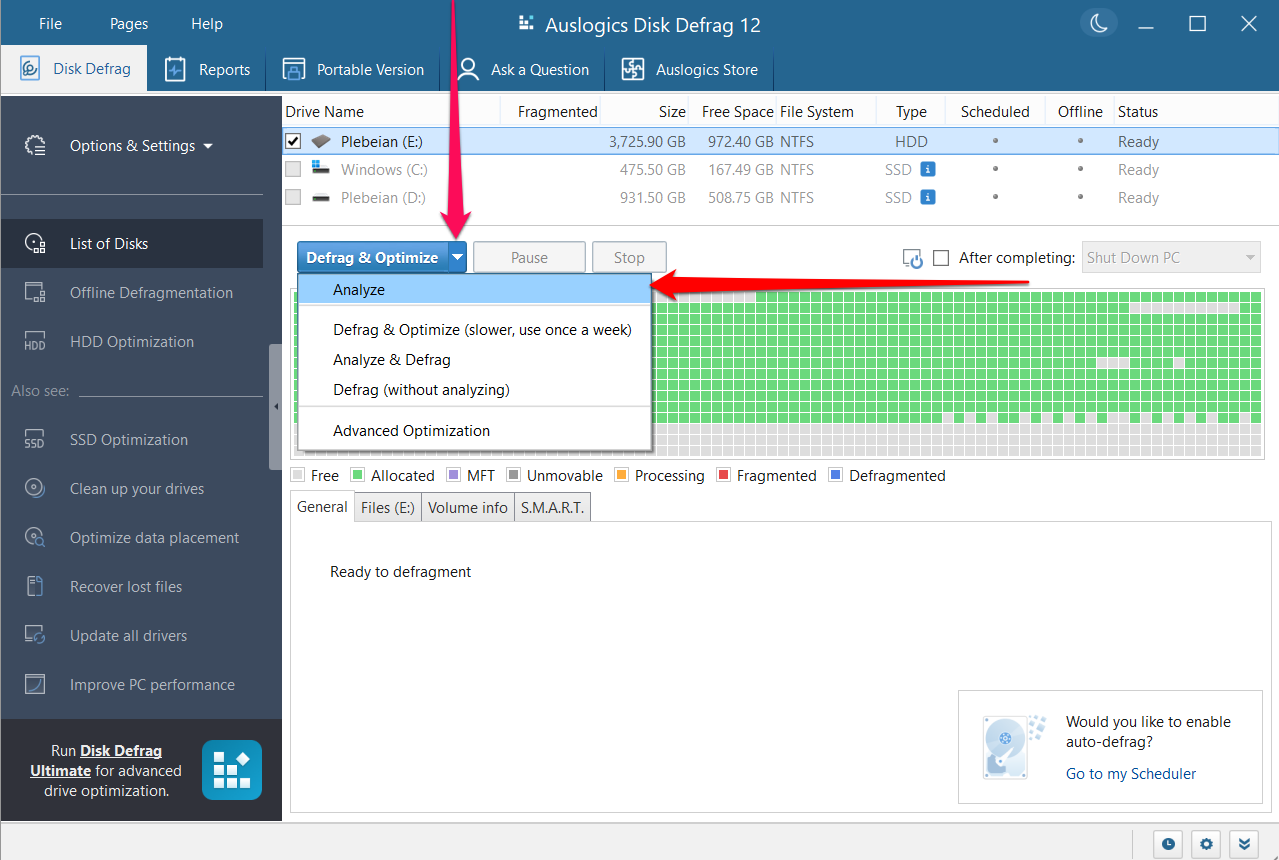
- You should see a visual report of your drive’s level of fragmentation.
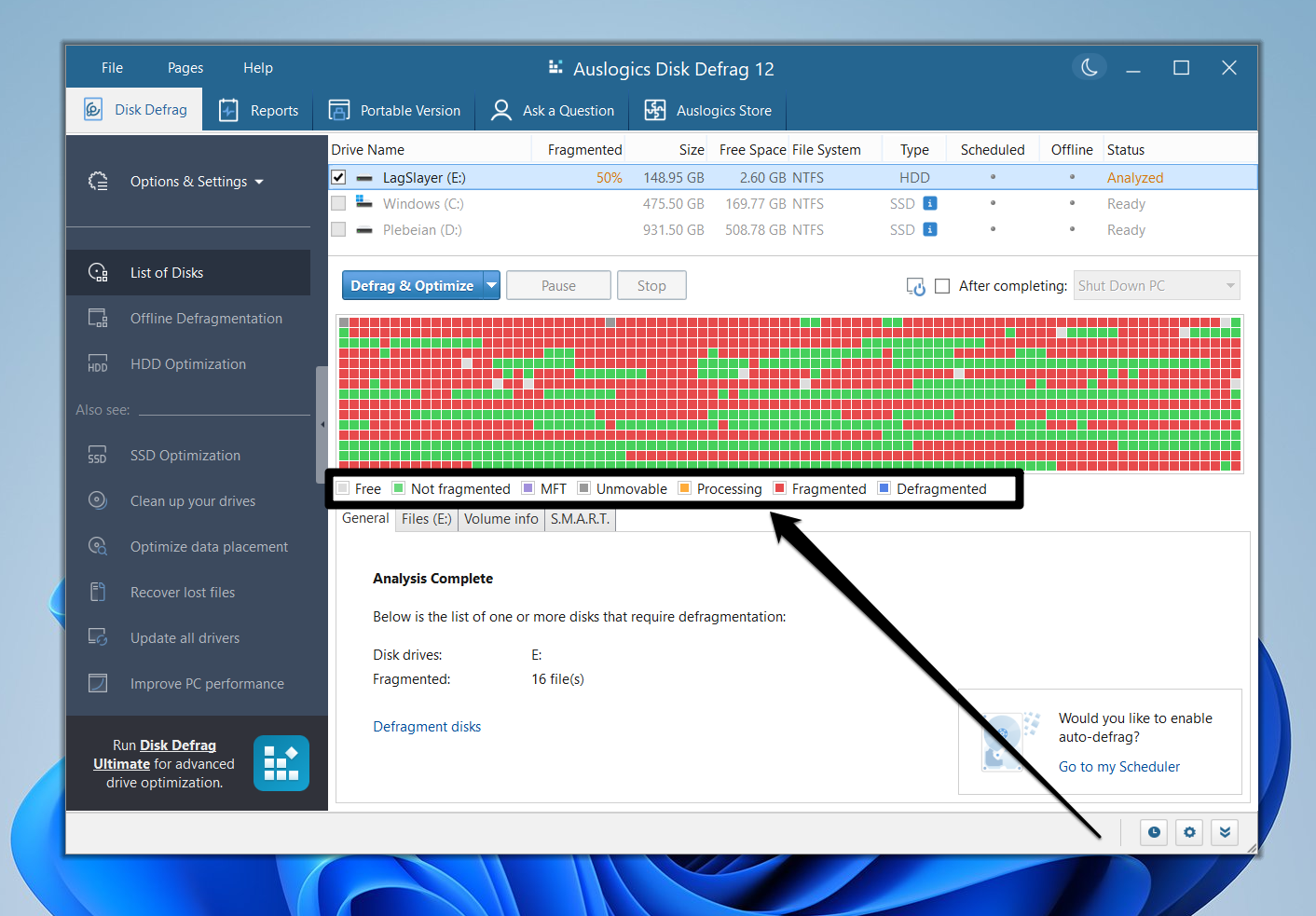
- To start defragging the hard drive, click the Defrag & Optimize button.
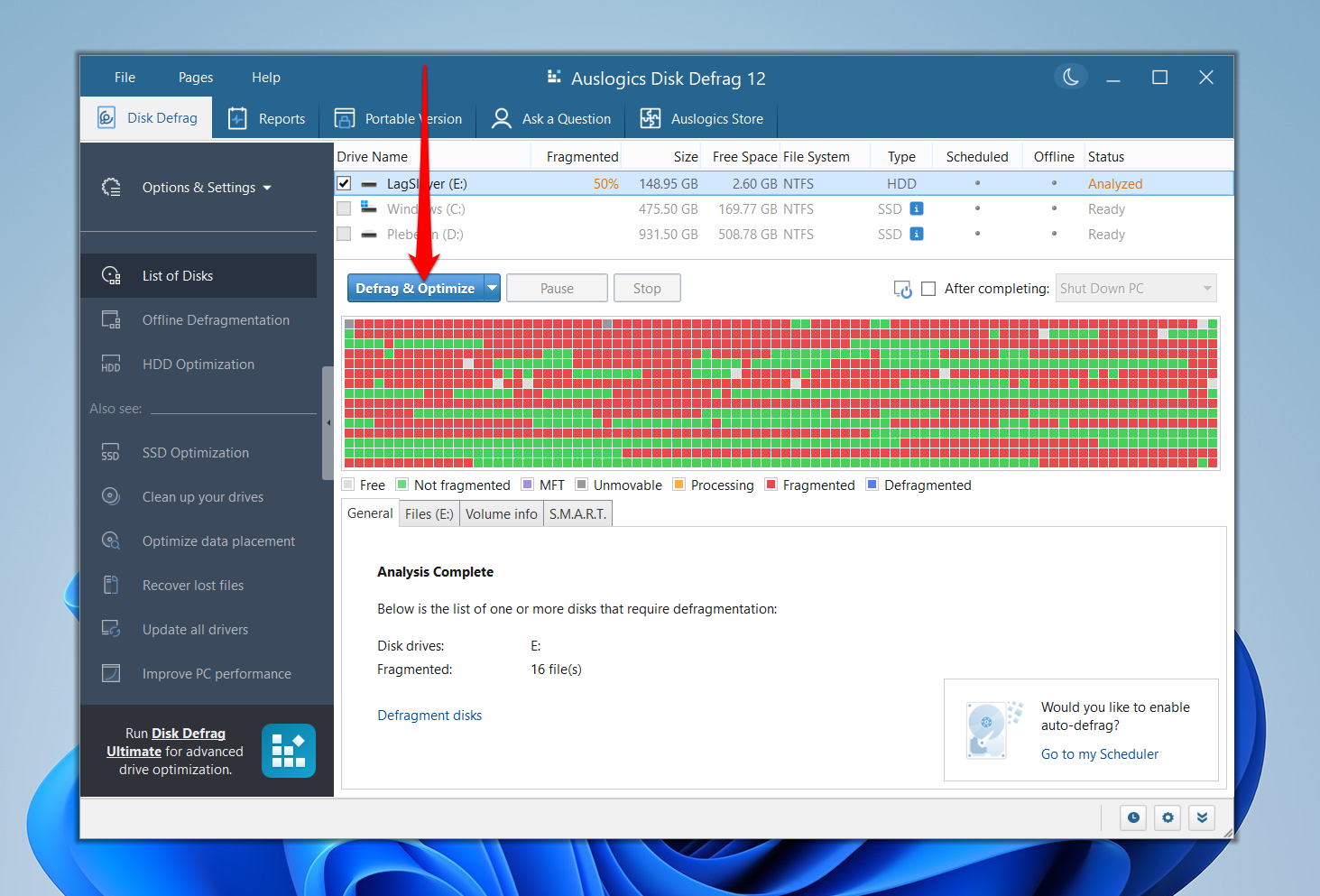
- You should see the file fragments being arranged in real time and the progress displayed under the General tab.
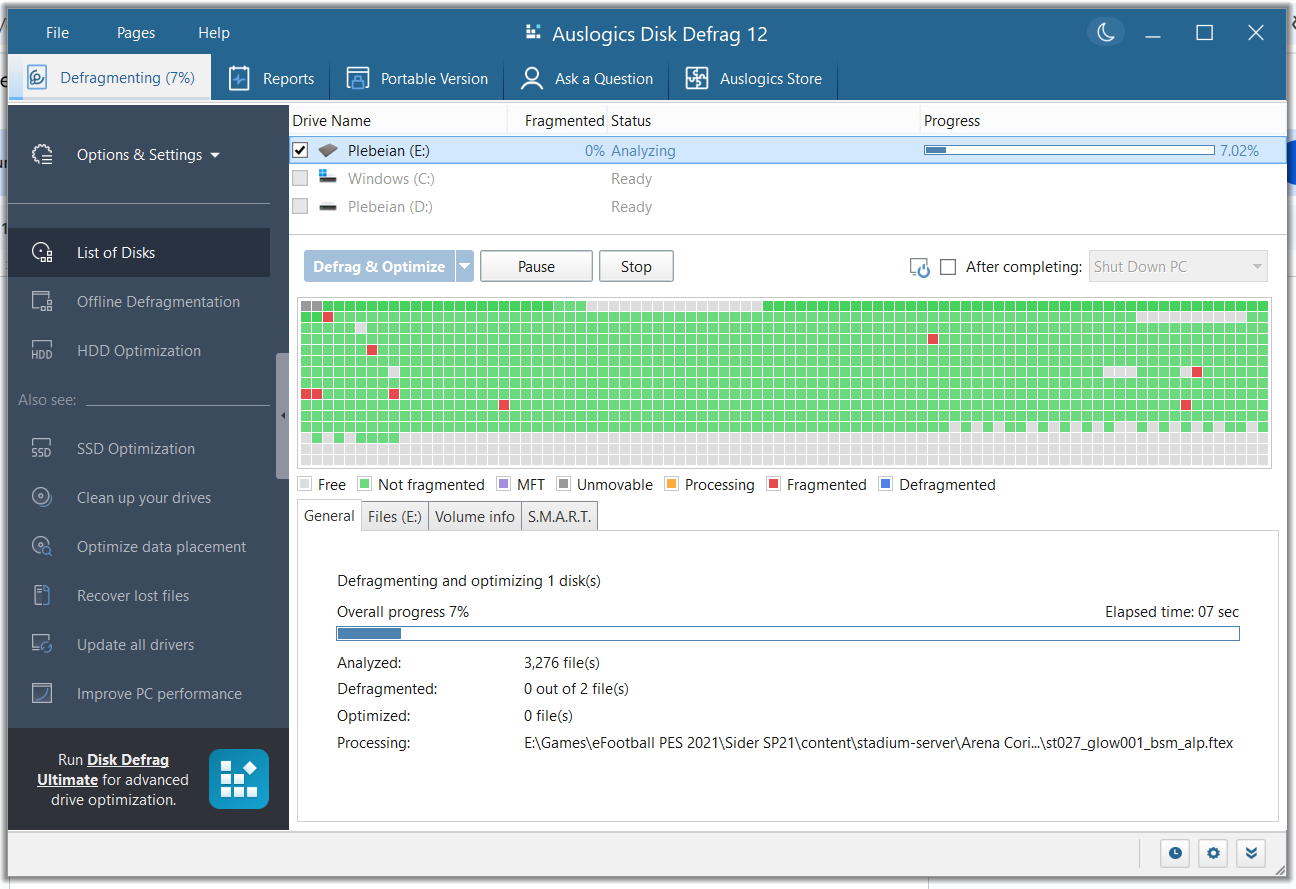
Auslogics Disk Defrag, like other third-party programs and Windows’ native tool, also offers scheduling.
Go to File > Settings > Scheduler. You can now go to the right side of the window to customize your preferred schedules.
How Does Disk Defrag Affect My Computer’s Performance?
Earlier, I mentioned how defragmentation helps to bring scattered pieces of files closer together, fine-tune file systems, and consolidate free space. Here’s what those processes translate to in real life:
- Enhanced system performance: When files are lined up how they should be on the drive, your apps and operating system will no longer struggle for access to items they need to function well.
- Faster startup: Since system files are defragmented, you should no longer experience slow boot times.
- Speedier file transfers: You will notice a bump in transfer speed when copying files to and from your hard disk drive.
- Better gaming and rendering performance: If you still run games on your hard disk or use an HDD for your rendering, defragmentation should help make things faster.
Are There Disadvantages to Disk Defragmentation?
For HDDs, yes. But these downsides are largely painless if you know your way around them. However, you’ll lose more than you gain when you defragment an SSD.
Let’s cover the disadvantages of defragmentation:

Defragmentation is not just a waste of time on SSDs but can also harm these drives. Every SSD’s lifespan is determined by a limited write cycle. These write cycles will go to waste (and for nothing) whenever you defragment your drive.

If you rarely write and delete files, the performance boost from defragmentation will likely be negligible, especially if you’ve run the process recently. Defragmentation is generally not recommended in cases like this, unless you’ve gone a long time without defragging.

Defragmentation can take forever to complete. This phenomenon is common with slower and heavily defragmented hard disk drives (HDDs are not known for their speeds). Given that the mechanical arm has to move across the disk to locate and reorganize files, it’s understandable how the process may take time.
However, the following factors can increase how much time your computer will take to complete the process:
- Level of fragmentation
- Disk size
- Computer speed
- Drive speed (some drives run slower than others)
- Ongoing system activity
Defragmentation can cause short-term performance drops. Apart from consuming time, defragmentation also consumes a significant amount of system resources. As I mentioned, the process involves moving files around the disk, which can easily cause 100% disk usage and slow down the entire system.
Some of the symptoms you’ll notice during defragmentation are slow app launch times, a lagging or freezing File Explorer, and general system glitches.

Using modern defragmentation tools is generally safe, as they account for risk factors before the defrag process. However, there’s still a real risk of data loss, no matter how small. I’ll explain.
We’ve established over and over that defragmentation involves moving file fragments around. As such, your files may become corrupt if the process is cut short due to power loss, system crashes, or forced shutdowns.
Low disk space, application errors, and aggressive third-party defrag tools are also risk factors that increase the chances of data loss.
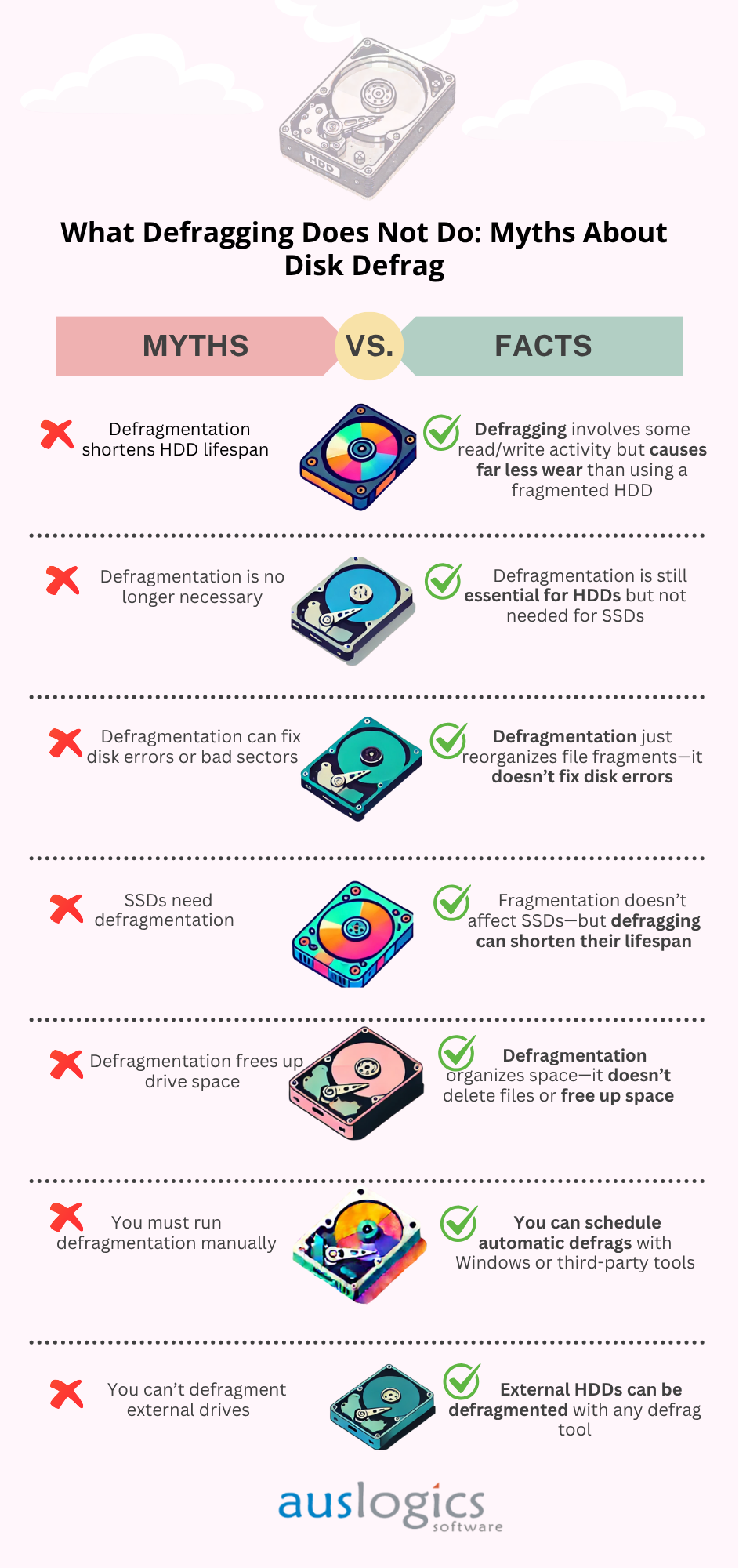
What Defragging Does Not Do: Myths About Disk Defrag
Make the Most of Defragmentation: What to Remember
We’ve established that defragmentation does your hard disk drive a world of good. Thankfully, you can create an optimization schedule so you don’t forget to defragment your drive. You can use my recommendations to set a schedule that fits your use case.
But remember:
- Do not defragment your SSD. Use an SSD optimizer instead if you want to keep your drive healthy.
- Third-party tools provide notifications, allow you to create customized schedules, and help you run file and folder defragmentation.
Let us know how you defragged your computer and feel free to ask any question.
FAQ
It depends on what you want to achieve.
Microsoft Drive Optimizer is the best option for light users who use HDDs and SSDs but don’t want to interfere with drive optimization processes.
However, if you have a hard disk drive and need a tool that cleans up before defragmenting, displays a visual map of fragmented files, and offers customized defragmentation capabilities, Auslogics Disk Defrag is your ideal utility.
At the same time, you may want to consider using Defraggler if you need to run performance benchmarks, check drive health, and use customizable scheduling options.

16 replies on “What Does Defragging Do: Easy Explanation of Disk Defragmentation”
i want to ask a question that my C drive is by mistake defragmented by me nw when ever i switch on my pc the space on the disk go on decreasing day by day until i do disk clean up it go on decreasing
plzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz help me watsholud i do nw
If you have An SSD hard drive you shouldn’t defrag it NEVER! because what you are basicly doing when you defragment it. everything goes to the middel of the memory, wich is good if you have an ordinary hard drive because it’s the middel where it reads it the fastest… but if Defrag an SSD it’s decreasing it’s life span dramaticly! So if you hate Defrag operations buy an SSD (sounds like a seller) wich is 2 times the faster but 5 times more expensive
PS: all new mac are with SSD, so don’t defrag them… There are some “old” ones to that have them too….
I have a Mac machine. When searched for some inbuilt tool to defrag my Mac, I found none. Infact, it was mentioned that its not necessary.
For various reasons, I have 30 or more files which the defrag system reports as > files that cannot be defragmented,< Should I delete these files How do I best delete them
I appreciate your suggestions and satisfy with you that defragging could cause problems.
hi i read your above comments and found a question. Is your software ‘Auslogic Disk Defrag’ check which type of hard drive the user have? i mean you said that and SSD type hard drive shouldn’t be defraged. So your software checks hard type or it just defrags no matter what type of hard it’s . If so then it will create a serious trouble to users! i will be happy if i get a good piece of advice!
nice advise
Love this software but it won’t allow users with Limited Rights to run it, much like the built in XP defrag.
Any ideas how to fix other than elevate everyone’s privileges?
Thanks,
Tom
Can defragmentation cause lost of some files in the harddisk
honey,
You should use a defrag that has VSS compatibility. NTFS, from Windows 7 on, makes shadow copies of all files when they are deleted. “Moving” a file when it is defragmented means “deleting it in one place and putting it in another place”. So copies are made of all defragmented files unless VSS is either turned off or some compatibility action is initiated. Auslogics has the VSS compatibility mode in its settings.
First Speak ENGLISH and second you can keep defragging the disk or (clean up) untill you got enough money to buy a new one.
Hi, I installed Windows 8 on my existing computer. My ‘harddrive’ C is now a SSD card. I did not install Auslogic because I do not know how it is going to handle this drive. Can you give me advice ? I mean I thouhgt that a SSD drive should not be defragmented.
what is the after effect of defragmenting with the systems inbuilt defrags?
Helo dear
The problem in my laptop is window corruption. when i install new window it work for max 1 week and if their is any sudden shutdown occur like my battery is week when any sudden shutdown occur it corrupt window then i have to install another window to run.
kindly help with this what should i do and for your information i did not format my laptop hard drive since one year because of important data.
this was helpful,wish to be sent more information about keeping my PC running smoothly.
Thank you!
Was a big help.