Did you run into the “The PC must support TPM 2.0” error when trying to upgrade to Windows 11? If so, then this article is for you.
Besides having minimum RAM and storage space, your system must support TPM 2.0. Microsoft has been strict about this requirement before the system’s official release to the public.
It seems the company started preparing users for Windows 11 in 2016 when it required TPM 2.0 support on all new computers that ran any version of Windows 10.
If you bought your PC after 2016, it will likely come with TPM 2.0 and support Windows 11.
If you’re getting the error “The PC must support TPM 2.0,” it may mean TPM is not enabled on your device.
This guide explains everything you need to know about this chip, why you need TPM 2.0 for Windows 11, and how to enable TPM 2.0 on a PC.
What Is TPM 2.0?
TPM, short for Trusted Platform Module, is a small chip in your PC’s motherboard that provides security-related features at the hardware level.
For example, TPM 2.0 generates an integrated cryptographic key to protect data used to authenticate your PC.
Hardware security is more effective than software security, which is more malleable. When you press the power button on your PC, the TPM chip communicates with other security features within the system.
It supplies a unique code (cryptographic key) that cannot be modified. If everything checks out, the computer will start up. However, if a problem with the key is detected, the PC won’t boot.
Think of TPM 2.0 as a security protocol intended to make the life of hackers a little bit harder.
Is TPM 2.0 Required for Windows 11?
Microsoft has clarified that Windows 11 will only run on computers with TPM 2.0 capabilities.
In a blog post, Microsoft explains that PCs require this “modern hardware root-of-trust to help protect from common and sophisticated attacks.”
The post adds that “requiring the TPM 2.0 elevates the standard for hardware security by requiring that built-in root-of-trust.”
The TPM also performs various authorization functions, including drive encryption and secure biometric sign-ins with Windows Hello.
Put another way, if a hacker steals your drive and plugs it into another computer, they can’t simply decrypt it and access the files without the keys stored in the TPM.
TPM is tamper-resistant, making unauthorized access to your files nearly impossible.
If you want to know how to enable TPM 2.0, the next section will show you how.
Related: How to Check if Windows 11 Is Activated and How to Activate the OS
How to Enable TPM 2.0 on a PC
There are several ways to enable TPM 2.0 on your PC. But first, use the steps below to check if your PC supports TPM 2.0.
Method 1: Use Microsoft’s PC health check app
If you’re a Windows Insider, Microsoft makes it easy to check if your PC is compatible with Windows 11 through the PC Health Check app. Simply download the app and launch it.
If enabled on your PC, you’ll see a list of your device’s specifications, including TPM 2.0. You’ll also be able to see how old your computer is.
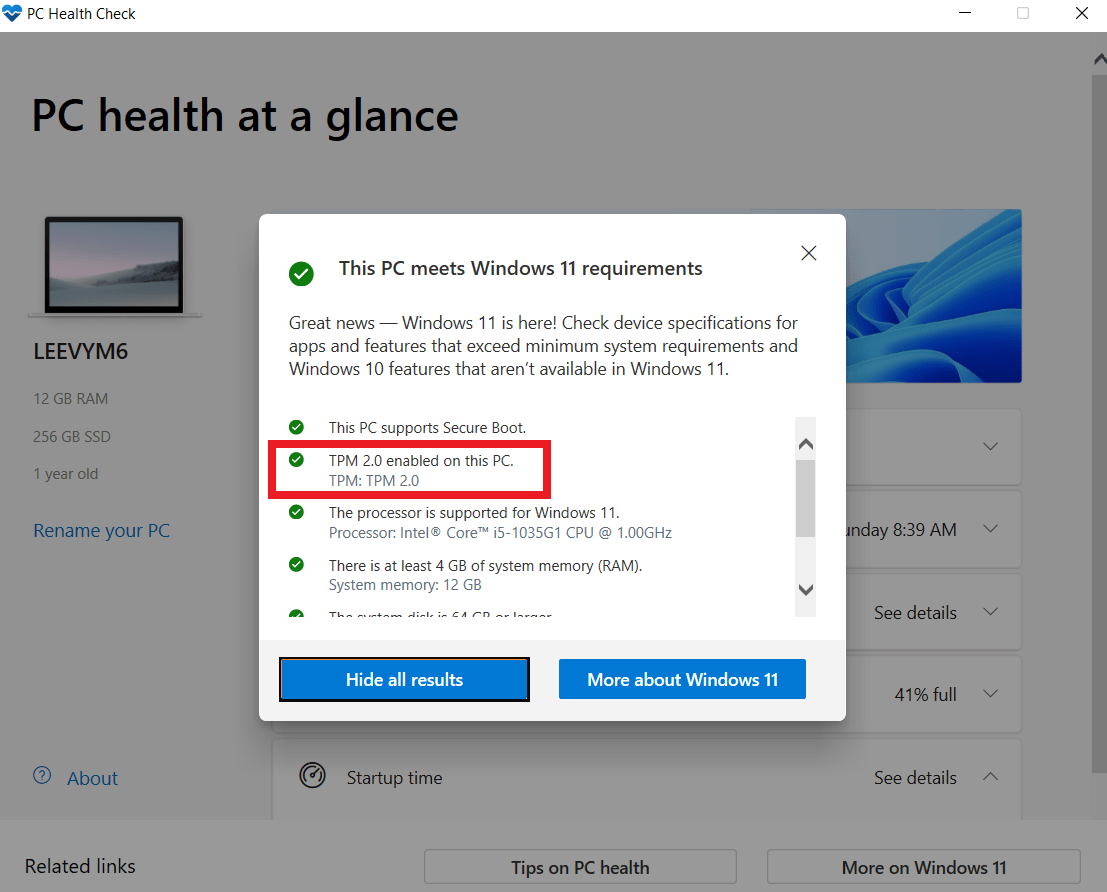
Method 2: Run the Tpm.msc command
Alternatively, you can check if your system has a TPM chip for Windows 11 and if it’s enabled using the tpm.msc command:
- Open Search and type tpm.msc.
- Select the first result, which says tpm.msc. Microsoft Common Console Document. This command launches the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management on Local Computer page.
- Under Status, you should see the notification The TPM is ready for use.
- Also, you can check if the TPM version says 2.0 under the TPM Manufacturer Information section.
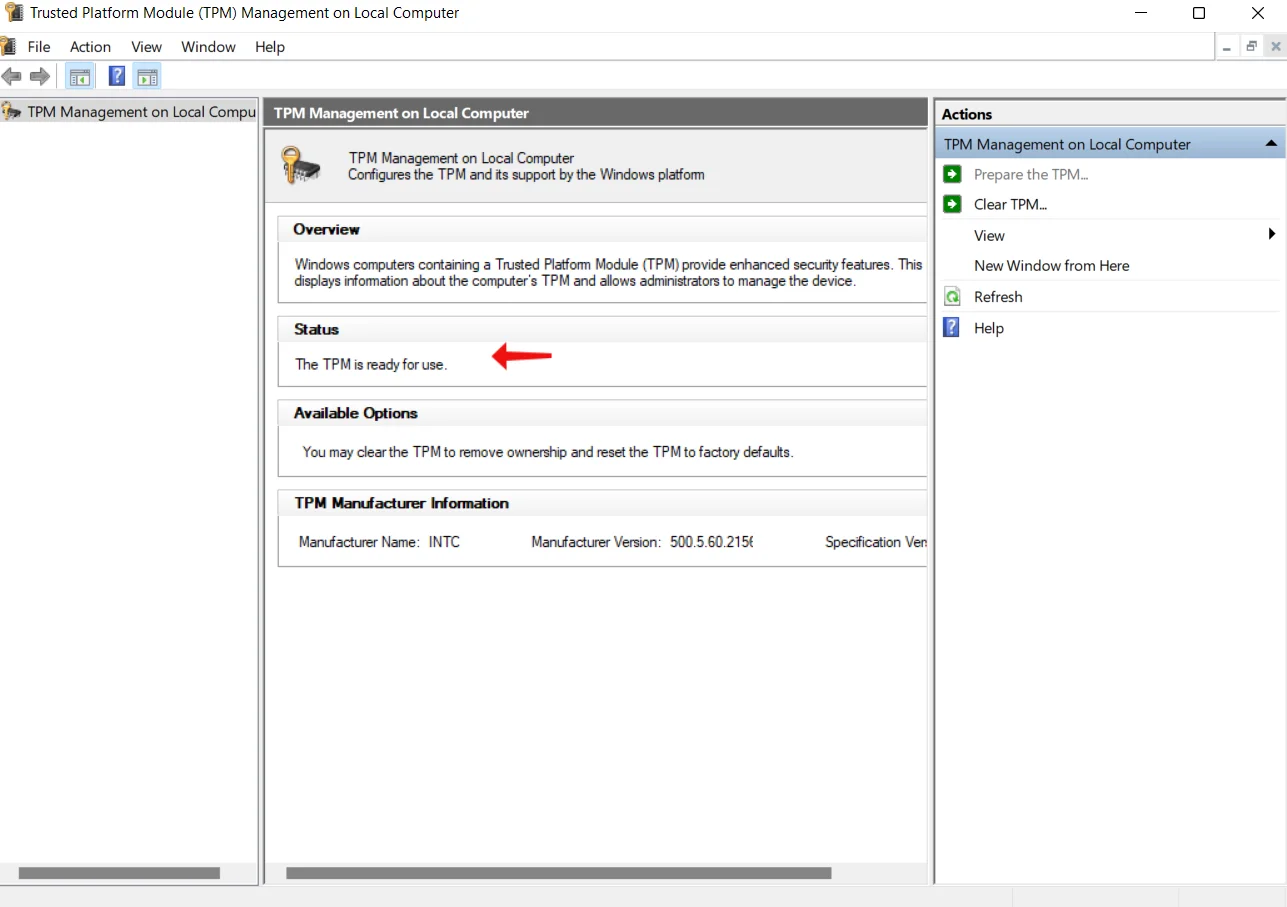
If TPM is not supported, you’ll see the notification Compatible TPM cannot be found under Status. If it is supported but disabled in BIOS or UEFI, you’ll see the notification The TPM is not ready for use.
Unfortunately, if your PC has TPM 1.2, that won’t work. Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0, which, as noted, should be supported by newer PCs.
If you’re getting the error This PC must support TPM 2.0, it could just be disabled by default, and you can activate it in your PC’s BIOS. It’s also called UEFI on modern computers.
If you want to know how to turn on TPM 2.0, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app by pressing
Windows + I, typing Recovery into the Find a setting text field and selecting Recovery options. - Under Advanced startup, click on the Restart now button and choose Troubleshoot on the next screen.
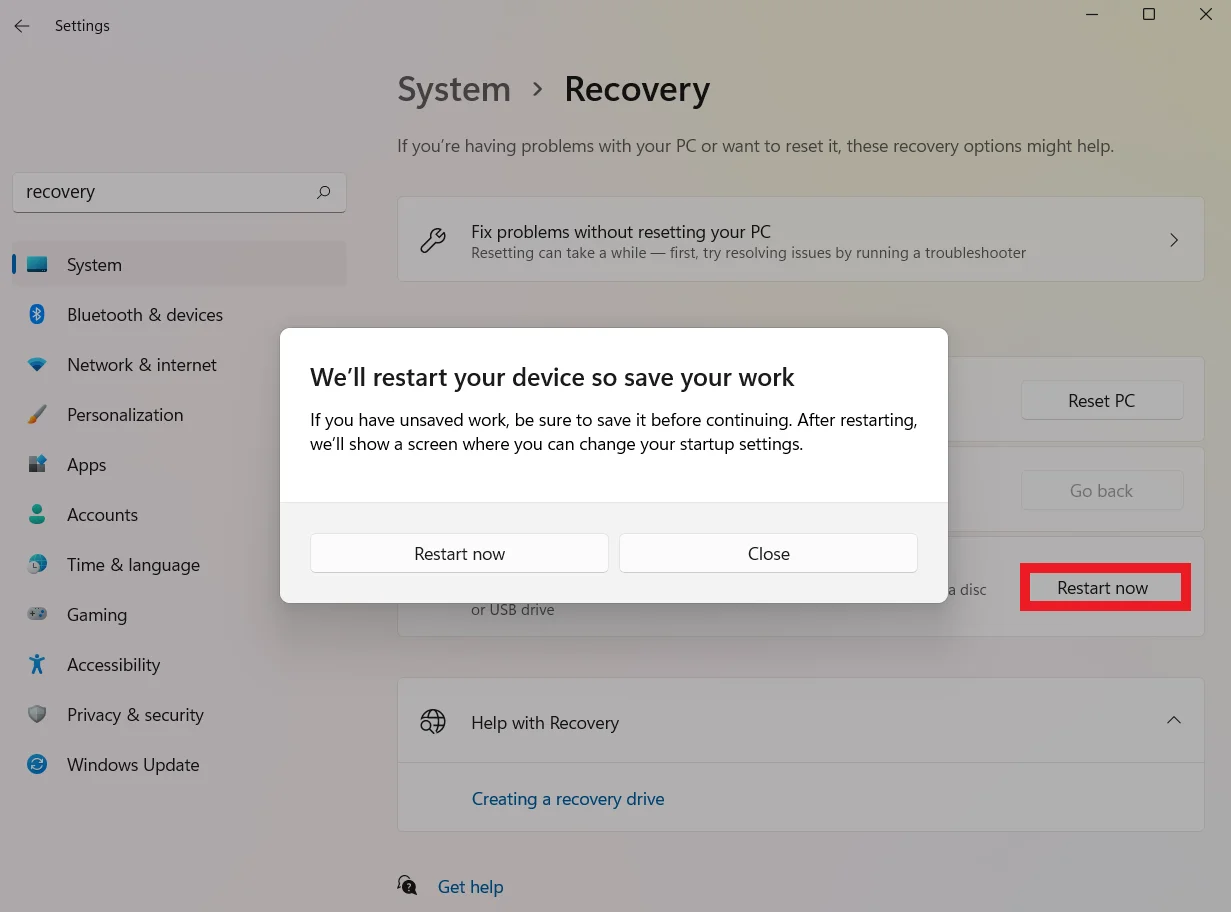
- Choose Advanced options and click the UEFI Firmware Settings option.
- On the UEFI Firmware Settings page, click on Restart.
- Locate Security Settings and enable TPM 2.0 if it is disabled. The option to activate TPM may sometimes be labeled TPM State, Security Device Support, Security Device, Intel PTT, Intel Platform Trust Technology, AMD fTPM switch, or AMD PSP fTPM.
- Once you are done, exit the settings and reboot your system.
Method 3: Clear the TPM keys
If the TPM device is not detected, the problem could be that it is not initialized correctly. Your system may also have multiple keys, causing all sorts of conflicts.
Windows does not support multiple active TPMs, especially if they have been toggled in the UEFI (BIOS) environment. The solution to this issue is clearing your system’s TPM keys.
Microsoft also recommends using this troubleshooting step to install a new operating system.
That’s because clearing TPM keys allows the new OS to deploy its TPM-based functionalities without issues. These functionalities can include BitLocker and attestation.
Clearing the TPM keys causes your operating system to lose ownership. However, Windows will automatically retake ownership once it’s been cleared.
If you want to enable TPM 2.0 on your PC, there are different ways to clear your computer’s TPM. For example, you can go through the TPM window or Windows Security.
Let’s start with Windows Security:
- Open your computer’s Start menu.
- Search for Windows Security.
- Once the Windows Security app appears in the search results, click Device Security under Protection Areas.
- Once the Device Security page of the Windows Security suite opens, head to Security Processor and click on Security Processor Details.
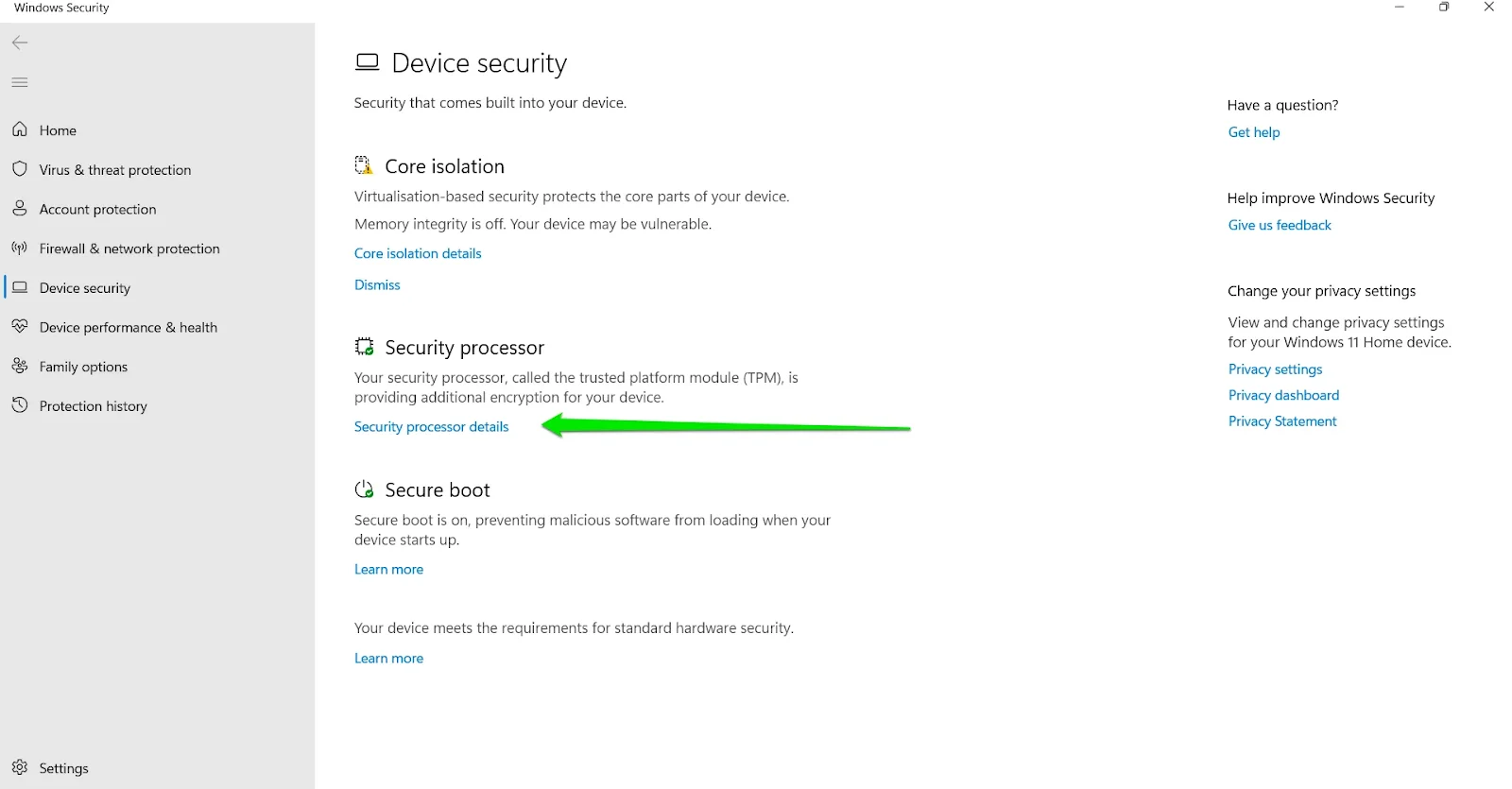
- The Security Processor Details page will now display your TPM chip’s specification, the manufacturer’s name, and the TPM version.
- Go under Status and click on Security processor troubleshooting.
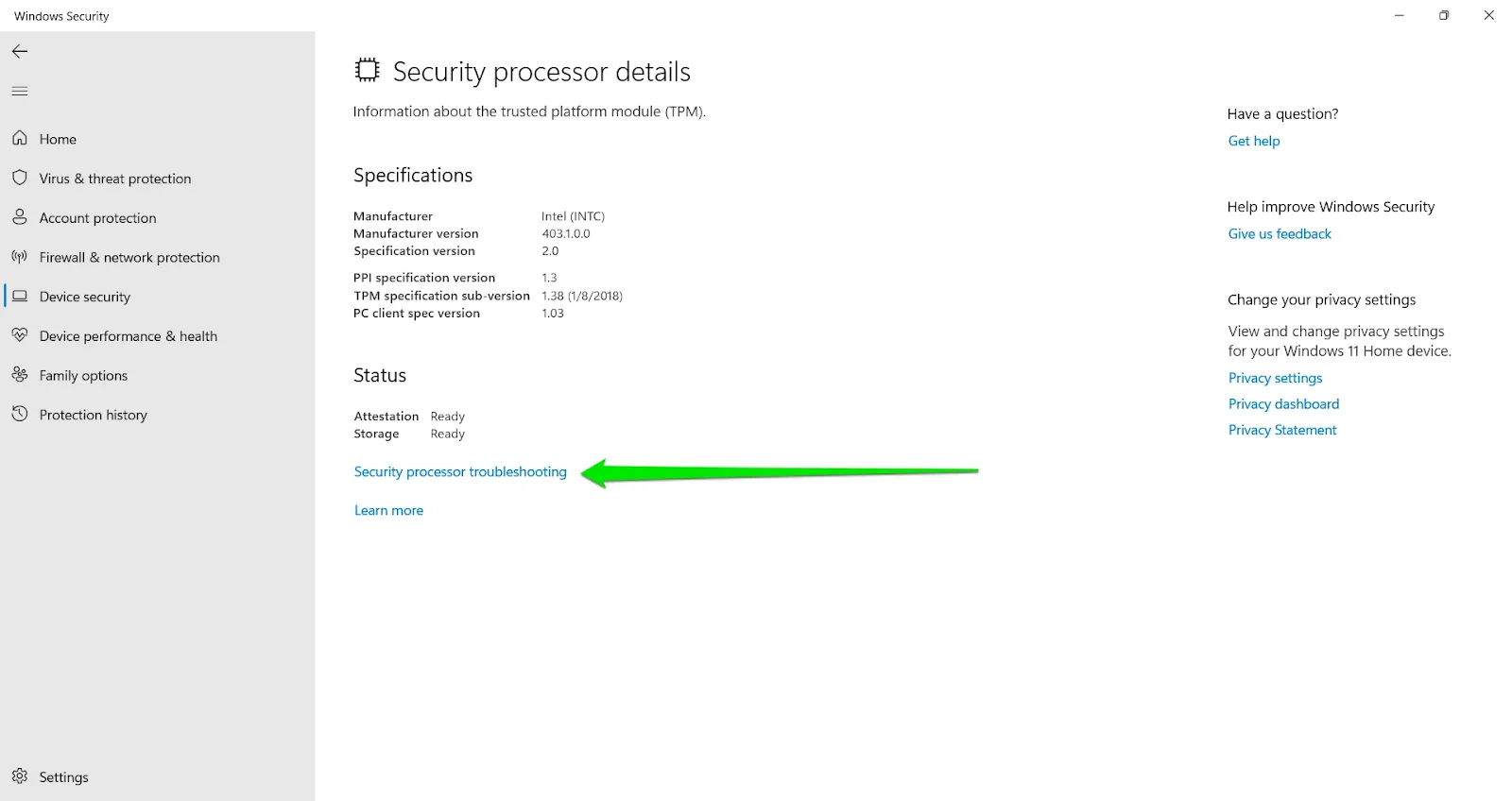
- After the Security processor troubleshooting page opens, head to the Clear TPM section and click the Clear TPM button.
As Windows recommends, you should consider backing up your data before clearing the TPM.
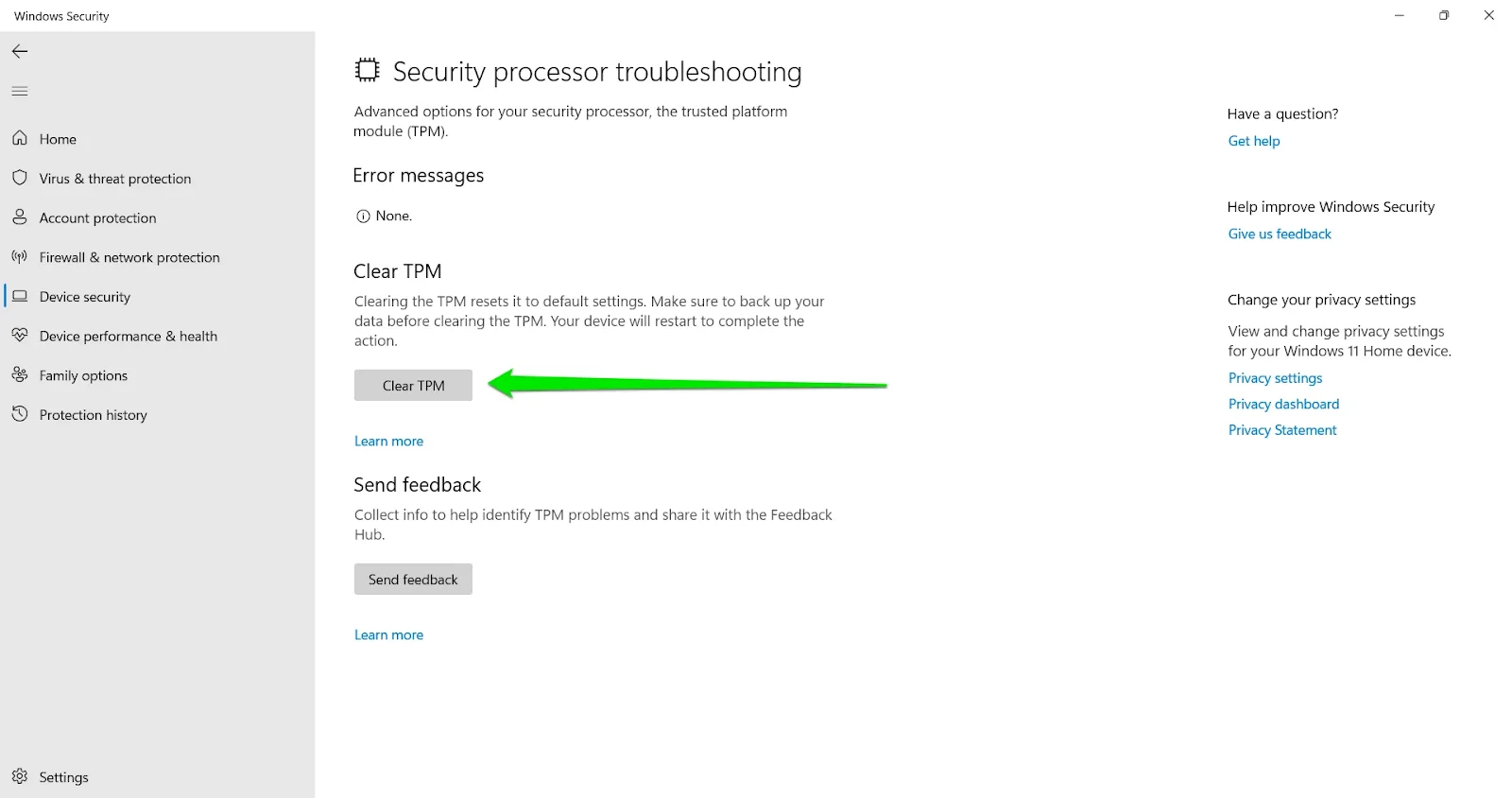
- A confirmation prompt will now appear. Next, click on the Clear and Restart button.
Once your computer restarts, you’ll likely see a prompt to complete the process. Confirm it to continue, and Windows will clear the keys of your Trusted Platform Module.
You can now try upgrading your operating system.
Using the TPM Management Window
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management on the Local Computer window shows the status of the TPM chip and carries other actions. For example, you can use it to clear your system’s existing TPM keys. Follow these steps:
- Open Search and type msc.
- Select the first result, which says tpm.msc. Microsoft Common Console Document. This command launches the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management on Local Computer page.
- Go to the Actions pane on the right and click Clear TPM. Next, click Action in the toolbar and select Clear TPM in the drop-down menu.
- You’ll see a dialog warning you about the implications of clearing TPM. Then, click on the Restart button.
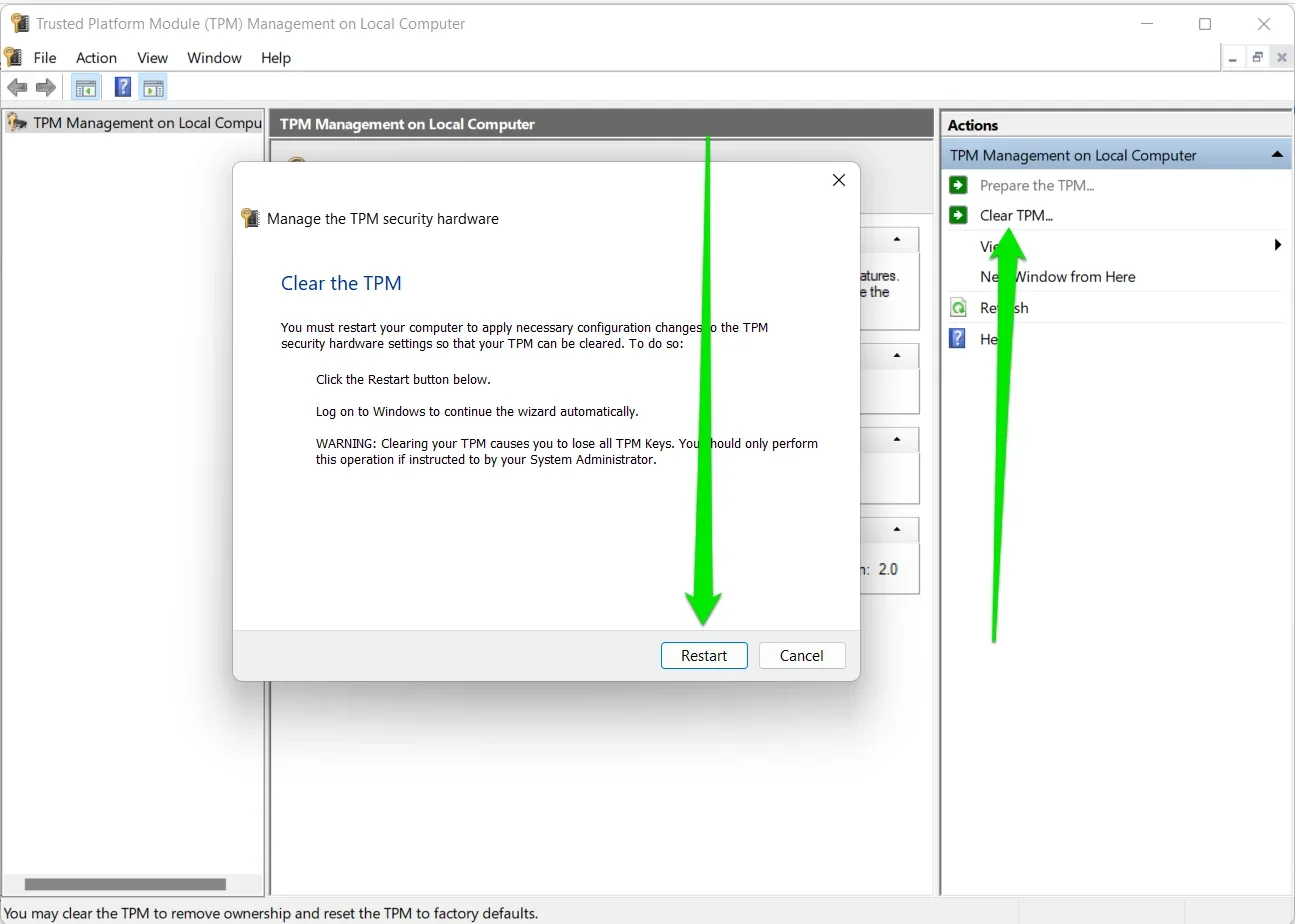
- After your PC restarts, accept any other confirmation prompt to complete the process.
- You can then check if you can now upgrade to Windows 11.
That’s how to clear the TPM keys to fix the TPM 2.0 error when installing Windows 11.
Method 4: Fix TPM driver issues
In rare cases, your computer’s TPM may malfunction because your installed TPM driver may be corrupt, missing, or incompatible with BitLocker.
Reinstalling the driver can resolve the issue. However, you must use a Microsoft-compatible driver for things to work.
That said, the driver provided by the device manufacturer may be all you need.
First, uninstall the driver through Device Manager. Follow these steps:
- Right-click the Windows icon in the taskbar and select Device Manager in the menu that pops up.
- After the Device Manager opens, go to the Security Devices category and expand it.
- Right-click on Trusted Platform Module 2.0 and click on Uninstall Device.
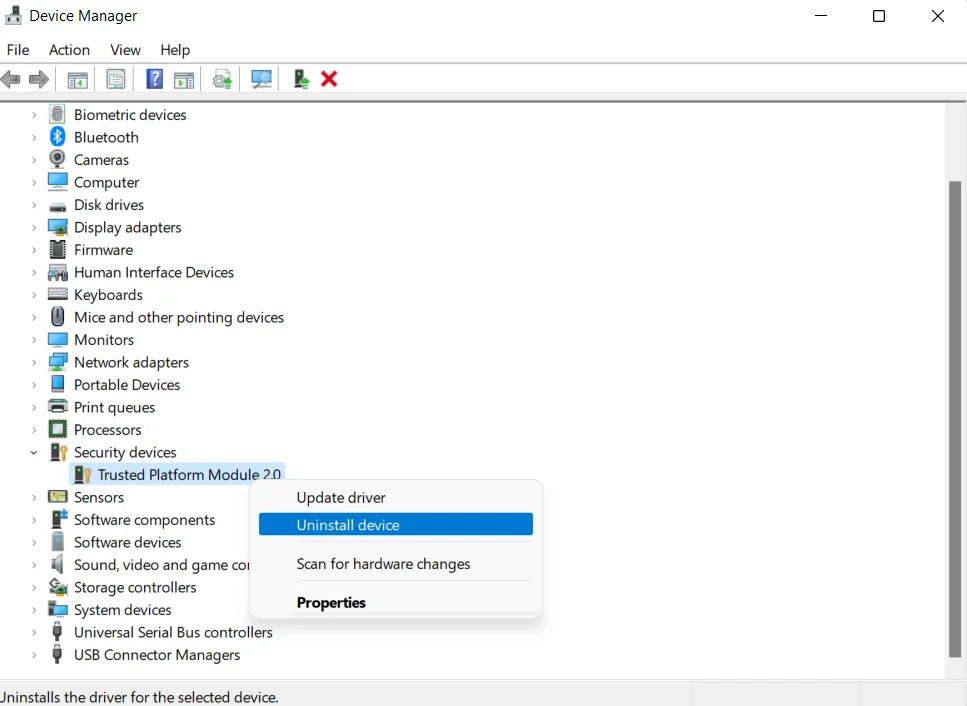
- Click on Uninstall again in the confirmation prompt.
- Restart your PC.
After your computer boots, Windows will attempt to reinstall the driver automatically. This may resolve the issue once and for all, and you can now upgrade your computer.
You may need to download and install the device’s driver manually. To learn more about updating your TPM driver, visit Microsoft’s page.
You could also go to the TPM manufacturer’s website to download and install the firmware.
To confirm your TPM’s manufacturer, launch the Windows Security app, then go to Device Security >> Security processor details.
Related: How to Protect BitLocker-Encrypted Documents from Online Threats?
How to Install Windows 11 Without a TPM 2.0 Chip
There has been a lot of confusion concerning Windows 11 not working on a PC without TPM 2.0. Some reports show you can bypass Windows 11 requirements and install it on an older PC.
However, Microsoft warned that the OS would run in an unsupported state.
Unsupported Windows 11 PCs are not entitled to Windows updates and could miss important security and driver updates, so bypassing Windows 11 requirements is not a good idea.
Therefore, only proceed if you’re willing to risk installing Windows 11 on unsupported devices.
Furthermore, the upgrade only works if you install Windows 11 manually using an ISO file rather than directly via Windows itself.
- Bypass the TPM requirement.
- Buy a compatible module for your motherboard
Method 1: Bypass the TPM requirement
You can bypass the TPM requirement in two ways:
1. Copy files from a Windows 10 ISO file to a Windows 11 ISO file
- Go to the official Microsoft website and download the Windows Media Creation Tool. After that, use the Media Creation Tool to download a Windows 10 ISO file.
- Once you are done, right-click on the Windows ISO file and select Mount.
- Launch File Explorer and select This PC. You should see the mounted file.
- Open it and locate the Sources folder.
- Copy this folder’s contents using the
Ctrl + Ashortcut – except install.esd (to deselect it, hold down the Ctrl key and click on the file). - Now, paste the copied items into the Source folder of your Windows 11 ISO file. If it requests permission to replace the files, select Yes and wait for them to be copied.
2. Edit your registry
Before you proceed, we should point out that this process can affect the performance and stability of your system.
Therefore, do so at your own risk. Before you begin, it is advisable to create a restore point and back up all your files.
- Download the Windows 11 beta version. You must join the Windows Insider Program to do so.
- Restart your PC and try installing it. Since your PC doesn’t meet all the requirements to support Windows 11 (there is no support for TPM 2.0), you’ll see the error notification This PC can’t run Windows 11. Don’t close the Windows setup page just yet. We’ll be coming back to it later.
- When the error appears, press the Shift + F10 shortcut. This action will launch a Command Prompt window.
- Type regedit into the Command Prompt and hit Enter. This command opens the Windows Registry Editor, where you’ll navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup.
- You should see the Setup key. Right-click it and select New > Key.
- Assign the new key the name LabConfig and press Enter.
- Right-click LabConfig and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name it BypassTPMCheck and set its value to 1.
- Repeat the same process to create the BypassRAMCheck and BypassSecureBootCheck values, setting their data values to 1.
- After creating the three values, exit the Registry Editor and close the Command Prompt window.
- Go to the Windows setup page with the error This PC can’t run Windows 11 and click on the Back button.
- Select Windows 11 and follow the prompts. You should now be able to install Windows 11 without TPM 2.0.
Method 2: Buy a compatible module for your motherboard.
If the above process doesn’t work, you can add a TPM to your PC by purchasing one of the TPM-supported chipsets.
However, the process is more complicated than it sounds. You must ensure that the new chipset is configured correctly in the BIOS/UEFI for the Windows OS to recognize it.
Keep Your PC Protected
BoostSpeed’s optimization tools provide an all-inclusive fix for typical PC slowdowns.
So, if you’re having trouble with your Windows or finding that resource-intensive programs are slowing down your computer, Auslogics BoostSpeed 13 can help.
BoostSpeed 13 allows you to defragment your registry and hard drive, clean up unnecessary files, fix registry issues, and speed up your PC.
The software package also includes various tools to improve your computer’s efficiency and effectiveness.
BoostSpeed 13 scans systems to locate and eliminate problems, including unnecessary files, crashes, and slowdowns. Cleaning up your hard disk is as simple as using the module provided.
Furthermore, it places a premium on your privacy by furnishing you with means to guard your sensitive data.
Also, BoostSpeed 13 automatically examines your system for common issues, allowing you to plan maintenance whenever convenient.
Try BoostSpeed 13 out for yourself and see how much faster and more effective your computer can be. If you want to get the most out of your computer and increase efficiency, download Auslogics BoostSpeed 13 right now.
Related: Speed Up Slow Computer as a Pro – Introducing Auslogics BoostSpeed 13
Conclusion
TPM 2.0 capability is required for Windows 11 upgrades, which many people may not like. However, to counter threats and protect private information, TPM 2.0 is essential.
Using either the PC Health Check program or the TPM Management window, TPM 2.0 can be enabled.
If your computer doesn’t have a TPM chip, you can avoid the requirement or get a suitable module.
However, avoiding TPM’s requirements is not recommended due to the risks it poses to your device’s security and performance.
Hardware-based security measures, such as TPM 2.0, must be prioritized as technology develops.
By realizing its relevance and turning it on, you can experience improved data security and meet Windows 11 system requirements.
FAQs
To access the BIOS configuration menu, restart the computer by pressing F2, Del, or Esc, depending on your PC model. Next, navigate the BIOS menus to locate the security or advanced settings area. Then, find a setting related to TPM and turn that on. After, save the changes and close the BIOS setup. Depending on your setup, you may be able to add TPM 2.0 compatibility by purchasing and installing a dedicated TPM module. If you want to check the TPM version, run the dialog by pressing the Windows key + R. Then type “tpm.msc” (without the quotations), and hit the Enter key. Your TPM’s version number and other details will be displayed in the TPM. However, unauthorized means and workarounds may be available to avoid the TPM requirement. These techniques typically require tinkering with system files or using unofficial software. Security and stability issues could exist if the TPM requirement isn’t met. If you don’t have TPM, you shouldn’t update to Windows 11 unless you’ve consulted official sources or found another workaround.



![[FIXED] ‘The PC Must Support TPM 2.0’ Error While Upgrading to Windows 11](https://www.auslogics.com/en/articles/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/shutterstock_219163159-1.jpg)